
-
 Extensive destruction in Beirut's southern suburbs following Israeli strikes
Extensive destruction in Beirut's southern suburbs following Israeli strikes
-
Most Asian equities drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 'Super special' Allen can light up big occasion for New Zealand
'Super special' Allen can light up big occasion for New Zealand
-
'Genie' Bumrah: India's yorker king who carries a billion hopes

-
 'There will be nerves': India face New Zealand for T20 World Cup glory
'There will be nerves': India face New Zealand for T20 World Cup glory
-
Lufthansa warns of heightened 'uncertainty' from Mideast war

-
 Mideast war enters 'next phase' as strikes hit Iran, Lebanon
Mideast war enters 'next phase' as strikes hit Iran, Lebanon
-
Equities mixed as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 Sri Lanka denounces war deaths, houses Iran sailors
Sri Lanka denounces war deaths, houses Iran sailors
-
Inoue primed for 'historic' Nakatani clash in Tokyo

-
 Italy challenges EU over key climate tool
Italy challenges EU over key climate tool
-
Home hero Piastri edges Antonelli in second Australian GP practice

-
 Australia forces porn sites to block under-18s from Monday
Australia forces porn sites to block under-18s from Monday
-
Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn

-
 Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems
Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems
-
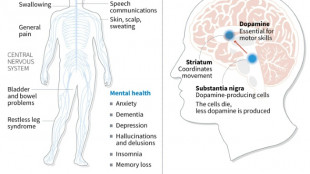
Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
-
 Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'
Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'
-
North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning

-
 Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer
Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer
-
Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse

-
 Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold
Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold
-
Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice

-
 Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips
Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips
-
Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election

-
 Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett
Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett
-
Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game

-
 French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche
French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche
-
Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output

-
 Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets
Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets
-
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut

-
 Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv

-
 US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored
-
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates

-
 Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor
-
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63

-
 Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms
-
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis

-
 El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group
-
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before

-
 Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace
-
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge

-
 Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog
-
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday

-
 'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages
-
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook

-
 France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'
-
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai

-
 Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem
-
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over


Green shoots spring from ashes in Brazil's fire-resistant savanna
The huge wildfires that ripped through Brazil recently did not spare its vast tropical savanna, but green shoots are already emerging from the ashes there, proof of the vast grasslands' rare gift for fire resistance.
The Cerrado, the most species-rich savanna in the world, covers some two million square kilometers of land (770,000 square miles) in central Brazil -- nearly one-fifth of the country's entire surface area.
In Brasilia National Park, on the outskirts of the nation's capital, blackened soil and charred tree trunks stand testimony to the ferocity of a fire that ripped through 1,470 hectares (3,600 acres) of land in September.
Brazil was then in the throes of a record drought -- the city of Brasilia had gone 169 days without a drop of rain -- which lit the torch under the worst wildfire season in over a decade, blamed by experts at least partly on climate change.
But the Cerrado, which is less well-known than the neighboring Amazon and Pantanal wetlands, has a superpower: over millions of years, it has developed some resistance to flames and high temperatures.
- Upside-down forest -
"The Cerrado is an inverted forest. We see only a fraction of it because the forest is all under our feet," said Keiko Pellizzaro, an environmental analyst at the Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation, a government agency.
The Cerrado's deep root system acts like a "pump," sucking up groundwater "even during extreme drought," she said.
Meanwhile, above ground the trees' thick bark and the shells of the fruit act as "thermal insulators," said Isabel Schmidt, professor of ecology at the University of Brasilia.
Even if temperatures reach up to 800 centigrade (1,470 Fahrenheit), the vegetation can survive "as if it were just another hot day," she said.
A month after the recent fires, the first rains saw grass and small plants quickly beginning to grow, and new leaves sprouted on charred trees in Brasilia National Park.
"Even if it hadn't rained, we would have seen some resilience," Pellizzaro said.
"I'm amazed by its capacity for regeneration," said Priscila Erthal Risi, a 48-year-old volunteer who took part in an operation by the Chico Mendes Institute to replant the reserve with native species such as donkey's tail and Magonia pubescens trees.
- Tested to the limit -
Brazilian police are still investigating the cause of the fire in Brasilia National Park.
Most wildfires in Brazil are started by farmers or agribusiness workers to clear land for cattle grazing or crops.
Schmidt said the Cerrado's vegetation had always survived sporadic fires caused by lightning strikes during the rainy season.
But she warned that if extreme droughts become more frequent the biome's resilience could be tested.
"The resistance that plants and animals have to any type of fire was developed over millions of years, but climate change has taken place in a matter of decades. No organism can adapt that quickly," she said.
- 'Cradle of waters' at risk -
The Cerrado is crucial not only for the survival of the thousands of species that call it home but for the water supply of a large part of South America.
The so-called "cradle of waters" is home to the sources of some of the continent's biggest rivers and aquifers.
But its role as a continental spring is endangered.
With the rainy season starting later and later each year and the amount of rain declining by eight percent on average over the past three decades, the flow of the Cerrado's rivers has fallen by 15 percent.
If wildfires become more frequent, Schmidt warned, "many ecosystems that are more vulnerable to fire," including in the Cerrado, "will simply not survive."
B.Baumann--VB




