
-
 Where does Iraq stand as US turns up heat on Iran?
Where does Iraq stand as US turns up heat on Iran?
-
Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up

-
 Denmark hails 'very constructive' meeting with US over Greenland
Denmark hails 'very constructive' meeting with US over Greenland
-
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission

-
 EU to put Iran Guards on 'terrorist list'
EU to put Iran Guards on 'terrorist list'
-
Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss

-
 All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy
All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy
-
Sabalenka says Serena return would be 'cool' after great refuses to rule it out

-
 Rybakina plots revenge over Sabalenka in Australian Open final
Rybakina plots revenge over Sabalenka in Australian Open final
-
Irish Six Nations hopes hit by Aki ban

-
 Britain's Starmer hails 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
Britain's Starmer hails 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
-
Parrots rescued as landslide-hit Sicilian town saves pets

-
 Gold surges further, oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat
Gold surges further, oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat
-
No handshake as Sabalenka sets up repeat of 2023 Melbourne final

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' set for EU terror listing
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' set for EU terror listing
-
EU eyes migration clampdown with push on deportations, visas

-
 Umpire call fired up Sabalenka in politically charged Melbourne clash
Umpire call fired up Sabalenka in politically charged Melbourne clash
-
Rybakina battles into Australian Open final against Sabalenka

-
 Iran vows 'crushing response', EU targets Revolutionary Guards
Iran vows 'crushing response', EU targets Revolutionary Guards
-
Northern Mozambique: massive gas potential in an insurgency zone

-
 Gold demand hits record high on Trump policy doubts: industry
Gold demand hits record high on Trump policy doubts: industry
-
Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor

-
 UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China
UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China
-
US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group

-
 'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites
'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites
-
Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe

-
 'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study
'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study
-
Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss

-
 Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits
Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits
-
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
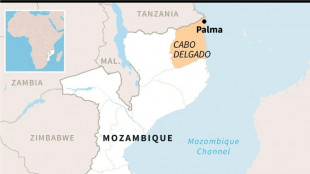
-
 Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi
-
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi

-
 Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures
-
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback

-
 China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing
-
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues

-
 South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release
-
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos

-
 Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle
-
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints

-
 Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China
-
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran

-
 Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics
-
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds

-
 Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike
-
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site

-
 Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis
-
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi

-
 New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip
-
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow


Climate finance: who is being asked to pay what at COP29?
"You owe us!" screamed a protest banner at the COP29 summit in Azerbaijan, where negotiations over how much rich nations most responsible for climate change should pay poorer ones are getting heated.
Striking a deal to provide the $1 trillion annually that experts say is needed by 2030 for developing countries is the top priority at COP29, but getting there will be a slog.
Countries are deeply divided: who should pay what, and how much, are just two of many obstacles standing in the way of an agreement being reached by November 22.
Here's a look at what developing countries need, and who is helping them foot the bill.
- How much is needed? -
A group of leading economists commissioned by the United Nations estimates that developing countries, excluding China, need $2.4 trillion a year in climate finance by 2030.
In a report published Thursday, these experts said two-thirds of this money was required to transition developing economies away from fossil fuels to cleaner forms of energy.
The rest should be divided between adaptation measures to cope with climate change, recovery funds when disaster hits, and conservation of nature.
Of the $2.4 trillion, an estimated $1.4 trillion will need to come from developing countries themselves.
But outside help will be required to cover the remaining $1 trillion.
That could be met by grants or zero-interest loans from foreign governments, private investment flows, or money raised from global taxes, according to the report.
- What should governments pay? -
How much comes directly from governments is the crux of the question for many at COP29, who feel wealthy donors like the United States and European Union are not doing enough.
Amar Bhattacharya, who co-authored the expert climate finance report, said that figure "would be somewhere in the kind of $300 to $400 billion range".
That is at least three times the current commitment -- a tall order for donors facing economic and political crises at home, and the prospect of Donald Trump withdrawing from global climate cooperation.
The cost keeps growing, too.
Developing countries are the least responsible for global warming, but the most exposed to climate shocks, which are accelerating as the planet warms.
By 2035, foreign donors will need to foot $1.3 billion a year to cover developing country needs, the report said.
- How much has been raised? -
Rich nations raised $116 billion in 2022 in climate finance, according to the latest available data from the OECD.
But is money used to make hotels more sustainable, in one stark example, really helping poorer countries adapt to climate change?
What about loans that add to national debt?
Developing countries and campaign groups have called for greater scrutiny of the money that's raised, and efforts have been made to quantify how much each nation gives.
One study done by British think tank ODI ranks progress toward each country's "fair share" based on its carbon footprint, population size and gross national income.
Based on this criteria, Norway led the pack in 2022, followed by France.
The United States -- the world's largest historic emitter -- ranked second to last among 23 nations assessed.
H.Gerber--VB



