
-
 Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
-
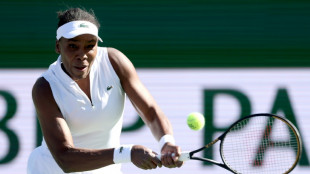
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
 Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
-
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored

-
 Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
-
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor

-
 Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
-
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms

-
 Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
-
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group

-
 With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
-
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace

-
 European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
-
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog

-
 Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
-
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages

-
 Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
-
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'

-
 Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
-
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem

-
 Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
-
Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error

-
 India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
-
Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated

-
 Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
-
Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race

-
 UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
-
EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop

-
 Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
-
India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase

-
 Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
-
Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup

-
 India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
-
Mideast war traps 20,000 seafarers, 15,000 cruise passengers in Gulf

-
 Italy bring back Brex to face England
Italy bring back Brex to face England
-
French policeman to be tried over 2023 killing of teen

-
 Oil prices rise, stocks slide as Middle East war stirs supply concerns
Oil prices rise, stocks slide as Middle East war stirs supply concerns
-
More flights take off despite continued fighting in Middle East

-
 Ukraine, Russia free 200 POWs each
Ukraine, Russia free 200 POWs each
-
Middle East war halts work at WHO's Dubai emergency hub

-
 Paramount's Ellison vows CNN editorial independence
Paramount's Ellison vows CNN editorial independence
-
US says attacks on alleged drug boats have spooked traffickers

-
 Dempsey returns as Scotland shuffle pack for Six Nations clash against France
Dempsey returns as Scotland shuffle pack for Six Nations clash against France
-
India pile up 253-7 against England in T20 World Cup semi-final

-
 Wary Europeans pledge 'defensive' military aid in Mideast war
Wary Europeans pledge 'defensive' military aid in Mideast war
-
Seven countries to boycott Paralympics ceremony over Russia: organisers

-
 UK's Crufts dog show opens with growing global appeal
UK's Crufts dog show opens with growing global appeal
-
PSG prepare for Chelsea clash with Monaco rematch

-
 Google opens AI centre as Berlin defends US tech reliance
Google opens AI centre as Berlin defends US tech reliance
-
Second Iranian ship nears Sri Lanka after submarine attack


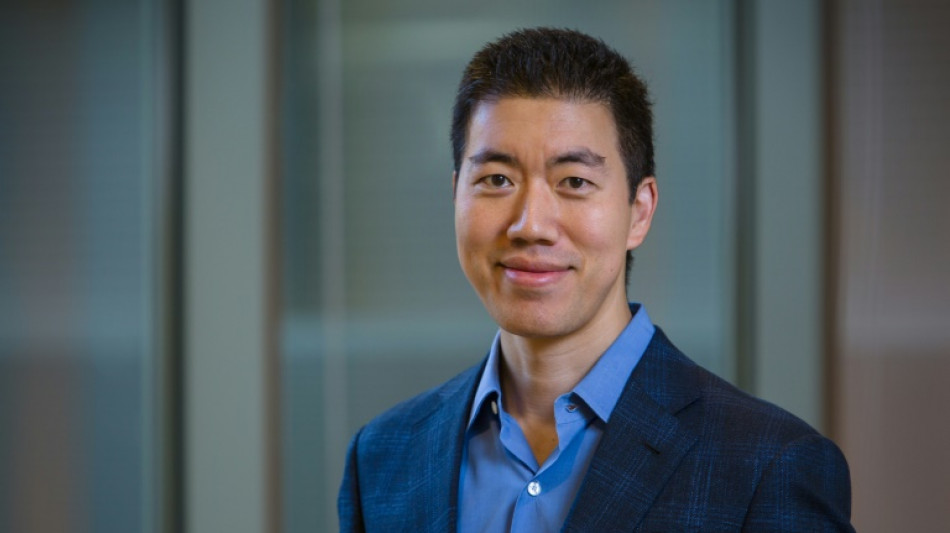
The scientist rewriting DNA, and the future of medicine
A revolution is underway in gene editing -- and at its forefront is David Liu, an American molecular biologist whose pioneering work is rewriting the building blocks of life with unprecedented precision.
A professor at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Liu was awarded a Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences on Saturday for developing two transformative technologies: one already improving the lives of patients with severe genetic diseases, the other poised to reshape medicine in the years ahead.
He spoke with AFP ahead of the Los Angeles ceremony for the prestigious Silicon Valley-founded award.
He will receive $3 million for his work on "base editing" and "prime editing," and plans to donate most of it to support his charitable foundation.
"The ability to change a DNA sequence of our choosing into a new sequence of our choosing is a fundamentally very powerful capability," the 51-year-old said, foreseeing uses not just in human medicine but areas like developing more nutritious or disease-resistant crops.
- Correcting the code -
DNA is made up of four chemical "letters" -- the nucleotide bases A, G, T and C. Mutations in this sequence cause thousands of human diseases, yet until recently, gene editing could only fix a limited number of them.
Even CRISPR-Cas9, the groundbreaking technology that earned a Nobel Prize in 2020, has major limitations.
It cuts both strands of the DNA helix, making it most useful to disrupt rather than correct genes, while the process can introduce new errors.
"Being able to use genome editing to treat genetic diseases requires, in most cases, ways to correct a DNA misspelling, not simply to disrupt a gene," Liu said.
That insight led his lab to develop base editing, which uses the Cas9 protein -- disabled so it can no longer cut both DNA strands -- to find a target DNA sequence and another enzyme to convert one letter to another -- for example, C to T or G to A.
Reversing the change -- from T to C or A to G -- was tougher. Liu's team overcame the challenge by engineering entirely new enzymes.
These base editors can now correct about 30 percent of the mutations that cause genetic diseases. The technology is already in at least 14 clinical trials.
In one of them, Beam Therapeutics -- which Liu co-founded -- announced it had treated patients of AATD, a rare genetic disorder affecting the lungs and liver, with a single drug infusion.
While traditional gene therapies often disrupt faulty genes or work around them, base editing repairs the mutation itself.
"This was the first time that humans have corrected a mutation that causes a genetic disease in a patient," Liu said.
- Cystic fibrosis hope -
Base editing, quickly dubbed "CRISPR 2.0," can't fix every mutation.
About 70 percent of the roughly 100,000 known disease-causing mutations remain out of its reach, including those caused by missing or extra letters.
To expand the toolkit, Liu's lab introduced prime editing in 2019 -- a method capable of replacing entire sections of faulty DNA with corrected sequences.
If CRISPR is like scissors that cut DNA, and base editors are like using a pencil to correct individual letters, then prime editing is the equivalent of a word processor's "find and replace" function.
Creating this tool required a series of breakthroughs Liu's team describes as "small miracles." The result is, he said, "the most versatile way we know of to edit the human genome."
Among the targets Liu and his team have already pursued with prime editing: cystic fibrosis, a common genetic disease usually caused by three missing DNA letters that causes thick mucus buildup in the lungs and digestive system.
Liu's lab has made much of its work freely accessible, sharing DNA blueprints through a nonprofit library used by tens of thousands of labs worldwide.
"The science we create -- which is ultimately funded by society, through governments and donors -- ultimately goes back to benefit society."
This year's Breakthrough Prize awards come at a fraught moment for US science, as President Donald Trump's government strips funding for institutions like the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
"The NIH is a treasure, not just for this country but for the world," said Liu. "Trying to dismantle the heart of what supports science in this country is like burning your seed corn."
P.Staeheli--VB



