
-
 Trump blasts Democrats as government shutdown becomes longest ever
Trump blasts Democrats as government shutdown becomes longest ever
-
Indian pilgrims find 'warm welcome' in Pakistan despite tensions

-
 Inter and AC Milan complete purchase of San Siro
Inter and AC Milan complete purchase of San Siro
-
Swedish authorities inspect worksite conditions at steel startup Stegra

-
 Keys withdraws from WTA Finals with illness
Keys withdraws from WTA Finals with illness
-
Prince Harry says proud to be British despite new life in US

-
 EU strikes last-ditch deal on climate targets as COP30 looms
EU strikes last-ditch deal on climate targets as COP30 looms
-
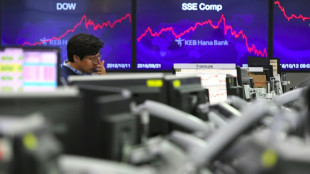
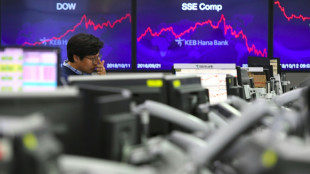
Stocks retreat as tech bubble fears grow
-
 Shein opens first permanent store amid heavy police presence
Shein opens first permanent store amid heavy police presence
-
West Indies edge New Zealand despite Santner brilliance

-
 French pair released by Iran await return home
French pair released by Iran await return home
-
German factory orders up but outlook still muted

-
 Death toll tops 100 as Philippines digs out after typhoon
Death toll tops 100 as Philippines digs out after typhoon
-
Attack on key city in Sudan's Kordofan region kills 40: UN

-
 'No one could stop it': Sudanese describe mass rapes while fleeing El-Fasher
'No one could stop it': Sudanese describe mass rapes while fleeing El-Fasher
-
Champagne and cheers across New York as Mamdani soars to victory

-
 Medieval tower collapse adds to Italy's workplace toll
Medieval tower collapse adds to Italy's workplace toll
-
BMW boosts profitability despite China, tariff woes

-
 South Africa's Wiese wary of 'hurt' France before re-match
South Africa's Wiese wary of 'hurt' France before re-match
-
Beyond limits: Croatian freediver's breathtaking record

-
 Tottenham supporting Udogie after alleged gun threat in London
Tottenham supporting Udogie after alleged gun threat in London
-
Thunder roll Clippers to stay unbeaten as SGA keeps streak alive

-
 In appeal, Australian mushroom murderer alleges 'miscarriage of justice'
In appeal, Australian mushroom murderer alleges 'miscarriage of justice'
-
Toyota hikes profit forecasts 'despite US tariffs'

-
 Ex-France lock Willemse challenges Meafou to become 'the bully'
Ex-France lock Willemse challenges Meafou to become 'the bully'
-
Ukrainians to honour sporting dead by building country they 'died for': minister

-
 At least 7 dead after UPS cargo plane crashes near Louisville airport
At least 7 dead after UPS cargo plane crashes near Louisville airport
-
US Supreme Court hears challenge to Trump tariff powers

-
 US government shutdown becomes longest in history
US government shutdown becomes longest in history
-
India's Modi readies bellwether poll in poorest state

-
 Green goals versus growth needs: India's climate scorecard
Green goals versus growth needs: India's climate scorecard
-
Where things stand on China-US trade after Trump and Xi talk

-
 Sri Lanka targets big fish in anti-corruption push
Sri Lanka targets big fish in anti-corruption push
-
NY elects leftist mayor on big election night for Democrats

-
 Injured Jordie Barrett to miss rest of All Blacks tour
Injured Jordie Barrett to miss rest of All Blacks tour
-
Asian markets tumble as tech bubble fears grow
-
 Pay to protect: Brazil pitches new forest fund at COP30
Pay to protect: Brazil pitches new forest fund at COP30
-
Iraq's social media mercenaries dying for Russia
-
 Young leftist Trump foe elected New York mayor
Young leftist Trump foe elected New York mayor
-
Concerns at ILO over expected appointment of close Trump advisor

-
 Venus Williams to return to Auckland Classic at the age of 45
Venus Williams to return to Auckland Classic at the age of 45
-
No deal yet on EU climate targets as COP30 looms

-
 Typhoon death toll climbs to 66 in the Philippines
Typhoon death toll climbs to 66 in the Philippines
-
NATO tests war preparedness on eastern flank facing Russia

-
 Uncapped opener Weatherald in Australia squad for first Ashes Test
Uncapped opener Weatherald in Australia squad for first Ashes Test
-
Liverpool down Real Madrid in Champions League, Bayern edge PSG

-
 Van Dijk tells Liverpool to keep calm and follow Arsenal's lead
Van Dijk tells Liverpool to keep calm and follow Arsenal's lead
-
PSG left to sweat on injuries to Dembele and Hakimi

-
 Reddit, Kick to be included in Australia's social media ban
Reddit, Kick to be included in Australia's social media ban
-
Ex-Zimbabwe cricket captain Williams treated for 'drug addiction'


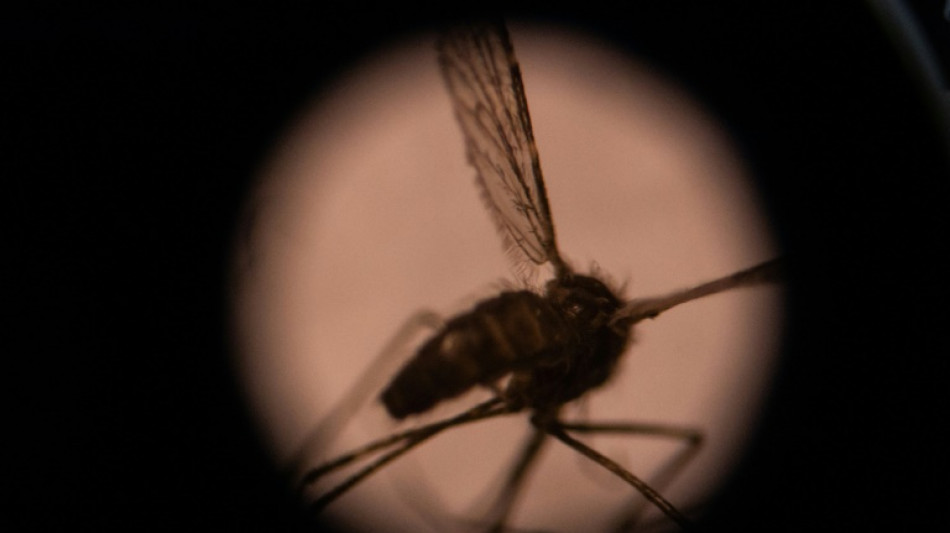
Invasive malaria mosquito spreading in Africa, researchers warn
New evidence has emerged that an invasive species of malaria-carrying mosquito from Asia is spreading in Africa, where it could pose a "unique" threat to tens of millions of city-dwellers, researchers warned Tuesday.
In Africa, home to more than 95 percent of the world's 627,000 malaria deaths in 2020, the parasite is mostly spread in rural areas preferred by the dominant Anopheles gambiae group of mosquitoes.
However the Anopheles stephensi mosquito, which has long been a main malaria spreader in Indian and Iranian cities, can breed in urban water supplies, meaning it can thrive during the dry season. It is also to resistant to commonly used insecticides.
Modelling research in 2020 found that if Anopheles stephensi spread widely in Africa it would put more than 126 million people in 44 cities at risk of malaria.
Djibouti became the first African nation to detect Anopheles stephensi in 2012. It had been close to eradicating malaria with just 27 reported cases that year.
However the number has skyrocketed since Anopheles stephensi's arrival, hitting 73,000 cases in 2020, according to the World Health Organization.
On Tuesday, researchers revealed the first evidence that a malaria outbreak in neighbouring Ethiopia earlier this year was caused by Anopheles stephensi.
In the eastern Ethiopian city of Dire Dawa, a transport hub between the capital Addis Ababa and Djibouti, 205 malaria cases were reported in all of 2019.
However this year more than 2,400 cases were reported between January and May. The outbreak was unprecedented because it took place during the country's dry season, when malaria has usually been rare.
- 'Surprising' -
As the numbers were rising, Fitsum Girma Tadesse, a molecular biologist at Ethiopia's Armauer Hansen Research Institute, and other researchers "jumped in to investigate," he told AFP.
They quickly determined that "Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes are responsible for the increase in cases," Tadesse said.
They linked Anopheles stephensi to the infections of the patients, and also found the mosquitoes -- carrying malaria -- in nearby water containers.
Tadesse warned that the mosquito's preference for open water tanks, common across many African cities, "makes it unique".
The research, which has not been peer reviewed, was presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene being held this week in Seattle, US.
Also presented at the conference were early findings that identified Anopheles stephensi at 64 percent of 60 test sites in nine states of neighbouring Sudan.
"In some instances, we have found that up to 94 percent of households have stephensi" mosquitoes nearby, Hmooda Kafy, the head of the integrated vector management department at Sudan's health ministry, said in a statement.
The findings come after the Nigerian Institute of Medical Research confirmed in July it had detected Anopheles stephensi in West Africa for the first time.
Sarah Zohdy, an Anopheles stephensi specialist at the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, told AFP it was "surprising" that the mosquito was detected so far west, as the focus had been on the Horn of Africa.
- 'A major threat' -
In the last couple of months it has been shown that Anopheles stephensi "is no longer a potential threat" in Africa, Zohdy said.
"In the Ethiopian context, this is a threat -- we now have data to show that," said Zohdy, who also works with the US President's Malaria Initiative, a partner of the Dire Dawa study.
"The evidence now exists to suggest that this is something that the world needs to act on," she added.
Anopheles stephensi has also been reportedly detected in Somalia, according to the WHO, which in September launched an initiative aimed at stopping the spread of the mosquito in Africa.
Because Anopheles stephensi can thrive in urban water tanks, "you get a shift from a seasonal disease to one that can persist year round," Zohdy said.
That shift poses "a major threat" to recent gains made against malaria, she added.
Deaths from malaria had more than halved from the start of the century to 2017 -- largely due to insecticide-treated mosquito nets, testing and drugs -- before progress stalled during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Zohdy called for increased surveillance to find out exactly how far Anopheles stephensi has spread across the continent.
"The true extent of the distribution of the mosquito is unknown," she said.
A.Gasser--BTB




