
-
 Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
-
French IT group Capgemini under fire over ICE links

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
-
Oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat; gold retreats from highs

-
 Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
-
Holders PSG, Real Madrid among clubs awaiting Champions League play-offs draw

-
 England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
-
US Senate vote to avert government shutdown expected to fail

-
 Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
-
Turkey to offer mediation in US-Iran showdown

-
 World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
-
EU designates Iran Guards as 'terrorist organisation'

-
 Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
Czechs wind up black coal mining in green energy switch
-
Where does Iraq stand as US turns up heat on Iran?

-
 Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
Vietnam designer makes history as Paris Haute Couture wraps up
-
Denmark hails 'very constructive' meeting with US over Greenland

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission
-
EU to put Iran Guards on 'terrorist list'

-
 Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
Pegula calls herself 'shoddy, erratic' in Melbourne semi-final loss
-
All hands on deck: British Navy sobers up alcohol policy

-
 Sabalenka says Serena return would be 'cool' after great refuses to rule it out
Sabalenka says Serena return would be 'cool' after great refuses to rule it out
-
Rybakina plots revenge over Sabalenka in Australian Open final

-
 Irish Six Nations hopes hit by Aki ban
Irish Six Nations hopes hit by Aki ban
-
Britain's Starmer hails 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi

-
 Parrots rescued as landslide-hit Sicilian town saves pets
Parrots rescued as landslide-hit Sicilian town saves pets
-
Gold surges further, oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat

-
 No handshake as Sabalenka sets up repeat of 2023 Melbourne final
No handshake as Sabalenka sets up repeat of 2023 Melbourne final
-
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' set for EU terror listing

-
 EU eyes migration clampdown with push on deportations, visas
EU eyes migration clampdown with push on deportations, visas
-
Umpire call fired up Sabalenka in politically charged Melbourne clash

-
 Rybakina battles into Australian Open final against Sabalenka
Rybakina battles into Australian Open final against Sabalenka
-
Iran vows 'crushing response', EU targets Revolutionary Guards

-
 Northern Mozambique: massive gas potential in an insurgency zone
Northern Mozambique: massive gas potential in an insurgency zone
-
Gold demand hits record high on Trump policy doubts: industry

-
 Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
-
UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China

-
 US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
-
'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites

-
 Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
-
'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study

-
 Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
-
Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits

-
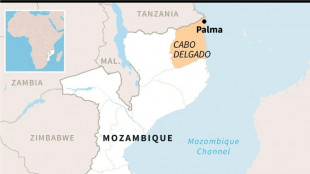 Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
-
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi

-
 Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
-
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures

-
 Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
-
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing

-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release


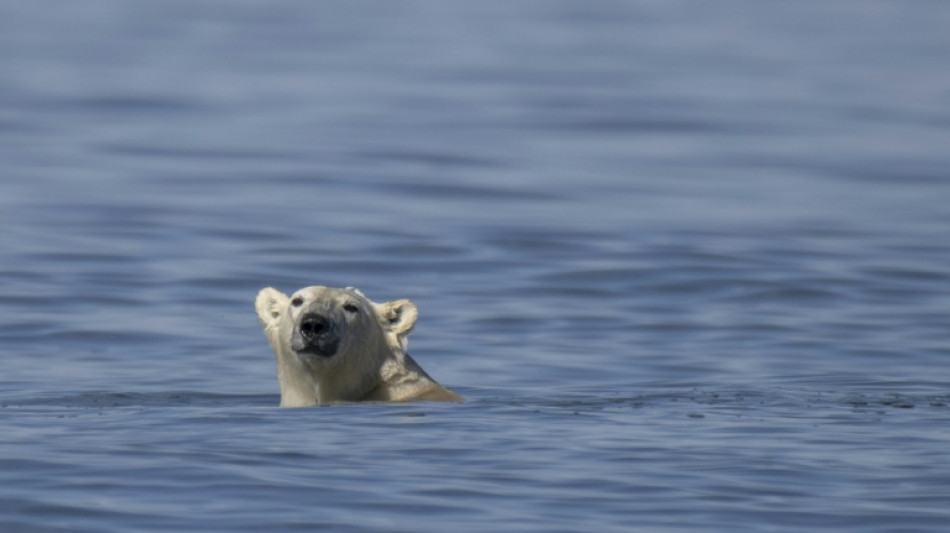
Polar bears could vanish from Canada's Hudson Bay if temperatures rise 2C
An international team of scientists said Thursday that polar bears faced local extinction in Canada's Hudson Bay by mid-century if global warming exceeds limits set under the Paris climate accords.
Climate change has sharply increased the number of days where Arctic sea ice is too thin for polar bears to hunt seals.
That forces them to spend longer stretches ashore without their main food source.
Using models, researchers considered how future rises in global temperatures could hit ice thickness in Hudson Bay and in turn, the fate of its iconic and endangered polar bears.
They found that if temperatures rose 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels the resulting ice-free period would simply be too long for many bears to survive.
Bear populations in southern Hudson Bay -- where it takes longer for winter ice to return -- would be the first to go, said the study's lead author Julienne Stroeve.
"Those bears are unlikely to survive in that region" and could disappear by the middle of this century, the Arctic climate scientist from the University of Manitoba told AFP.
The collapse of Hudson Bay's other major bear population in the west would not be far behind, she added. Global warming above 2C would render this habitat increasingly unsuitable for hunting and breeding.
- Struggle to survive -
Under the 2015 Paris agreement, nations agreed to limit temperature rises to well below 2C to avoid the worst effects of climate change, and to strive for a safer 1.5C cap.
Global temperatures are already 1.2C higher than the 1850-1900 pre-industrial era and the world is tracking toward 2.9C of warming by 2100, according to the United Nations.
This has lengthened periods without ice in the fast-warming Arctic, directly affecting polar bears, which need a firm platform to cross the seas and hunt seals, their main prey.
During the summer melt the bears are forced ashore to await the return of winter sea ice, and can shed up to two kilograms a day during this fasting period.
But human-caused climate change has extended the ice-free period in Hudson Bay by a month over the past decade, said the study, published in the journal Communications Earth and Environment.
With 2C of warming, the southern Hudson Bay would be ice-free for more than 180 days -- beyond the "hard limit" of what bears can endure, said Stroeve.
"It might start getting too long, then they won't be able to survive," she added.
This same threshold would be breached in western Hudson Bay at between 2.2C and 2.6C of warming, she said.
- 'Wake up call' -
Longer ice-free periods in Hudson Bay were already impacting polar bear breeding and population numbers, meaning their extinction locally "may already be inevitable", said the study.
"That environment is rapidly changing, and I don't think these ecosystems can adapt as quickly as they need to," Stroeve said. "That's really quite sad for me."
Other research has found that Hudson Bay's bears were trying to adapt to longer periods on land by finding other food, but could not match the calories of their normal marine diets.
The past 12 months have been the hottest in recorded history, with land and ocean temperatures hitting unprecedented highs.
Stroeve said southern parts of Hudson Bay were already ice-free, something that does not normally start happening until early July.
"This is the earliest breakout of ice we've ever seen," she said. "That doesn't spell good news for the bears."
Their findings were a harbinger of polar bear survival elsewhere in the Arctic, she added.
As Hudson Bay's bears are further south than any others, they have long been considered an indicator of how their counterparts further north will fare in the future.
"It sort of gives us a wake-up call. This is starting to be the fate of these bears," Stroeve said.
A.Zbinden--VB



