
-
 All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy
All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy
-
Sabalenka says Serena return would be 'cool' after great refuses to rule it out

-
 Rybakina plots revenge over Sabalenka in Australian Open final
Rybakina plots revenge over Sabalenka in Australian Open final
-
Irish Six Nations hopes hit by Aki ban

-
 Britain's Starmer hails 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
Britain's Starmer hails 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
-
Parrots rescued as landslide-hit Sicilian town saves pets

-
 Gold surges further, oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat
Gold surges further, oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat
-
No handshake as Sabalenka sets up repeat of 2023 Melbourne final

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' set for EU terror listing
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' set for EU terror listing
-
EU eyes migration clampdown with push on deportations, visas

-
 Umpire call fired up Sabalenka in politically charged Melbourne clash
Umpire call fired up Sabalenka in politically charged Melbourne clash
-
Rybakina battles into Australian Open final against Sabalenka

-
 Iran vows 'crushing response', EU targets Revolutionary Guards
Iran vows 'crushing response', EU targets Revolutionary Guards
-
Northern Mozambique: massive gas potential in an insurgency zone

-
 Gold demand hits record high on Trump policy doubts: industry
Gold demand hits record high on Trump policy doubts: industry
-
Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor

-
 UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China
UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China
-
US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group

-
 'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites
'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites
-
Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe

-
 'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study
'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study
-
Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss

-
 Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits
Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits
-
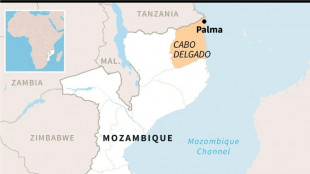
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
-
 Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
-
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi

-
 Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures
-
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback

-
 China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing
-
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues

-
 South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release
-
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos

-
 Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle
-
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints

-
 Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China
-
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran

-
 Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics
-
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds

-
 Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike
-
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site

-
 Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
-
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi

-
 New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
-
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow

-
 Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace
-
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat

-
 Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
-
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
-
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map


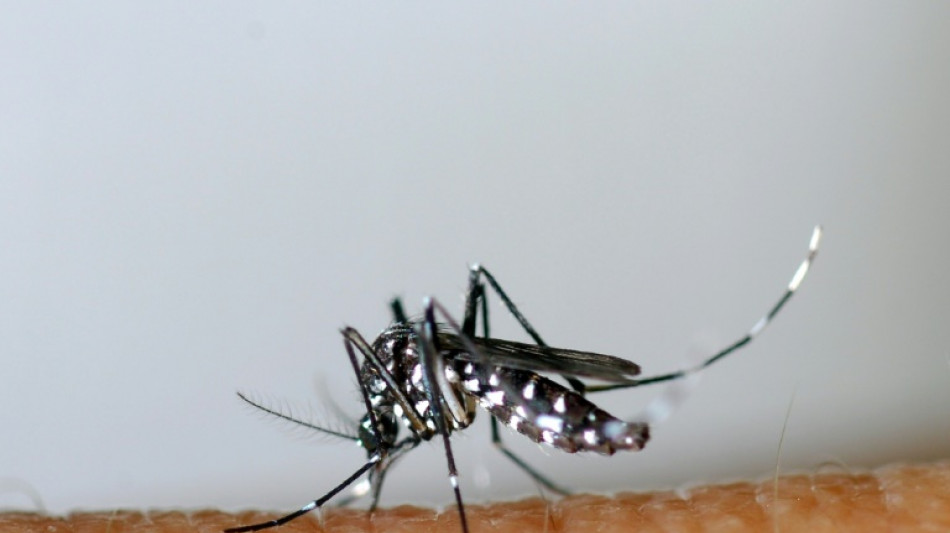
Fifth of dengue cases due to climate change: researchers
Climate change is responsible for nearly a fifth of the record number of dengue cases worldwide this year, US researchers said on Saturday, seeking to shine a light on how rising temperatures help spread disease.
Researchers have been working to swiftly demonstrate how human-driven climate change directly contributes to individual extreme weather events such as the hurricanes, fires, droughts and floods that have battered the world this year.
But linking how global warming affects health -- such as driving outbreaks or spreading disease -- remains a new field.
"Dengue is a really good first disease to focus on because it's very climate sensitive," Erin Mordecai, an infectious disease ecologist at Stanford University, told AFP.
The viral disease, which is transmitted via bites from infected mosquitoes, causes fever and body aches and can, in some cases, be deadly.
It has typically been confined to tropical and sub-tropical areas but rising temperatures have led to mosquitoes encroaching on new areas, taking dengue with them.
For the new study, which has not yet been peer-reviewed, a US team of researchers looked at how hotter temperatures were linked to dengue infections in 21 countries across Asia and the Americas.
On average, around 19 percent of current dengue cases around the world are "attributable to climate warming that has already happened", said Mordecai, the senior author of the pre-print study.
Temperatures between 20-29 degrees Celsius (68-84 degrees Fahrenheit) are ideal for spreading dengue, Mordecai said.
Elevated areas of Peru, Mexico, Bolivia and Brazil that will warm into this temperature range could see dengue cases rising by as much as 200 percent in the next 25 years, the researchers found.
The analysis estimated that at least 257 million people are currently living in areas where global heating could double the rate of dengue during that period.
This danger is just "another reason you should care about climate change", Mordecai said.
- Bacteria to the rescue? -
More than 12.7 million dengue cases were recorded worldwide this year as of September, nearly double 2023's total record, according to World Health Organization figures.
But Mordecai said a "massive amount of under-reporting" meant the real number was likely to be closer to 100 million.
The research was presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene in New Orleans.
Another set of research, also not peer-reviewed, raised hopes of a potential tool to help fight the rise of dengue.
It involves breeding mosquitoes infected with a common bacteria called Wolbachia that can block the insect's ability to transmit dengue.
Five years ago, Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes were introduced across most of the Brazilian city of Niteroi.
When Brazil endured its worst-ever dengue outbreak this year, there was only a small increase in dengue in Niteroi, they found.
The number of cases was also 90-percent lower than before the Wolbachia mosquitoes were deployed -- and "nothing like what was happening in the rest of Brazil", said Katie Anders of the World Mosquito Program.
That the city fared so well showed that "Wolbachia can provide long-term protection for communities against the increasingly frequent surges in dengue that we're seeing globally", Anders said.
The researchers said they have partnered with the Brazilian government to build a Wolbachia mosquitoes production facility, in the hope of protecting millions of people.
J.Marty--VB



