
-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China

-
 Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
-
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics

-
 China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
-
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike

-
 Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
-
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis

-
 Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
-
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace

-
 No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain

-
 Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
-
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
-
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge

-
 Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans

-
 Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report

-
 Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
-
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate

-
 Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
-
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
-
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16


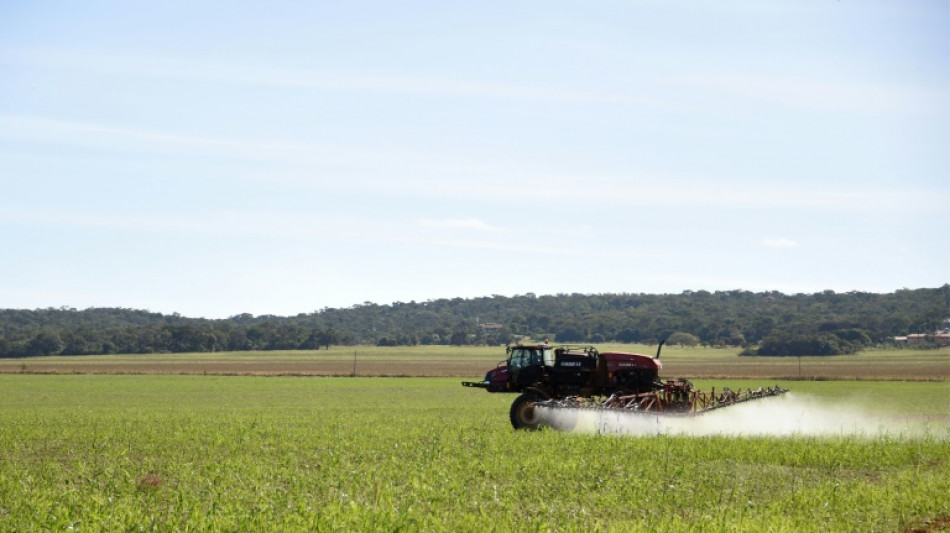
Emissions from fertilisers could be slashed by 2050: study
The production and use of nitrogen fertilisers accounts for five percent of global greenhouse gas emissions, which can be massively reduced with a few available interventions, a new study said Thursday.
Nitrogen fertilisers -- produced and used across the world -- are crucial for global food security.
But their harmful emissions contributing to global warming exceed the aviation sector, and are on par with the iron and steel, cement and plastics industries.
Most existing research has focused on emissions associated with the production of fertilisers, but Thursday's study showed that the majority -- two thirds -- come from the use of the fertilisers in croplands.
"There is the perception that the petrochemical industry has been causing the emissions producing the fertilisers, but actually that doesn't seem to be the case. That was very surprising for us," co-author Andre Cabrera Serrenho from Cambridge University told AFP.
The findings are important because they show "where we should prioritise action to reduce emissions," he added.
Carbon emissions could be reduced by up to 80 percent by 2050 while still producing enough food to feed a growing global population, said the study published Thursday in the journal Nature Food.
"The interventions we propose in our study do not imply loss in crop productivity, and they consider the future growing demand for food to feed a growing global population," Serrenho confirmed.
- Boost efficiency, use less -
Emissions associated with production are mostly associated with ammonia, a key ingredient in most fertilisers.
Making ammonia not only uses a lot of energy, but also requires hydrogen production, which causes emissions.
Some factories in China, for example, use coal to make hydrogen. Hydrogen can be made from water using electricity generated by renewables, which would greatly reduce emissions, though it is often a lot more expensive.
And since many factories producing ammonia for fertilisers, especially in Asia, are relatively new, they are less likely to covert technologies to be more environmentally friendly.
Switching to renewable energy in factories is another way to help reduce that carbon footprint.
But Serrenho said the main way to reduce emissions linked to fertilisers is on the use side, by increasing their efficiency and thus reducing their use.
"We are currently really inefficient in the way we use fertilisers," he said. "We put much more fertilisers in croplands than the amount of nitrogen that actually crops need to grow."
The main emissions in the use phase come from the degradation of fertiliser by bacteria that exist in the soil and produce nitrous oxide, one of the most powerful greenhouse gases.
Carbon dioxide and methane are also emitted in the use phase, but simply using less fertiliser could help to slash those harmful emissions.
But convincing farmers to use fertilisers more efficiently -- for example, applying them daily in smaller quantities instead of spraying in large doses them once a season -- will require policy shifts.
"If we could have more economic incentives to farmers to change practices to reduce emissions, that seems to be the most obvious place to start," Serrenho said.
J.Horn--BTB




