
-
 Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes
Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes
-
Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six

-
 'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win
'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win
-
Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week

-
 Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs
Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs
-
Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic

-
 Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three
Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three
-
Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport

-
 Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
-
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'

-
 Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs

-
 Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
-
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes

-
 Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran
-
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration

-
 Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level
-
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures

-
 Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
-
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh

-
 Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
-
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig

-
 Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales
-
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says

-
 Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January
-
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo

-
 PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown
-
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals

-
 Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march
-
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational

-
 Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
-
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
 Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
-
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun

-
 Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
-
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial

-
 Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
-
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening

-
 Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
-
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports

-
 UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
-
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets

-
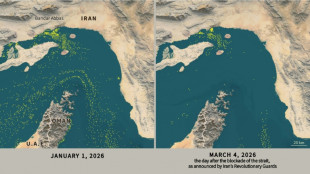 Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup

-
 Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
-
Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up

-
 UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
-
Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs


Nature at risk of 'cascading' species extinction: study
Climate change and habitat degradation will cause extinctions that cascade through communities of animals and plants and drive dramatic biodiversity loss, according to new research published on Friday.
The study, in the journal Science Advances, found that chain-reaction extinctions are unavoidable and predicted Earth's ecosystems will see average biodiversity loss of between six and 10 percent by 2050, depending on different carbon emissions scenarios.
By 2100, losses of animals and plants could rise to as much as 27 percent, they found in their research that used virtual Earths to map out thousands of food webs.
The authors said their modelling suggested that the biggest changes will come before mid-century, predicting "the bleakest time for natural communities might be imminent and that the next few decades will be decisive for the future of global biodiversity".
With life on Earth under threat from human destruction, overexploitation and pollution, scientists have warned that a million species are facing extinction in what many fear heralds the planet's sixth mass extinction event.
Climate change is expected to dramatically accelerate the losses, with impacts of warming ranging from the effects of extreme weather, to changes in behaviour and habitat.
But authors of the new study said previous modelling has not included estimates for co-extinctions, based on the "cascading effect" of losses on interdependent species.
The researchers in Australia and Europe built hundreds of virtual Earths each populated with more than 33,000 vertebrate species in thousands of food webs across the planet –- "massive computer latticeworks of 'who eats whom'," said co-author Corey Bradshaw, a professor at Flinders University.
They then simulated different climate change scenarios and projections of habitat degradation -- like deforestation -- to predict local biodiversity loss, the proportion of animalslost in a given area.
- 'Life support' -
The virtual worlds allowed researchers to watch as species moved around and adapted to new environmental conditions and the implications of individual extinctions across food webs.
They found that climate change would be responsible for the greatest proportion of extinction events.
"If you look out your window in 87 years, on average you'll see nearly 30 percent fewer animal species than you do today based on the business-as-usual climate scenario," Bradshaw told AFP.
The study found the greatest threat was in places with the greatest biodiversity -- 36 highly-vulnerable areas containing the most unique species.
"This is because the erosion of species-rich food webs makes biological communities more susceptible to future shocks," said Bradshaw, adding it was "a case of the rich losing their riches the fastest."
The research comes as a UN summit in Montreal attempts to seal a historic "peace pact with nature" and end the rampant destruction.
Global efforts to curb global warming have often eclipsed efforts to tackle the devastation being wrought on nature, but experts have increasingly warned that the two crises are inextricably linked.
"In many ways, biodiversity loss from climate change is far more serious than what climate change will do to human societies, because biodiversity is the very fabric of the Earth's life-support system that makes our lives possible," said Bradshaw.
"The imperative of massive and rapid emissions-reduction policies is made much more urgent knowing this."
L.Janezki--BTB


