
-
 Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
-
UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China

-
 US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
-
'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites

-
 Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
-
'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study

-
 Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
-
Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits

-
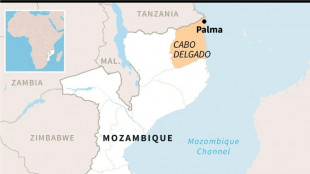 Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
-
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi

-
 Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
-
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures

-
 Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
-
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing

-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China

-
 Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
-
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics

-
 China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
-
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike

-
 Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
-
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis

-
 Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
-
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace

-
 No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
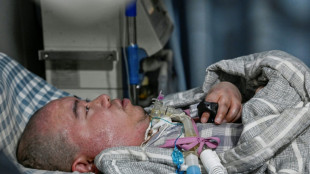
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain


Combining climate measures key to slashing emissions: study
A major new study published Thursday on the effectiveness of climate measures such as taxes or subsidies in reducing greenhouse gases has found stand-alone measures fail to make a big difference.
Published in the journal Science, the study examined 25 years of public policies in 41 countries across six continents.
It concluded that out of the 1,500 policies analysed in sectors including energy, transport and construction, "only 63 cases of successful climate policies, each leading to average emission reductions of 19 percent, were identified."
"The researchers show that bans on coal-fired power plants or combustion engine cars do not result in major emissions reductions when implemented alone," said the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) that led the study with Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC).
"Successful cases only arise in tandem with tax or price incentives in well-designed policy mixes, as shown in the UK for coal-fired power generation or in Norway for cars," the researchers said.
The study used a new OECD database and an innovative approach that combined machine learning methods with established statistical analyses.
It "identified 63 successful policy interventions with total emission reductions between 0.6 billion and 1.8 billion tonnes CO2".
By comparison, humanity emitted 57.4 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent in 2022, according to United Nations estimates.
Among the successes identified was Britain's introduction in 2013 of a minimum carbon price, subsidies for renewable energy, and a coal phase-out plan.
The researchers hope their work will influence the climate roadmaps countries are updating and must submit to the UN by February 2025.
The aim of these roadmaps is to keep alive the Paris Agreement's flagship goal of limiting warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius from pre-industrial levels.
- 'Right mix is crucial' -
An interactive website, "Climate Policy Explorer", provides an overview of the results, analysis and methods, and is accessible to the public.
"Our findings demonstrate that more policies do not necessarily equate to better outcomes. Instead, the right mix of measures is crucial," explained the study's lead author Nicolas Koch of PIK and MCC.
"For example, subsidies or regulations alone are insufficient; only in combination with price-based instruments, such as carbon and energy taxes, can they deliver substantial emission reductions."
"But by focusing only on 69 statistically identifiable large trend breaks, they miss the impact of thousands of smaller efforts globally, and the cumulative and often self-reinforcing impact of many smaller measures", said Michael Grubb at University College London.
He also acknowledged "the most sophisticated study to date".
"Their conclusion that big impacts require combinations of policies makes absolute sense," he added.
"The study only looks for policies making sudden reductions, whereas most climate policies work on the efficiency of new things or the long-term trajectory of emissions, taking many years to build up greener infrastructure or ways of living," said Robin Lamboll at Imperial College London.
M.Betschart--VB



