
-
 Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
-
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
-
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map

-
 Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
-
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security

-
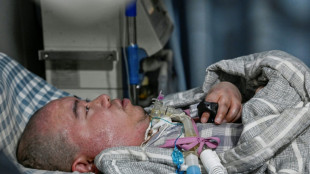 Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran

-
 China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
-
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military

-
 As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
-
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence

-
 Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
-
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
-
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season

-
 Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
-
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art

-
 Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
-
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest

-
 Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16

-
 Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
-
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
-
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
-
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16

-
 PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
-
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot

-
 Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
-
Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV

-
 Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
-
US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting

-
 US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
-
Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary

-
 US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
-
Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom

-
 Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
-
Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub

-
 Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
-
SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report

-
 White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state
White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state
-
Iran vows to resist any US attack, insists ready for nuclear deal

-
 Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador
Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador
-
Former Masters champ Reed returning to PGA Tour from LIV

-
 US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure
US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure
-
Norway's McGrath tops first leg of Schladming slalom


Overshooting 1.5C risks 'irreversible' climate impact: study
Any breach of what climate scientists agree is the safer limit on global warming would result in "irreversible consequences" for the planet, said a major academic study published on Wednesday.
Even temporarily exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius before bringing temperatures back down -- a scenario known as an "overshoot" -- could cause sea level rises and other disastrous repercussions that might last millenia.
This "does away with the notion that overshoot delivers a similar climate outcome" to a future where more was done earlier to curb global warming, said Carl-Friedrich Schleussner, who led the study co-authored by 30 scientists.
The findings, three years in the making, are urgent, as the goal of capping global temperature rises at 1.5C above pre-industrial levels is slipping out of reach.
Emissions of heat-trapping greenhouse gases must nearly halve by 2030 if the world is to reach 1.5C -- the more ambitious target enshrined in the 2015 Paris climate accord.
Currently however, they are still rising.
Some kind of overshoot of 1.5C is increasingly being seen as inevitable by scientists and policymakers.
This new study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature, cautions against "overconfidence" in such a scenario when the dangers are not fully appreciated.
An overshoot could trigger impacts that last hundreds if not thousands of years, or cross "tipping points" that prompt large and unrepairable changes in earth's climate system, the scientists warn.
It could mean the thawing of permafrost and peatlands, carbon-rich landscapes that would release huge volumes of planet-heating greenhouse gases if lost.
And sea levels could rise an additional 40 centimetres (16 inches) if 1.5C is exceeded for a century, the authors said, an existential difference for vulnerable low-level island nations.
"For most climate indicators, there are irreversible consequences due to the temporary exceedance of, for example, the 1.5 degree limit," said Schleussner from the Austria-based International Institute of Applied Systems Analysis.
"Even if you brought temperatures back down again, the world that we are looking at is not the same as if you didn't overshoot."
- Act now -
Taken together, the world's existing pledges for climate action would result in nearly 3C of warming by 2100, according to the UN.
To reach 1.5C, emissions must be at net zero by 2050, which means balancing the amount of carbon dioxide produced against the amount humanity can remove from the atmosphere via technology.
This process, known as carbon removal, would need to be massively scaled up to pull global temperatures back down in the event of an overshoot, something that is far from guaranteed.
"We cannot be confident that temperature decline after overshoot is achievable within the timescales expected today," the authors wrote.
Schleussner said their findings reinforced "the urgency of governments acting to reduce emissions now and not later down the line, to keep peak warming as low as possible".
"If you want to limit the climate risks in an effective manner, the race to net zero needs to be seen for what it is," he said.
K.Hofmann--VB



