
-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
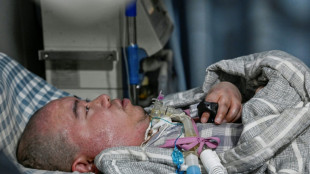
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain

-
 Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
-
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
-
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge

-
 Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans

-
 Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report

-
 Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
-
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate

-
 Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
-
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
-
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16

-
 Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV
Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV
-
Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli

-
 US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting
US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting
-
US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak

-
 Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary
Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary
-
US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics

-
 Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom
Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom
-
Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims

-
 Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub
Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub
-
Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave

-
 SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report
SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report
-
White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state

-
 Iran vows to resist any US attack, insists ready for nuclear deal
Iran vows to resist any US attack, insists ready for nuclear deal
-
Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador

-
 Former Masters champ Reed returning to PGA Tour from LIV
Former Masters champ Reed returning to PGA Tour from LIV
-
US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure

-
 Norway's McGrath tops first leg of Schladming slalom
Norway's McGrath tops first leg of Schladming slalom
-
Iraq PM candidate Maliki denounces Trump's 'blatant' interference

-
 Neil Young gifts music to Greenland residents for stress relief
Neil Young gifts music to Greenland residents for stress relief
-
Rubio upbeat on Venezuela cooperation but wields stick


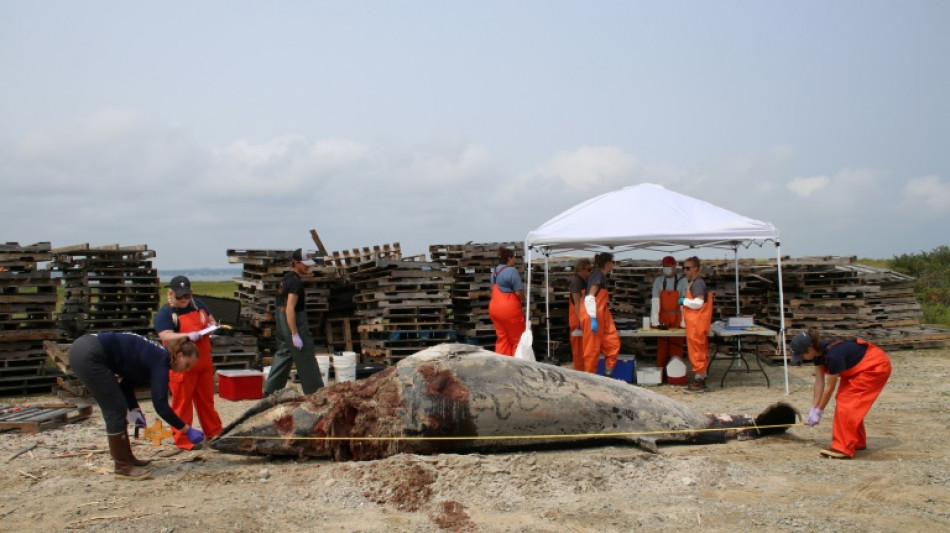
On US coast, wind power foes embrace 'Save the Whales' argument
Whether from real concern for marine animals or doubts about renewable energy, the anti-wind power movement has been growing along the US East Coast, with some trying to blame a surge in whale strandings on the growth of offshore energy projects.
Their attempt to link the two seems to be resonating, despite what scientists say is a clear lack of evidence.
When Lauren Brandkamp and her team from the nonprofit Whale and Dolphin Conservation organization in Massachusetts carry out a rescue on an area beach, one of the first questions bystanders ask is: "Was this wind?"
Facebook groups vehemently opposing offshore wind projects have been growing, with some citing NIMBY (Not in My Back Yard) concerns, and others claiming that soaring wind turbines do real harm to sea creatures or the environment.
Wind power critics have organized coastal town gatherings, posted "Save the Whales" signs and filed lawsuits in a bid to bury new wind projects under crushing litigation fees.
A recent surge in whale strandings or deaths has given them added ammunition.
From coastal Virginia to Maine in the far northeast, the region has in fact witnessed unusual mortality among Atlantic Minke whales, Atlantic humpback whales and endangered North Atlantic right whales.
This has coincided with efforts by President Joe Biden's administration to ramp up offshore wind projects, curb emissions and encourage a shift to renewable energy.
The administration has approved 10 commercial-scale offshore projects since 2021. Three domestic offshore farms have been operating for several years, and three are under construction.
Yet scientists have found no evidence linking wind power to the deaths of large marine mammals.
They point instead to collisions with ships in crowded sea lanes, entanglements with fishing nets, and disease.
- 'Misplaced' concerns -
"I'm glad that there is such attention being paid now to whales, but it is a little bit misplaced," said Brandkamp, whose title with Whale and Dolphin Conservation is stranding coordinator.
Local residents and beachgoers, she said, are usually receptive to her team's conservation awareness talks during a rescue.
Online, however, the discourse is harsher, with "more hostility, more skepticism."
The US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) points to interactions with ships as the leading cause of strandings, stating that there are "no known links between large whale deaths and ongoing offshore wind activities."
Ashley Stokes, director of marine mammal conservation at Seacoast Science Center in Rye, New Hampshire, told AFP that despite extensive research, scientists have found no "evidence to show any linkage between the two."
"The leading factors found have been ship-strike, entanglement and infectious disease," she said.
- Construction noise -
Anti-wind activists and conspiracy theorists on social media contend that the noise of wind turbine construction can dangerously disorient whales -- which use sonar to orient themselves -- leading to strandings.
But scientists question that.
Douglas Nowacek is part of a $10.5 million research project commissioned by the US Energy Department to investigate "construction nuisance" -- including noise -- around offshore wind activities along the East Coast.
Nowacek said he has seen wind turbine installers using the pile-driving method -- repeatedly hammering steel or concrete piles into the seabed -- in proximity to whales and yet observed no "overt or obvious behaviors."
There was no "evidence whatsoever that any offshore wind activities have resulted in anything even approaching the mortality of oil," he said.
He said surveyors for the oil and gas industry use a tool called the seismic air gun, which is roughly 10,000 times louder than pile-driving.
Jenna Reynolds, director of Save Coastal Wildlife in New Jersey, told AFP that if offshore wind projects were "having an impact, there'd be some whistleblower somewhere around in Europe or Asia, saying, 'I've seen offshore wind do all this damage to whales, dolphins or seals.'"
Both Reynolds and Brandkamp pointed to shifts in marine ecosystems linked to warmer waters in recent decades -- with more species pushing northward into increasingly busy shipping areas.
"I am not pro- or anti-offshore wind," Reynolds said. But "I'm very concerned about global warming, because it is having a huge impact on coastal wildlife.
"I know that offshore wind is going to have impacts. Nothing is perfect. (But) I would rather have offshore wind than oil platforms out in the ocean."
P.Staeheli--VB



