
-
 Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16

-
 Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
-
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
-
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
-
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16

-
 PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
-
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot

-
 Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
-
Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV

-
 Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
-
US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting

-
 US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
-
Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary

-
 US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
-
Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom

-
 Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
-
Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub

-
 Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
-
SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report

-
 White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state
White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state
-
Iran vows to resist any US attack, insists ready for nuclear deal

-
 Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador
Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador
-
Former Masters champ Reed returning to PGA Tour from LIV

-
 US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure
US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure
-
Norway's McGrath tops first leg of Schladming slalom

-
 Iraq PM candidate Maliki denounces Trump's 'blatant' interference
Iraq PM candidate Maliki denounces Trump's 'blatant' interference
-
Neil Young gifts music to Greenland residents for stress relief

-
 Rubio upbeat on Venezuela cooperation but wields stick
Rubio upbeat on Venezuela cooperation but wields stick
-
'No. 1 fan': Rapper Minaj backs Trump

-
 Fear in Sicilian town as vast landslide risks widening
Fear in Sicilian town as vast landslide risks widening
-
'Forced disappearance' probe opened against Colombian cycling star Herrera

-
 Seifert, Santner give New Zealand consolation T20 win over India
Seifert, Santner give New Zealand consolation T20 win over India
-
King Charles III warns world 'going backwards' in climate fight

-
 Minneapolis activists track Trump's immigration enforcers
Minneapolis activists track Trump's immigration enforcers
-
Court orders Dutch to protect Caribbean island from climate change

-
 Sterling agrees Chelsea exit after troubled spell
Sterling agrees Chelsea exit after troubled spell
-
Rules-based trade with US is 'over': Canada central bank head

-
 Lucas Paqueta signs for Flamengo in record South American deal
Lucas Paqueta signs for Flamengo in record South American deal
-
Holocaust survivor urges German MPs to tackle resurgent antisemitism

-
 'Extraordinary' trove of ancient species found in China quarry
'Extraordinary' trove of ancient species found in China quarry
-
Villa's Tielemans ruled out for up to 10 weeks

-
 Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
-
UK proposes to let websites refuse Google AI search

-
 'I wanted to die': survivors recount Mozambique flood terror
'I wanted to die': survivors recount Mozambique flood terror
-
Trump issues fierce warning to Minneapolis mayor over immigration

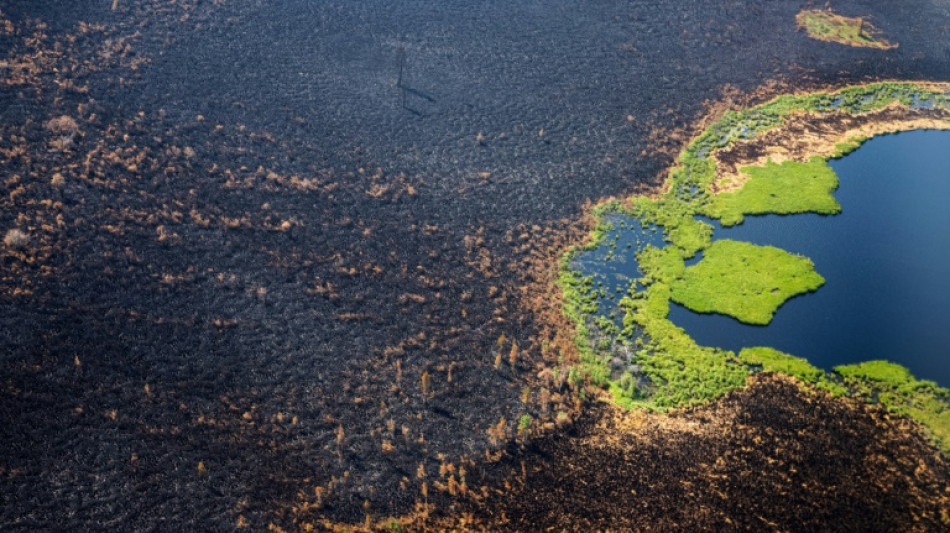
Arctic fires could release catastrophic amounts of C02: study
Global warming is responsible for bigger and bigger fires in Siberia, and in the decades ahead they could release huge amounts of carbon now trapped in the soil, says a report out Thursday.
Researchers fear a threshold might soon be crossed, beyond which small changes in temperature could lead to an exponential increase in area burned in that region.
In 2019 and 2020, fires in this remote part of the world destroyed a surface area equivalent to nearly half of that which burned in the previous 40 years, said this study, which was published in the journal Science.
These recent fires themselves have spewed some 150 million tonnes of carbon into the atmosphere, the scientists estimate, contributing to global warming in what researchers call a feedback loop.
The area above the Arctic circle heats up four times faster than the rest of the planet and "it is this climate amplification which causes abnormal fire activity," David Gaveau, one of the authors of this study, told AFP.
Researchers concentrated on an area five and a half times the size of France and with satellite pictures observed the surface area burned each year from 1982 to 2020.
In 2020, fire charred more than 2.5 million hectares (6.2 million acres) of land and released, in CO2 equivalent, as much as that emitted by Spain in one year, the scientists concluded.
That year, summer in Siberia was on average three times hotter than it was in 1980. The Russian city of Verkhoyansk hit 38 degrees Celsius in summer, a record for the Arctic.
The average air temperature in summer, from June to August, surpassed 10 degrees Celsius only four times in the period under study: in 2001, 2018, 2019 and 2020. These turned out to be the years with the most fires too.
The team fears that this threshold at 10 degrees Celsius will be a breaking point that is surpassed more and more often, said Gaveau.
"The system goes out of whack, and for a small increase beyond 10 degrees Celsius we suddenly see lots of fires," he said.
- Source of permafrost -
Arctic soils store huge amounts of organic carbon, much of it in peatlands. This is often frozen or marshy, but climate warming thaws and dries peatland soil, making large Arctic fires more likely.
Fire damages frozen soil called permafrost, which releases even more carbon. In some cases it has been trapped in ice for centuries or more.
"This means that carbon sinks are transformed into sources of carbon," Gaveau said.
"If there continue to be fires every year, the soil will be in worse and worse condition. So there will be more and more emissions from this soil, and this is what is really worrisome."
An elevated amount of CO2 was released in 2020 but things "could be even more catastrophic than that in the future," said Gaveau, whose company, TheTreeMap, studies deforestation and forest fires.
Higher temperatures have a variety of effects: more water vapor in the atmosphere, which causes more storms and thus more fire-sparking lightning. And vegetation grows more, providing more fuel for fire, but it also breathes more, which dries things out.
- Different scenarios -
Looking ahead to the future, the study analyzed two possible scenarios.
In the first one, nothing is done to fight climate change and temperatures keep rising steadily. In this case fires of the same gravity as in 2020 may occur every year.
In the second scenario, concentrations of greenhouse gases stabilize and temperatures level out by the second half of this century. In this case severe fires like those of 2020 would break out on average every 10 years, said Adria Descals Ferrando, the main author of the study.
Either way "summers with fires like those of 2020 are going to be more and more frequent starting in 2050 and beyond," said Gaveau.
B.Shevchenko--BTB



