
-
 Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn
Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn
-
Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems

-
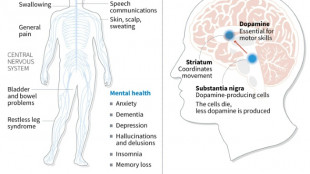 Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
-
Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'

-
 North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
-
Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer

-
 Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
-
Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold

-
 Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
-
Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
-
Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett

-
 Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
-
French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche

-
 Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
-
Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets

-
 Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
-
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
 Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
-
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored

-
 Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
-
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor

-
 Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
-
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms

-
 Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
-
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group

-
 With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
-
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace

-
 European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
-
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog

-
 Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
-
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages

-
 Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
-
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'

-
 Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
-
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem

-
 Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
-
Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error

-
 India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
-
Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated

-
 Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
-
Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race

-
 UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
-
EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop

-
 Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
-
India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase

-
 Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
-
Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup

-
 India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
-
Mideast war traps 20,000 seafarers, 15,000 cruise passengers in Gulf


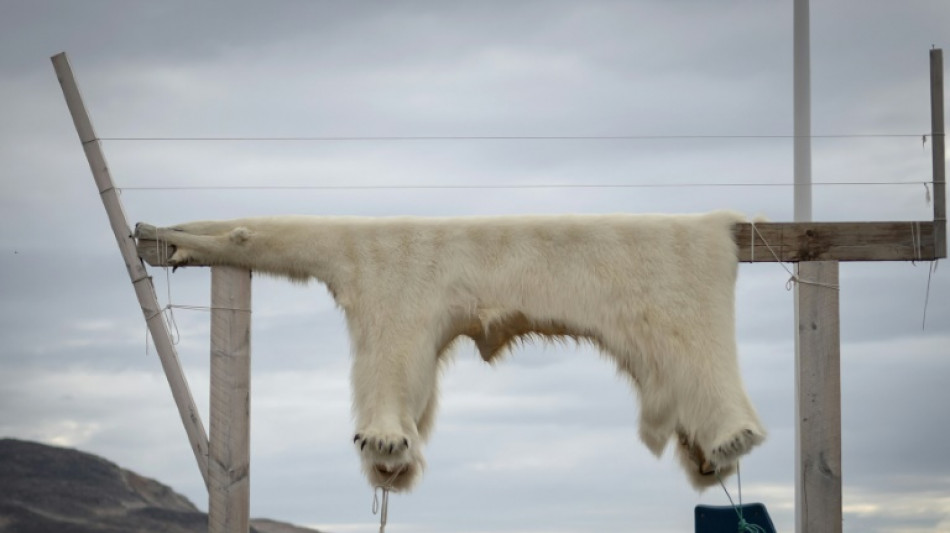
Diet puts Greenland Inuit at risk from 'forever chemicals': study
Scientists warned on Thursday that the long-term health of Inuit hunters in eastern Greenland was under threat, due to so-called "forever chemicals" in the atmosphere and their diet of polar bear and seal meat.
Christian Sonne, from Denmark's Aarhus University, said the Ittoqqortoormiit fishing and hunting community had levels of the chemicals -- also known as PFAS -- in their blood 13 times higher than the risk threshold.
The remote zone is particularly affected by the contamination because the chemicals are carried there by nearby sea and air currents, said Sonne, author of a study of the issue published in the journal Cell.
"East Greenland is really a hotspot of human contamination because you can both eat polar bears, which you don't hunt in Russia or Svalbard, and ringed seals that accumulate PFAS and other harmful substances," he told AFP.
"These substances are so persistent in the environment and in the body that the concentrations will still be very high over the next 75 to 100 years."
The area, home to just 300 people, has the highest PFAS levels in the world, excluding those affecting firefighters, factory workers and that linked to groundwater contamination in Sweden and Italy, said Sonne.
He attributed that to the long-range transfer of the chemicals in the air and water, which end up in the bodies of animals, particularly those that are then eaten.
To lower their levels, he advised the Inuit community to diversify what they eat.
He also called for tighter regulations to force industry to manufacture fewer toxic compounds that are less likely to be spread widely.
- High mercury, PCB levels -
PFAS are synthetic chemicals first developed in the 1940s to withstand intense heat and repel water and grease.
They have since been used in a vast range of household and industrial products, including food packaging, make-up, stain-proof fabrics, non-stick cookware and flame retardants.
Studies have suggested that exposure to PFAS chemicals is associated with increased rates of cancer, obesity, thyroid, liver and kidney disease, higher cholesterol, low birthweight and even weaker response to vaccines.
Polychlorinated biphenyls -- banned by the United States in 1979 -- are industrial chemicals, which affect immune, reproductive, nervous and endocrine systems, and are likely to cause cancer.
They also bind to sediment, threatening fish and wildlife.
Depending on ocean currents and winds, the situation varies across the Arctic territories.
Sonne said Inuit hunters also had very high levels of mercury and probably the highest levels of toxic man-made PCB chemicals in the world.
H.Gerber--VB




