
-
 Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
-
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security

-
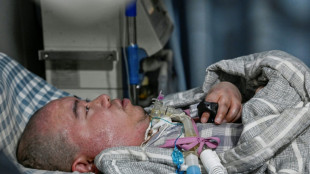 Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran

-
 China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
-
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military

-
 As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
-
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence

-
 Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
-
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
-
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season

-
 Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
-
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art

-
 Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
-
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest

-
 Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16

-
 Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
-
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
-
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
-
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16

-
 PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
-
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot

-
 Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
-
Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV

-
 Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
-
US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting

-
 US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
-
Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary

-
 US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
-
Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom

-
 Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
-
Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub

-
 Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
-
SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report

-
 White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state
White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state
-
Iran vows to resist any US attack, insists ready for nuclear deal

-
 Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador
Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador
-
Former Masters champ Reed returning to PGA Tour from LIV

-
 US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure
US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure
-
Norway's McGrath tops first leg of Schladming slalom

-
 Iraq PM candidate Maliki denounces Trump's 'blatant' interference
Iraq PM candidate Maliki denounces Trump's 'blatant' interference
-
Neil Young gifts music to Greenland residents for stress relief

-
 Rubio upbeat on Venezuela cooperation but wields stick
Rubio upbeat on Venezuela cooperation but wields stick
-
'No. 1 fan': Rapper Minaj backs Trump


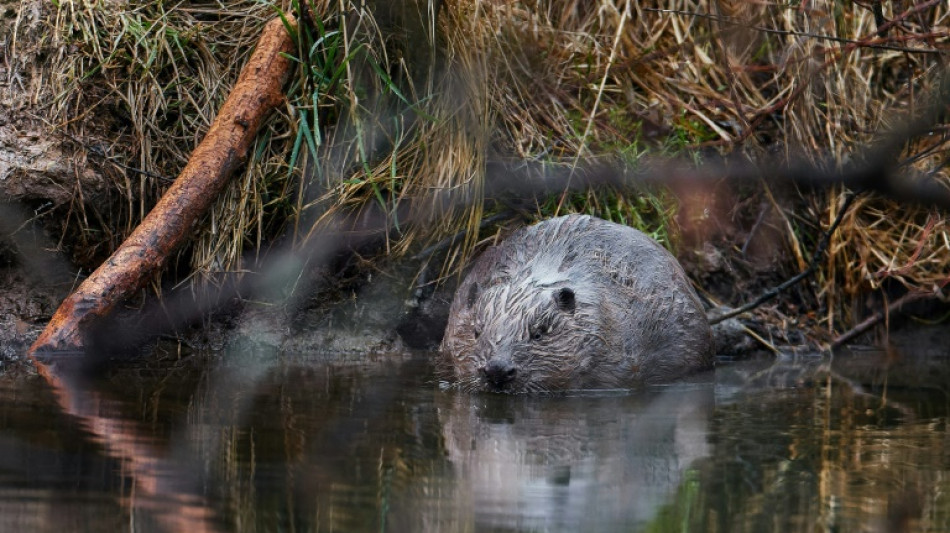
Many animal 'geomorphs' under threat, study warns
More than a quarter of our planet's natural "geomorphs" -- animals such as beavers and hippos that, collectively, can reshape entire landscapes -- are threatened or have shrinking populations, a new study says.
The research, by Queen Mary University of London, found the scale of the impact these animals had on habitats -- by building dams, trampling new river courses, excavating earth and other activities -- rivals that caused by major floods.
Yet "more than a quarter (28 percent) of zoogeomorphic species are vulnerable to future population decline or regional or global extinction," the study's authors warned.
Their research, published mid-February, identified more than 600 species of land and freshwater animals that worked to redesign their ecosystems.
While beavers, of dam-building fame, and hippopotamuses and elephants, which in herds can flatten stretches of earth, are the best-known, there are many others -- often overlooked -- that could also be dubbed animal architects.
Among them are Brazilian termites, which have built high mounds connected by tunnels that cover an area larger than Iceland.
Others identified by the researchers included Australian marsupials, South American shrimp, Asian ants, as well as salmon, moles, earthworms and freshwater insects.
"What we tend to do is overlook the smaller animals that are less visible to us. Perhaps they're living underground or they're living underwater, but those animals can be really kind of important as well," one of the authors, Gemma Harvey, told AFP.
- 'Big cumulative effect' -
Harvey, a professor in biogeomorphology and landscape rewilding, said: "People can underestimate the effects of small animals, because individually their effects are small, but collectively they tend to be more abundant in the landscape so they can have a big cumulative effect."
She added that "it's the collective importance of the animals that is being discovered right now".
She noted the study did not look at marine ecosystems, and that "there will be many more animals that have not yet been studied or perhaps not even been discovered yet".
Of the more than 600 species identified in the research, 57 were classed as endangered, vulnerable or near-threatened on the International Union for the Conservation of Nature's Red List of Threatened Species.
Many others were at risk of declining populations.
"As we lose species from our landscapes, we lose those unique processes" of reshaping the habitats, Harvey said.
And the power these landscaping animals possess is staggering.
Harvey said her team's study estimated that the species they had identified together exerted 76,000 gigajoules of energy each year -- equivalent to that of "hundreds of thousands of extreme floods".
She said much was still unknown about the animals' geomorphing processes and she planned to further her research, notably by factoring in the effects of climate change.
"We're also interested in thinking kind of back in time in the past, about what we've already lost, you know, from our landscapes as species have become extinct or reduced a lot in terms of their population," she said.
L.Stucki--VB



