
-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
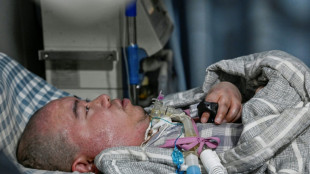
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain

-
 Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
-
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
-
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge

-
 Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans

-
 Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report

-
 Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
-
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate

-
 Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
-
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
-
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16

-
 Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV
Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV
-
Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli

-
 US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting
US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting
-
US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak

-
 Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary
Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary
-
US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics

-
 Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom
Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom
-
Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims

-
 Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub
Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub
-
Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave

-
 SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report
SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report
-
White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state

-
 Iran vows to resist any US attack, insists ready for nuclear deal
Iran vows to resist any US attack, insists ready for nuclear deal
-
Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador

-
 Former Masters champ Reed returning to PGA Tour from LIV
Former Masters champ Reed returning to PGA Tour from LIV
-
US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure

-
 Norway's McGrath tops first leg of Schladming slalom
Norway's McGrath tops first leg of Schladming slalom
-
Iraq PM candidate Maliki denounces Trump's 'blatant' interference


What campaigners want to see in UN nature deal
As high-stakes UN biodiversity talks in Montreal draw to a close, delegates will be presented Sunday with a draft deal to safeguard the planet's ecosystems and species by 2030.
Will it amount to the "peace pact with nature" that UN chief Antonio Guterres said the world desperately needs? Campaigners say the devil lies in the details. Here's what they're looking out for:
- '30 by 30' -
The cornerstone of the agreement is the so-called 30 by 30 goal -- a pledge to protect 30 percent of the world's land and seas by 2030.
Currently, only about 17 percent of land and seven percent of oceans are protected.
And some experts say 30 percent is a low aim, insisting that protecting 50 percent would be better.
So far, more than 100 countries have publicly pledged support for the 30 by 30 target, and observers say it has received broad support among negotiators.
"For COP15 to be a success, we need to hold the line on our existing level of ambition," Alfred DeGemmis, of the Wildlife Conservation Society, told AFP.
Brian O'Donnell of the Campaign for Nature added it was key that the text applies to oceans, as well as land, which had been in doubt.
- Indigenous rights -
The question of Indigenous rights will be crucial.
About 80 percent of the Earth's remaining biodiverse land is currently managed by Indigenous people, and it's broadly recognized that biodiversity is better respected on Indigenous territory.
Many activists want to make sure their rights are not trampled in the name of conservation -- previous efforts to safeguard land have seen Indigenous communities marginalized or displaced in what has been dubbed "green colonialism."
Advocates say therefore these rights have to be adequately addressed throughout the text, including within the 30 by 30 pledge, so that Indigenous people are not subject to mass evictions.
Failure on this front would be a "complete red line for us," said O'Donnell.
"We are the ones doing the work. We protect biodiversity. You won't replace us. We won't let you," said Valentin Engobo, leader of the Lokolama community in the Congo Basin, which protects the world's largest tropical peatland.
"You can be our partners, if you want. But you cannot push us out."
- Loopholes matter -
As a general principle, it is vital that the targets envisioned in the text aren't significantly weakened through loopholes that will weaken actual implementation, said Georgina Chandler of the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds.
For example, during some plenary sessions, some ministers had suggested stripping out language about numerical targets for ecosystem restoration.
"Keeping those measurable elements...and making sure that they are ambitious, is really, really important," said Chandler.
Other things she'll be watching include whether there will be a commitment to halve pesticide use, and whether businesses will be mandated to assess and report on the biodiversity impacts.
- Finance -
As ever, money remains a difficult question.
Developing countries say developed nations grew rich by exploiting their resources and the South should be paid to preserve its ecosystems.
Several countries have announced new commitments either at the COP or recently, with Europe emerging as a key leader. The European Union has committed seven billion euros ($7.4 billion) for the period until 2027, double its prior pledge.
But Brazil has led a charge by developing countries for far more, proposing flows of $100 billion annually, compared to the roughly $10 billion at present.
Developing countries are also seeking a new funding mechanism, as a signal of the rich world's commitment to this goal.
Whether international aid is delivered via a new fund, an existing mechanism called the Global Environment Facility (GEF), or a halfway solution involving a new "trust fund" within the GEF is still up for debate.
J.Fankhauser--BTB



