-
 Beyond limits: Croatian freediver's breathtaking record
Beyond limits: Croatian freediver's breathtaking record
-
Tottenham supporting Udogie after alleged gun threat in London

-
 Thunder roll Clippers to stay unbeaten as SGA keeps streak alive
Thunder roll Clippers to stay unbeaten as SGA keeps streak alive
-
In appeal, Australian mushroom murderer alleges 'miscarriage of justice'

-
 Toyota hikes profit forecasts 'despite US tariffs'
Toyota hikes profit forecasts 'despite US tariffs'
-
Ex-France lock Willemse challenges Meafou to become 'the bully'

-
 Ukrainians to honour sporting dead by building country they 'died for': minister
Ukrainians to honour sporting dead by building country they 'died for': minister
-
At least 7 dead after UPS cargo plane crashes near Louisville airport

-
 US Supreme Court hears challenge to Trump tariff powers
US Supreme Court hears challenge to Trump tariff powers
-
US government shutdown becomes longest in history

-
 India's Modi readies bellwether poll in poorest state
India's Modi readies bellwether poll in poorest state
-
Green goals versus growth needs: India's climate scorecard

-
 Where things stand on China-US trade after Trump and Xi talk
Where things stand on China-US trade after Trump and Xi talk
-
Sri Lanka targets big fish in anti-corruption push

-
 NY elects leftist mayor on big election night for Democrats
NY elects leftist mayor on big election night for Democrats
-
Injured Jordie Barrett to miss rest of All Blacks tour

-
 Asian markets tumble as tech bubble fears grow
Asian markets tumble as tech bubble fears grow
-
Pay to protect: Brazil pitches new forest fund at COP30

-
 Iraq's social media mercenaries dying for Russia
Iraq's social media mercenaries dying for Russia
-
Young leftist Trump foe elected New York mayor

-
 Concerns at ILO over expected appointment of close Trump advisor
Concerns at ILO over expected appointment of close Trump advisor
-
Venus Williams to return to Auckland Classic at the age of 45

-
 No deal yet on EU climate targets as COP30 looms
No deal yet on EU climate targets as COP30 looms
-
Typhoon death toll climbs to 66 in the Philippines

-
 NATO tests war preparedness on eastern flank facing Russia
NATO tests war preparedness on eastern flank facing Russia
-
Uncapped opener Weatherald in Australia squad for first Ashes Test

-
 Liverpool down Real Madrid in Champions League, Bayern edge PSG
Liverpool down Real Madrid in Champions League, Bayern edge PSG
-
Van Dijk tells Liverpool to keep calm and follow Arsenal's lead

-
 PSG left to sweat on injuries to Dembele and Hakimi
PSG left to sweat on injuries to Dembele and Hakimi
-
Reddit, Kick to be included in Australia's social media ban

-
 Ex-Zimbabwe cricket captain Williams treated for 'drug addiction'
Ex-Zimbabwe cricket captain Williams treated for 'drug addiction'
-
Padres ace Darvish to miss 2026 MLB season after surgery

-
 Diaz hero and villain as Bayern beat PSG in Champions League showdown
Diaz hero and villain as Bayern beat PSG in Champions League showdown
-
Liverpool master Real Madrid on Alexander-Arnold's return

-
 Van de Ven back in favour as stunning strike fuels Spurs rout
Van de Ven back in favour as stunning strike fuels Spurs rout
-
Juve held by Sporting Lisbon in stalling Champions League campaign

-
 New lawsuit alleges Spotify allows streaming fraud
New lawsuit alleges Spotify allows streaming fraud
-
Stocks mostly drop as tech rally fades

-
 LIV Golf switching to 72-hole format in 2026: official
LIV Golf switching to 72-hole format in 2026: official
-
Manchester City have become 'more beatable', says Dortmund's Gross

-
 Merino brace sends Arsenal past Slavia in Champions League
Merino brace sends Arsenal past Slavia in Champions League
-
Djokovic makes winning return in Athens

-
 Napoli and Eintracht Frankfurt in Champions League stalemate
Napoli and Eintracht Frankfurt in Champions League stalemate
-
Arsenal's Dowman becomes youngest-ever Champions League player

-
 Cheney shaped US like no other VP. Until he didn't.
Cheney shaped US like no other VP. Until he didn't.
-
Pakistan edge South Africa in tense ODI finish in Faisalabad

-
 Brazil's Lula urges less talk, more action at COP30 climate meet
Brazil's Lula urges less talk, more action at COP30 climate meet
-
Barca's Lewandowski says his season starting now after injury struggles

-
 Burn urges Newcastle to show their ugly side in Bilbao clash
Burn urges Newcastle to show their ugly side in Bilbao clash
-
French pair released after 3-year Iran jail ordeal


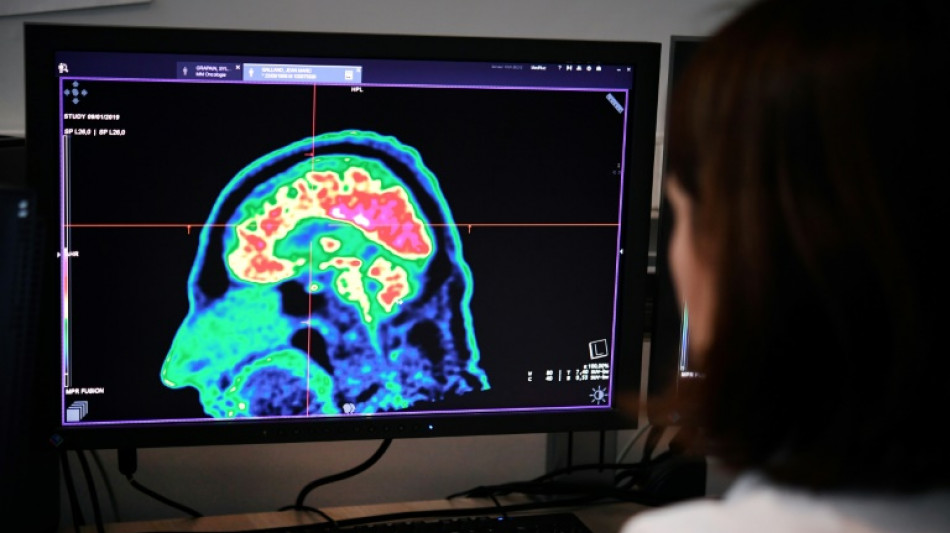
First child cured of rare brain tumour 'offers real hope'
When Lucas was diagnosed with a rare type of brain tumour at the age of six, there was no doubting the prognosis.
French doctor Jacques Grill gets emotional when he remembers having to tell Lucas's parents that their son was going to die,
However, seven years later, Lucas is now 13 years old and there is no trace of the tumour left.
The Belgian boy is the first child in the world to have been cured of brainstem glioma, a particularly brutal cancer, according to the researchers who treated him.
"Lucas beat all the odds" to survive, said Grill, head of the brain tumour programme at the Gustave Roussy cancer centre in Paris.
The tumour, which has the full name diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG), is diagnosed every year in around 300 children in the United States, and up to 100 in France.
Ahead of International Childhood Cancer Day on Thursday, the medical community has praised advances that mean 85 percent of children now survive more than five years after being diagnosed with cancer.
But the outlook for children with the DIPG tumour remains grim -- most do not live a year beyond diagnosis. A recent study found that only 10 percent were alive two years on.
Radiotherapy can sometimes slow the rapid march of the aggressive tumour, but no drug has been shown to be effective against it.
- 'No other case like him' -
Lucas and his family travelled from Belgium to France so that he could become one of the first patients to join the BIOMEDE trial which tests potential new drugs for DIPG.
From the start, Lucas responded strongly to the cancer drug everolimus, which he was randomly assigned.
"Over a series of MRI scans, I watched as the tumour completely disappeared," Grill told AFP.
But the doctor did not dare stop the treatment regimen -- at least until a year and a half ago, when Lucas revealed he was no longer taking the drugs anyways.
"I don't know of any other case like him in the world," Grill said.
Exactly why Lucas so fully recovered, and how his case could help other children like him in the future, remains to be seen.
Seven other children in the trial survived years after being diagnosed, but only Lucas's tumour completely vanished.
The reason these children responded to the drugs, while others did not, was likely due to the "biological particularities" of their individual tumours, Grill said.
"Lucas's tumour had an extremely rare mutation which we believe made its cells far more sensitive to the drug," he added.
- Reproducing Lucas -
The researchers are studying the genetic abnormalities of patients' tumours as well as creating tumour "organoids," which are masses of cells produced in the lab.
"Lucas's case offers real hope," said Marie-Anne Debily, a researcher supervising the lab work.
"We will try to reproduce in vitro the differences that we have identified in his cells," she told AFP.
The team want to reproduce his genetic differences in the organoids to see if the tumour can then be killed off as effectively as it was in Lucas.
If that works, the "next step will be to find a drug that has the same effect on tumour cells as these cellular changes," Debily said.
While the researchers are excited about this new lead, they warned that any possible treatment is still a long way off.
"On average, it takes 10-15 years from the first lead to become a drug -- it's a long and drawn-out process," Grill said.
David Ziegler, a paediatric oncologist at Sydney Children's Hospital in Australia, said that the landscape for DIPG has dramatically changed over the last decade.
Breakthroughs in the lab, increased funding and trials such as BIOMEDE make "me convinced that we will soon find that we are able to cure some patients," Ziegler told AFP.
A.Ruegg--VB




