
-
 Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
-
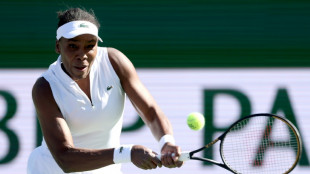
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
 Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
-
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored

-
 Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
-
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor

-
 Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
-
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms

-
 Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
-
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group

-
 With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
-
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace

-
 European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
-
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog

-
 Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
-
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages

-
 Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
-
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'

-
 Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
-
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem

-
 Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
-
Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error

-
 India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
-
Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated

-
 Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
-
Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race

-
 UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
-
EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop

-
 Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
-
India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase

-
 Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
-
Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup

-
 India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
-
Mideast war traps 20,000 seafarers, 15,000 cruise passengers in Gulf

-
 Italy bring back Brex to face England
Italy bring back Brex to face England
-
French policeman to be tried over 2023 killing of teen

-
 Oil prices rise, stocks slide as Middle East war stirs supply concerns
Oil prices rise, stocks slide as Middle East war stirs supply concerns
-
More flights take off despite continued fighting in Middle East

-
 Ukraine, Russia free 200 POWs each
Ukraine, Russia free 200 POWs each
-
Middle East war halts work at WHO's Dubai emergency hub

-
 Paramount's Ellison vows CNN editorial independence
Paramount's Ellison vows CNN editorial independence
-
US says attacks on alleged drug boats have spooked traffickers

-
 Dempsey returns as Scotland shuffle pack for Six Nations clash against France
Dempsey returns as Scotland shuffle pack for Six Nations clash against France
-
India pile up 253-7 against England in T20 World Cup semi-final

-
 Wary Europeans pledge 'defensive' military aid in Mideast war
Wary Europeans pledge 'defensive' military aid in Mideast war
-
Seven countries to boycott Paralympics ceremony over Russia: organisers

-
 UK's Crufts dog show opens with growing global appeal
UK's Crufts dog show opens with growing global appeal
-
PSG prepare for Chelsea clash with Monaco rematch

-
 Google opens AI centre as Berlin defends US tech reliance
Google opens AI centre as Berlin defends US tech reliance
-
Second Iranian ship nears Sri Lanka after submarine attack


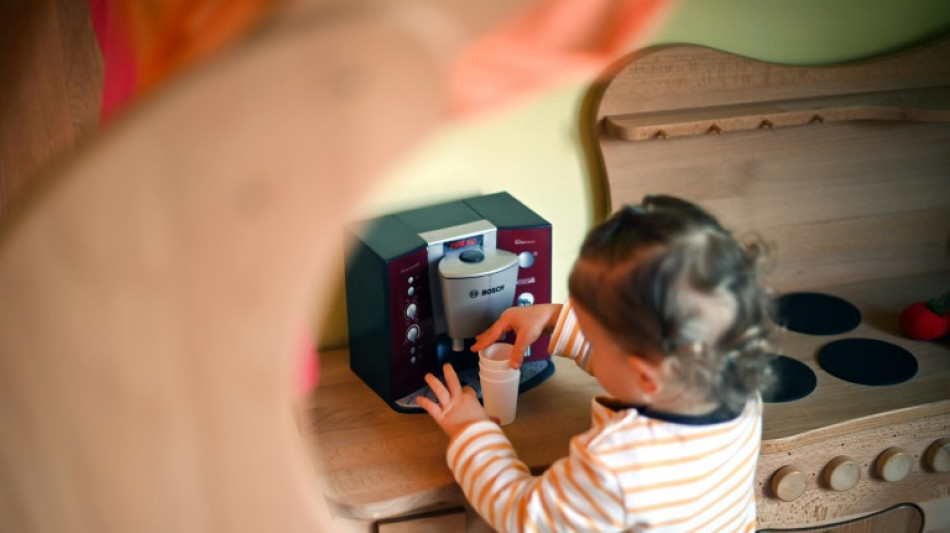
Infants remember more than you think, new study reveals
Our earliest years are a time of rapid learning, yet we typically cannot recall specific experiences from that period -- a phenomenon known as infantile amnesia.
A new study published in Science on Thursday challenges assumptions about infant memory, showing that young minds do indeed form memories. The question remains, however, why these memories become difficult to retrieve later in life.
"I've always been fascinated by this mysterious blank spot we have in our personal history," Nick Turk-Browne, professor of psychology at Yale and the study's senior author, told AFP.
Around the age of one, children become extraordinary learners -- acquiring language, walking, recognizing objects, understanding social bonds, and more. "Yet we remember none of those experiences -- so there's a sort of mismatch between this incredible plasticity and learning ability that we have," he said.
Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, hypothesized that early memories are repressed, though science has since largely dismissed the idea of an active suppression process. Instead, modern theories focus on the hippocampus, a part of the brain critical for episodic memory, which is not fully developed in infancy.
Turk-Browne, however, was intrigued by clues from previous behavioral research. Since babies cannot verbally report memories before acquiring language, their tendency to gaze longer at familiar things provides important hints.
Recent rodent studies monitoring brain activity have also shown that engrams -- patterns of cells that store memories -- form in the infant hippocampus but become inaccessible over time -- though they can be artificially reawakened through a technique that uses light to stimulate neurons.
But until now, pairing observations of infants with brain imaging had been out of reach, as babies are famously uncooperative when it comes to sitting still inside a Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) machine -- the device that tracks blood flow to "see" brain activity.
- Psychedelic patterns -
To overcome this challenge, Turk-Browne's team used methods his lab has refined over the years -- working with families to incorporate pacifiers, blankets, and stuffed animals; holding babies still with pillows; and using psychedelic background patterns to keep them engaged.
Still, inevitable wiggling led to blurry images that had to be discarded, but the team accounted for this by running hundreds of sessions.
In total, 26 infants participated -- half under a year old, half over -- while their brains were scanned during a memory task adapted from adult studies.
First, they were shown images of faces, scenes, or objects. Later, after viewing other images, they were presented with a previously seen image alongside a new one.
"We quantify how much time they spend looking at the old thing they've seen before, and that's a measure of their memory for that image," said Turk-Browne.
By comparing brain activity during successful memory formation versus forgotten images, the researchers confirmed that the hippocampus is active in memory encoding from a young age.
This was true for 11 of 13 infants over a year old but not for those under one. They also found that babies who performed best on memory tasks showed greater hippocampal activity.
"What we can conclude accurately from our study is that infants have the capacity to encode episodic memories in the hippocampus starting around one year of age," said Turk-Browne.
- Forgotten Memories -
"The ingenuity of their experimental approach should not be understated," researchers Adam Ramsaran and Paul Frankland wrote in an accompanying Science editorial.
But what remains unresolved is what happens to these early memories. Perhaps they are never fully consolidated into long-term storage -- or perhaps they persist but become inaccessible.
Turk-Browne suspects the latter and is now leading a new study testing whether infants, toddlers, and children can recognize video clips recorded from their own perspective as younger babies.
Early, tentative results suggest these memories might persist until around age three before fading. Turk-Browne is particularly intrigued by the possibility that such fragments could one day be reactivated later in life.
H.Weber--VB



