
-
 Fela Kuti: first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
Fela Kuti: first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award
-
'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara dead at 71

-
 Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
Curran hat-trick seals 11 run DLS win for England over Sri Lanka
-
Cubans queue for fuel as Trump issues energy ultimatum

-
 France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
France rescues over 6,000 UK-bound Channel migrants in 2025
-
Surprise appointment Riera named Frankfurt coach

-
 Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm
Maersk to take over Panama Canal port operations from HK firm
-
US arrests prominent journalist after Minneapolis protest coverage

-
 Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair
Analysts say Kevin Warsh a safe choice for US Fed chair
-
Trump predicts Iran will seek deal to avoid US strikes

-
 US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
US oil giants say it's early days on potential Venezuela boom
-
Fela Kuti to be first African to get Grammys Lifetime Achievement Award

-
 Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
Trump says Iran wants deal, US 'armada' larger than in Venezuela raid
-
US Justice Dept releases new batch of documents, images, videos from Epstein files

-
 Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
Four memorable showdowns between Alcaraz and Djokovic
-
Russian figure skating prodigy Valieva set for comeback -- but not at Olympics

-
 Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
Barcelona midfielder Lopez agrees contract extension
-
Djokovic says 'keep writing me off' after beating Sinner in late-nighter

-
 US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files
US Justice Dept releasing new batch of Epstein files
-
South Africa and Israel expel envoys in deepening feud

-
 French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing
French eyewear maker in spotlight after presidential showing
-
Olympic dream 'not over', Vonn says after crash

-
 Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery
Brazil's Lula discharged after cataract surgery
-
US Senate races to limit shutdown fallout as Trump-backed deal stalls

-
 'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown
'He probably would've survived': Iran targeting hospitals in crackdown
-
Djokovic stuns Sinner to set up Australian Open final with Alcaraz

-
 Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest
Mateta omitted from Palace squad to face Forest
-
Djokovic 'pushed to the limit' in stunning late-night Sinner upset

-
 Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains
Tunisia's famed blue-and-white village threatened after record rains
-
Top EU official voices 'shock' at Minneapolis violence

-
 Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday
Kremlin says agreed to halt strikes on Kyiv until Sunday
-
Carrick calls for calm after flying start to Man Utd reign

-
 Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon
Djokovic to meet Alcaraz in Melbourne final after five-set marathon
-
Italian officials to testify in trial over deadly migrant shipwreck

-
 Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation
Iran says defence capabilities 'never' up for negotiation
-
UN appeals for more support for flood-hit Mozambicans

-
 Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race
Lijnders urges Man City to pile pressure on Arsenal in title race
-
Fulham sign Man City winger Oscar Bobb

-
 Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup
Strasbourg's Argentine striker Panichelli sets sights on PSG, World Cup
-
Jesus 'made love': Colombian president irks Christians with steamy claim

-
 IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns
IAEA board meets over Ukraine nuclear safety concerns
-
Eurozone growth beats 2025 forecasts despite Trump woes

-
 Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
Dutch PM-elect Jetten says not yet time to talk to Putin
-
Social media fuels surge in UK men seeking testosterone jabs

-
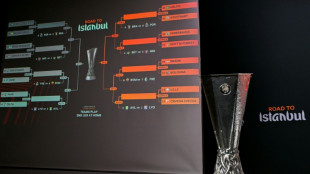 Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
Forest face Fenerbahce, Celtic draw Stuttgart in Europa League play-offs
-
US speed queen Vonn crashes at Crans-Montana, one week before Olympics

-
 Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
Trump nominates former US Fed official as next central bank chief
-
New Dutch government pledges ongoing Ukraine support

-
 Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
Newcastle still coping with fallout from Isak exit, says Howe
-
Chad, France eye economic cooperation as they reset strained ties

| CMSC | 0.02% | 23.7 | $ | |
| RIO | -3.92% | 91.54 | $ | |
| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.05% | 24.049 | $ | |
| BCC | 0.74% | 80.77 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.58% | 13.03 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.82% | 60.71 | $ | |
| GSK | 1.77% | 51.57 | $ | |
| BCE | 1.28% | 25.815 | $ | |
| BP | -0.46% | 37.865 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 1.65% | 83.78 | $ | |
| NGG | -0.04% | 85.015 | $ | |
| RELX | -1.19% | 35.74 | $ | |
| AZN | 0.69% | 93.235 | $ | |
| VOD | -0.48% | 14.64 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -2.69% | 16 | $ |

Cicada-palooza! Billions of bugs to blanket America
They're loud. They're sexually aroused. And for one special, cacophonous month up to a trillion of them will engulf suburbs and woodlands across America.
Two cicada "broods" are set for a rare double emergence that last occurred in 1803, when Thomas Jefferson was president and the United States purchased Louisiana from France.
The prospect of another natural wonder just weeks after a total solar eclipse across much of the country has gripped scientists and the public alike.
- 'Insects of history' -
Cicadas comprise a diverse family of over 3,000 insect species found globally, with the majority of their lives spent underground in a larval state.
They emerge as adults to transform and mate, with some species appearing annually and others, known as periodical cicadas, synchronizing their emergence every 13 or 17 years. Mathematicians have long been intrigued by the question of why periodical cicadas follow prime number cycles, despite the lack of a clear evolutionary explanation.
This year's event involves the 13-year Brood XIX, currently emerging in the Carolinas, followed by the 17-year Brood XIII in the Midwest. There could be a small area of overlap in central Illinois.
"When they do come out, they come out in big numbers, parents get excited, the kids get excited," said entomologist Gene Kritsky of Mount St. Joseph University, who developed the Cicada Safari app for citizen-scientists to gather data, explaining the appeal of the harmless red-eyed bugs.
They're also "creatures of history": People vividly recall where they were when the cicadas last appeared in their area, and these personal stories become embedded in family lore, passed down to the next generation.
Just like witnessing a rare eclipse, Kritsky notes that there's a unique value in seeing scientific predictions come to life. "That's what science does: you come up with hypotheses that lead to predictions, the predictions are verified...and there's something valuable about this in a time when some people have thought to disregard science."
- Scientific marvel -
Relatively defenseless, periodical cicadas' strength lies in their sheer numbers that satiates the appetites of the birds, foxes, racoons, turtles and other predators, John Lill, a professor of biology at the George Washington University told AFP.
In a recent paper published in Science, Lill and colleagues revealed a number of broader impacts on the wider ecosystem. They found the 2021 emergence of Brood X in the capital Washington proved a windfall for insectivorous birds, leading to a surge in caterpillar populations as the birds focused on feasting on the cicadas.
This reprieve allowed caterpillars to thrive, resulting in increased consumption of oak saplings.
Other new research showed that "mast years" -- when oak trees produce an abundance of acorns -- follow like clockwork two years after cicada emergence. More acorns support larger populations of the mammals that feed on them, ultimately leading to more Lyme disease risk for humans.
"The fact that the cicadas determine when the masting event occurs, which then determine when the Lyme disease occurs, just sort of highlights that there are these potentially longer term ecological impacts that reverberate for years after the cicada emergence events," said Lill.
Then of course there's the males' distinctive -- and deafening -- mating chorus.
"We have had several calls about a noise in the air that sounds like a siren, or a whine, or a roar," Newberry Sheriff's Office in South Carolina posted this week on Facebook.
- Human impacts -
Chris Simon of the University of Connecticut, who studies the chemical changes in cicada DNA that track their life cycle, warns that climate change is disrupting their internal clocks. As the US warms up, a longer plant growing season provides more food, accelerating cicada growth.
"I predict that more 17 year cicadas will turn into permanent 13 year cicadas," she says, "and eventually that trait will be genetically assimilated."
What that means for the species in the long run is hard to know. It's also unclear whether drastic land transformation since the colonial period has been a net positive or negative for cicadas, said Lill.
On the one hand, many historic broods have been lost to rampant deforestation. But the remaining broods are flourishing in suburban environments where well-lit trees provide ideal conditions for females to lay their eggs.
Then the adults die, the newly hatched cicada nymphs fall off the trees and burrow underground, and the cycle begins anew.
L.Meier--VB




