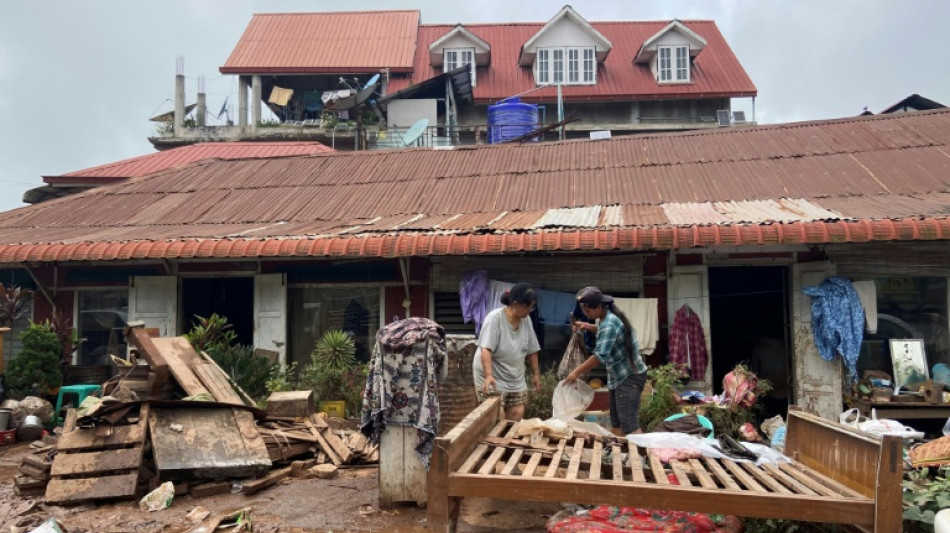

-
 Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi
-
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos
-
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map

-
 Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
-
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security

-
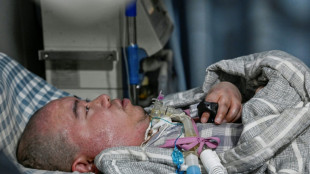 Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran

-
 China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port
-
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military

-
 As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
-
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence

-
 Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop
-
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
-
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season

-
 Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs
-
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art

-
 Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain
-
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest

-
 Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16

-
 Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
-
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans
-
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss

-
 Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report
-
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16

-
 PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate
-
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16
-
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot

-
 Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16
-
Bayern inflict Kane-ful Champions League defeat on PSV

-
 Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
Pedro double fires Chelsea into Champions League last 16, dumps out Napoli
-
US stocks move sideways, shruggging off low-key Fed meeting

-
 US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
US capital Washington under fire after massive sewage leak
-
Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary

-
 US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
US ambassador says no ICE patrols at Winter Olympics
-
Norway's Kristoffersen wins Schladming slalom

-
 Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims
-
Brady latest to blast Belichick Hall of Fame snub

-
 Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
Trump battles Minneapolis shooting fallout as agents put on leave
-
SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report

-
 White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state
White House, Slovakia deny report on Trump's mental state
-
Iran vows to resist any US attack, insists ready for nuclear deal

-
 Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador
Colombia leader offers talks to end trade war with Ecuador
-
Former Masters champ Reed returning to PGA Tour from LIV

-
 US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure
US Fed holds interest rates steady, defying Trump pressure
-
Norway's McGrath tops first leg of Schladming slalom


Supercharged storms: how climate change amplifies cyclones
From Hurricane Helene to Typhoon Yagi, powerful storms are battering the globe, and scientists warn that a warming planet is amplifying their destructive force to unprecedented levels.
Here's what the latest research reveals about how climate change is supercharging tropical cyclones -- the generic term for both weather phenomenon.
- Packing more punch -
First, the basics: warmer ocean surfaces release more water vapor, providing additional energy for storms, which intensifies their winds. A warming atmosphere also allows them to hold more water, boosting heavy rainfall.
"On average, the destructive potential of hurricanes has increased about 40 percent due to the 1 degrees Celsius (roughly 2 degrees Fahrenheit) warming that has already taken place," Michael Mann, a climatologist at University of Pennsylvania, told AFP.
In a recent paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Mann added his voice to calls for the Saffir-Simpson scale to be expanded to include a "new class of monster storms" -- Category 6, where sustained winds exceed 192 miles per hour (308 kph).
According to experts, climate change set the stage for Helene, which peaked as a Category 4 hurricane.
"The oceanic heat content was at a record level, providing plenty of fuel and potential for a storm like this to gain strength and become a large and very damaging storm," David Zierden, Florida's state climatologist, told AFP.
- Rapid intensification -
"Rapid intensification," defined as a hurricane speeding up by 30 knots within a 24-hour period, is also becoming more common.
"If intensification happens very close to the coast in the lead up to landfall, it can have a huge effect, which you saw last week in the case of Helene," Karthik Balaguru, a climate scientist at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, told AFP.
Balaguru was the lead author on a paper this year in journal Earth's Future that used decades of satellite data to show "a robust increase in the rates at which storms intensified close to the coast, and this is across the world."
The explanation is two-fold.
Warming climate patterns are reducing wind shear -- changes in wind speed and direction with height -- along both the Atlantic Coast of North America and the Pacific Coast of Asia.
"When you have strong wind shear, it tends to tear apart the core of the storm," explained Balaguru.
Climate change is also driving higher humidity along coastlines compared to the open ocean.
This is likely due to a thermal gradient created as land heats faster than water, causing changes in pressure and wind circulation that push moisture into the mid-troposphere where storms can access it. More data is needed to confirm this hypothesis.
Additionally, rising sea levels -- about a foot over the past century -- mean cyclones are now operating from a higher baseline, amplifying storm surges, said Zierden.
- How often? -
While the impact of climate change on how often cyclones happen is still an active area of research, studies suggest it can either increase or decrease frequency, depending on the region.
Particle pollution generated by industry, vehicles, and the energy sector blocks sunlight, partially offsetting the warming effects of greenhouse gases.
In a Science Advances paper, Hiroyuki Murakami, a physical scientist at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, found that particle emissions from the US and Europe peaked around 1980, and their decline leading to a rise in hurricane frequency in the Atlantic.
Conversely, in Asia, high pollution levels in China and India may be suppressing more frequent storm in the western Pacific, Murakami told AFP.
Another study he led found that human activity has increased tropical cyclone activity off Japan’s coast, raising the risk of rare precipitation events in the country's west through frontal rainbands—even when the storms themselves don’t make landfall.
This year's North Atlantic hurricane season was initially projected to be highly active. However, various meteorological factors created a lull from August through September, according to Zierden and Murakami.
Now, though "we've seen a dramatic ramp-up over the past week," said Mann. With hurricane season running until November 30, we're not in the clear yet, he stressed.
G.Frei--VB



