
-
 Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
-
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi

-
 New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
-
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow

-
 Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace
-
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat

-
 Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
-
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
-
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map

-
 Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
-
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security

-
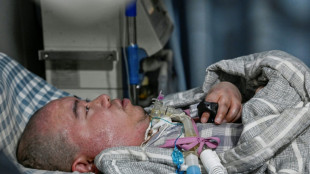 Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran

-
 China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
-
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military

-
 As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
-
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence

-
 Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
-
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
-
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season

-
 Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
-
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art

-
 Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
-
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest

-
 Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16

-
 Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
-
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
-
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
-
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16

-
 PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
-
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot

-
 Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
-
Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV

-
 Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
-
US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting

-
 US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
-
Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary

-
 US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
-
Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom

-
 Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
-
Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub

-
 Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
-
SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report


January sets 'surprising' heat record: EU monitor
Last month was the hottest January on record, Europe's climate monitor said Thursday, despite expectations that cooler La Nina conditions might quell a streak of record-breaking global temperatures.
The Copernicus Climate Change Service said January was 1.75C hotter than pre-industrial times, extending a persistent run of history-making highs over 2023 and 2024, as human-caused greenhouse gas emissions crank up the global thermostat.
Climate scientists had expected this exceptional spell to subside after a warming El Nino event peaked in January 2024 and conditions gradually shifted to an opposing, cooling La Nina phase.
But the heat has lingered at record or near record levels ever since, sparking debate among scientists about what other factors could be driving heating to the top end of expectations.
"This is what makes it a bit of a surprise... you're not seeing this cooling effect, or temporary brake at least, on the global temperature that we were expecting to see," Julien Nicolas, a climate scientist from Copernicus, told AFP.
La Nina is expected to be weak and Copernicus said prevailing temperatures in parts of the equatorial Pacific Ocean suggested "a slowing or stalling of the move towards" the cooling phenomenon.
Nicolas said it could disappear completely by March.
- Ocean warmth -
Last month, Copernicus said that global temperatures averaged across 2023 and 2024 had exceeded 1.5 degrees Celsius for the first time.
This did not represent a permanent breach of the long-term 1.5C warming target under the Paris climate accord -- but a clear sign that the limit was being tested.
Scientists warn that every fraction of a degree of warming above 1.5C increases the intensity and frequency of extreme weather events like heatwaves, heavy rainfall and droughts.
Copernicus said Arctic sea ice in January hit a monthly record low, virtually tied with 2018. Analysis from the US this week put it at the second-lowest in that dataset.
Overall, 2025, is not expected to follow 2023 and 2024 into the history books: scientists predict it will rank the third hottest year yet.
Copernicus said it would be closely monitoring ocean temperatures throughout 2025 for hints about how the climate might behave.
Oceans are a vital climate regulator and carbon sink, and cooler waters can absorb greater amounts of heat from the atmosphere, helping to lower air temperatures.
They also store 90 percent of the excess heat trapped by humanity's release of greenhouse gases.
"This heat is bound to resurface periodically," said Nicolas.
"I think that's also one of the questions -- is this what has been happening over the past couple of years?"
Sea surface temperatures have been exceptionally warm over 2023 and 2024, and Copernicus said readings in January were the second highest on record.
"That is the thing that is a little puzzling -- why they remain so warm," Nicolas said.
- Debate -
Scientists are unanimous that burning fossil fuels has largely driven long-term global warming, and that natural climate variability can also influence temperatures one year to the next.
But natural warming cycles like El Nino could not alone explain what had taken place in the atmosphere and seas, and answers were being sought elsewhere.
One theory is that a global shift to cleaner shipping fuels in 2020 accelerated warming by reducing sulphur emissions that make clouds more mirror-like and reflective of sunlight.
In December, another peer-reviewed paper looked at whether a reduction in low-lying clouds had let more heat reach Earth's surface.
"It's really still a matter of debate," said Nicolas.
The EU monitor uses billions of measurements from satellites, ships, aircraft and weather stations to aid its climate calculations.
Its records go back to 1940, but other sources of climate data -- such as ice cores, tree rings and coral skeletons -- allow scientists to expand their conclusions using evidence from much further in the past.
Scientists say the period being lived through right now is likely the warmest the Earth has been for the last 125,000 years.
T.Germann--VB



