
-
 Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
-
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi

-
 New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
-
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow

-
 Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace
-
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat

-
 Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
-
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
-
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map

-
 Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
-
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security

-
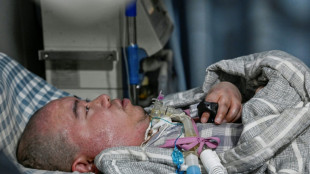 Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran

-
 China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
-
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military

-
 As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
-
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence

-
 Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
-
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
-
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season

-
 Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
-
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art

-
 Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
-
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest

-
 Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16

-
 Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
-
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
-
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
-
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16

-
 PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
-
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot

-
 Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
-
Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV

-
 Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
-
US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting

-
 US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
-
Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary

-
 US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
-
Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom

-
 Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
-
Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub

-
 Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
-
SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report


Hong Kong scientists fight to save fragrant incense trees
Geneticist Zhang Huarong walks through the forest near his Hong Kong research lab, gesturing towards a rotting incense tree stump that is one of over a dozen illegally felled for the valuable wood inside.
A stone's throw from the city's urban centre are forests home to trees that produce fragrant -- and valuable -- agarwood, used in a number of high-end products from incense and perfume to traditional Chinese medicine.
Environmentalists say illegal incense tree felling is on the rise in Hong Kong, fueled by black market demand.
Scientists like Zhang are fighting back by taking DNA samples from each plant and creating a database that can help authorities crack down -- as well as offer insights into how the trees can be better conserved.
"In one night, over 20 trees had been cut down by poachers," Zhang, a researcher at Kadoorie Farm and Botanic Garden, told AFP.
"We have to take action."
Hong Kong has long been a hub for sweet-smelling aromatic products. The city's name -- translating to "fragrant harbour" -- is commonly linked to the area's history of incense production and sale.
Agarwood is created when incense trees are cut, which causes the plant to produce a dark resin to prevent infection.
The product then takes the form of fragrant resinous wood.
- 'Black gold' -
Hong Kong authorities say that illegal incense tree felling soared twelvefold in 2023 compared to the previous year.
Often described as "black gold", the highest-grade products can fetch up to $10,000 per kilo.
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has labelled Chinese Agarwood as "vulnerable" -- blaming logging and wood harvesting for the population decline.
Aiming to reverse that, Zhang and other field researchers hiked for hours through swathes of Hong Kong's dense jungle to access remote populations of incense trees.
Rural communities keen to protect the forests near their homes also assisted in developing the incense tree database, he told AFP.
"We have communications with those villages, and they share information with us about the remaining trees, and we also share our findings with them," he said.
The database serves a joint purpose: assisting authorities in stopping illegal incense tree felling and helping researchers understand the species' evolutionary potential.
Zhang said this research has identified unique genetic groups located in different areas of Hong Kong -- diversity that could be key to cultivating a resilient wild population of the vulnerable species.
Larger genetic diversity protects populations from environmental changes, Zhang explained.
For Hong Kong's incense trees, that includes the effects of climate change and surges in logging activity.
This information lets conservationists know where to transplant certain incense trees from nurseries into the wild.
Authorities can then use this genetic data to cross-reference seized agarwood and check if it was taken from protected incense trees.
Hong Kong shop owner Aaron Tang sells wares that attest to the many uses of agarwood, from carved jewellery to oils and hand-rolled joss sticks.
To help protect the wild agarwood population, he said he verifies with raw material suppliers that their product comes from cultivated trees.
And when he teaches a class on making joss sticks, he warns his students against buying wild stock, or falling for illegally gotten products.
"The name of Hong Kong is because of agarwood so I want to keep this culture," he said.
- 'Gone completely' -
Unlike sustainable agarwood producers, the illegal ones create deep cuts on the tree in a bid to make it produce agarwood more quickly.
Then "they chop down the whole tree" for harvesting, Chinese University of Hong Kong scientist David Lau told AFP, pointing to a preserved incense tree trunk on campus.
A spokesperson for the city said they have set up patrols at "specific locations with important incense tree populations".
They also insisted that illegal felling has decreased since measures implemented in 2018, including metal cages and surveillance around the most accessible trees.
But horticulturist Paul Melsom attributes the fall to there being "less trees to poach".
And the illegal trade has continued to thrive despite government efforts.
Last year, Hong Kong's customs department said it seized a tonne of agarwood in a single operation -- its largest haul in two decades.
Authorities estimated it was worth about $2.3 million.
"The trees have been cut down and gone completely in many forests in Hong Kong," Melsom said, adding he's been planting incense trees in secret locations for over a decade in response.
"I've seen many incense trees disappear," he said.
T.Egger--VB



