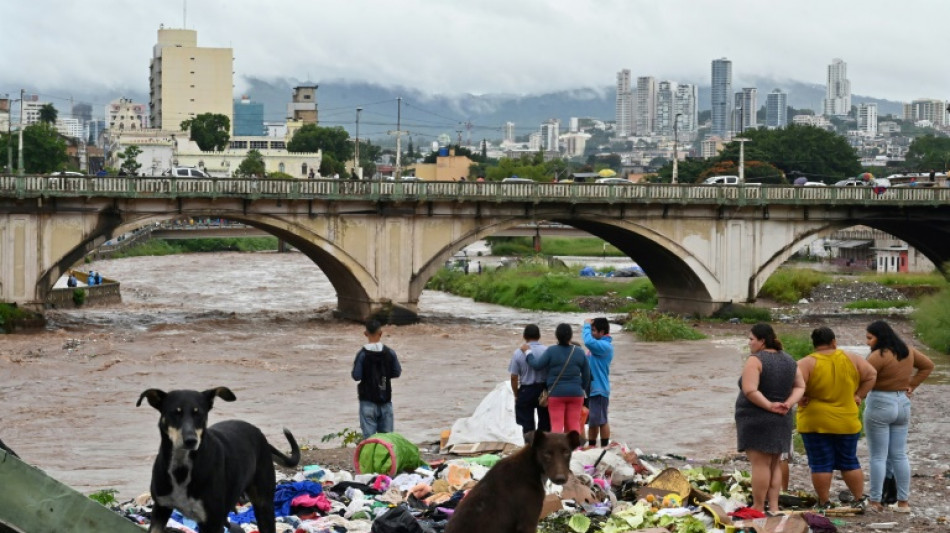

-
 All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy
All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy
-
Sabalenka says Serena return would be 'cool' after great refuses to rule it out

-
 Rybakina plots revenge over Sabalenka in Australian Open final
Rybakina plots revenge over Sabalenka in Australian Open final
-
Irish Six Nations hopes hit by Aki ban

-
 Britain's Starmer hails 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
Britain's Starmer hails 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
-
Parrots rescued as landslide-hit Sicilian town saves pets

-
 Gold surges further, oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat
Gold surges further, oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat
-
No handshake as Sabalenka sets up repeat of 2023 Melbourne final

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' set for EU terror listing
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' set for EU terror listing
-
EU eyes migration clampdown with push on deportations, visas

-
 Umpire call fired up Sabalenka in politically charged Melbourne clash
Umpire call fired up Sabalenka in politically charged Melbourne clash
-
Rybakina battles into Australian Open final against Sabalenka

-
 Iran vows 'crushing response', EU targets Revolutionary Guards
Iran vows 'crushing response', EU targets Revolutionary Guards
-
Northern Mozambique: massive gas potential in an insurgency zone

-
 Gold demand hits record high on Trump policy doubts: industry
Gold demand hits record high on Trump policy doubts: industry
-
Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor

-
 UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China
UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China
-
US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group

-
 'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites
'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites
-
Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe

-
 'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study
'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study
-
Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss

-
 Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits
Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits
-
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
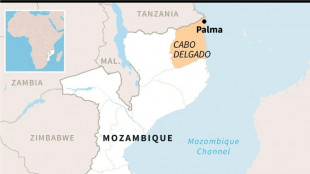
-
 Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
-
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi

-
 Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures
-
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback

-
 China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing
-
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues

-
 South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release
-
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos

-
 Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle
-
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints

-
 Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China
-
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran

-
 Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics
-
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds

-
 Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike
-
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site

-
 Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
-
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi

-
 New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
-
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow

-
 Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace
-
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat

-
 Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
-
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
-
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map


Climate finance's 'new era' shows new political realities
Rich countries' promise of $300 billion a year in climate finance brought fury at talks in Baku from poor nations that found it too paltry, but it also shows a shift in global political realities.
The two-week marathon COP29 climate conference opened days after the decisive victory in the US presidential election of Donald Trump, a sceptic both of climate change and foreign aid.
In the new year, Germany, Canada and Australia all hold elections in which conservatives less supportive of green policies stand chances of victory.
Britain is an exception, with the new Labour government putting climate high back on the agenda, but in much of the West, concerns about inflation and budgetary shocks from Russia's invasion of Ukraine have dented enthusiasm for aggressive climate measures.
At COP29, Germany and the European Union maintained their roles championing climate but also advocated a noticeably practical approach on how much money historical polluters should give poorer countries.
"We live in a time of truly challenging geopolitics, and we should simply not have the illusion" otherwise, European climate commissioner Wopke Hoekstra told bleary-eyed delegates at COP29's pre-dawn closing session Sunday, as activists in the back loudly coughed to drown him out.
But he vowed leadership by Europe, hailing COP29 as "the start of a new era for climate finance".
German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock, a Green party member and longtime climate advocate, called for flexibility on ways to provide funding.
Europe should "live up to its responsibilities, but in a way that it doesn't make promises it can't keep", she said.
Avinash Persaud, special advisor on climate change to the president of the Inter-American Development Bank, called the final deal "the boundary between what is politically achievable today in developed countries and what would make a difference in developing countries".
Activists say that climate funding is a duty, not choice, for wealthy nations whose decades of greenhouse gas emissions most contributed to the crisis that most hits the poorest.
This year is again set to be the hottest on record on the planet. Just since COP29, deadly storms have battered the Philippines and Honduras, and Ecuador declared a national emergency due to drought and forest fires.
- 'Creative accounting'? -
Wealthy historic emitters' promise of $300 billion a year by 2035 is a step up from an expiring commitment of $100 billion annually, but all sides acknowledge it is not enough.
The COP29 agreement cites the need for $1.3 trillion per year, meaning a whopping $1 trillion a year needs to come from elsewhere.
Even within the $300 billion commitment, some activists see too much wiggle room.
"It is, to some extent, almost an empty promise," said Mariana Paoli, the global advocacy lead at London-based development group Christian Aid.
She described the target as "creative accounting", saying there was not enough clarity on how much money would come from public funds and in grants rather than loans.
She acknowledged the politics of the moment but said that wealthy nations had options such as taxation on fossil fuel companies.
"There is a backlash because there is no political will," she said.
- Role for multinational banks -
In one closely scrutinised part of the Baku deal, countries will be able to count climate finance through international financial institutions toward the $300 billion goal.
The text states that it is "voluntary" -- potentially opening the way to include China, which is the world's largest emitter but refuses to have requirements like long-developed countries.
In a joint statement at COP29, multilateral development banks led by the Washington-based World Bank Group but also including the Beijing-based Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank -- which has long faced US criticism -- expected that they together can provide $120 billion annually in climate financing and mobilise another $65 billion from the private sector by 2030.
Melanie Robinson, director of the global climate program at the World Resources Institute, said there were good reasons to rely on multinational development banks, including how much capital they can leverage and their tools to advance green policies.
"They are the most effective way to turn each dollar of finance into impact on the ground," she said.
She agreed that the $300 billion was insufficient but added, "It's a down payment on what we need."
Beyond the debate on dollar figures, she pointed to an initiative within the G20 by Brazil, which holds COP30 next year, to reform financial institutions so as to incorporate debtor nations as well as climate concerns.
"There is really a much bigger opportunity for us -- which is shifting the whole financial system," she said.
W.Huber--VB



