
-
 Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn
Ukraine accuses Hungary of taking 'hostage' bank staff carrying $40 mn
-
Aston Martin chief Newey says no quick fix to vibration problems

-
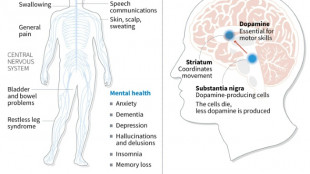 Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
Japan approves stem-cell treatment for Parkinson's in world first
-
Heavy attacks hit Tehran as Israel says war in 'new phase'

-
 North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
North Korea thrash Bangladesh in Women's Asian Cup warning
-
Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai will not appeal national security conviction: lawyer

-
 Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
Eight dead, four missing in Brazil seniors home collapse
-
Paralympics brace for tense opening as Russia comes in from the cold

-
 Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
Leclerc edges Hamilton to go fastest in first Australian GP practice
-
Equities mostly drop as Mideast crisis rages, though oil dips

-
 Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
Nepal counts votes after key post-uprising election
-
Italy half-backs can make difference against England: ex-coach Mallett

-
 Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
Scotland coach Townsend hails 'instinctive' France ahead of key Six Nations game
-
French starlet Seixas to take on Pogacar at Strade Bianche

-
 Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
Brazil's Petrobras sees profit soar on record output
-
Arsenal, Chelsea aim to avoid FA Cup upsets

-
 Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
Middle East war enters seventh day as Israel strikes Beirut
-
Qualifier Parry ends Venus's desert dream
-
 Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
Iran missile barrage sparks explosions over Tel Aviv
-
US says Venezuela to protect mining firms as diplomatic ties restored

-
 Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
Trump honors Messi and MLS Cup champion Miami teammates
-
Dismal Spurs can still avoid relegation vows Tudor

-
 Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
Berger sets early pace at Arnold Palmer with 'unbelievable' 63
-
Morocco part company with coach Regragui as World Cup looms

-
 Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
Lens beat Lyon on penalties to reach French Cup semis
-
El Salvador's Bukele holding dozens of political prisoners: rights group

-
 With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
With Iran war, US goes it alone like never before
-
Spurs slip deeper into relegation trouble after loss to Palace

-
 European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
European, US stocks back in sell-off mode as oil prices surge
-
Pete Hegseth: Trump's Iran war attack dog

-
 Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
Celtics' Tatum could make injury return on Friday
-
'Enemy at home': Iranian authorities tighten grip as war rages

-
 Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
Bethell set for 'hell of a career', says England captain Brook
-
France coach Galthie slams Scotland for 'smallest changing room in the world'

-
 Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
Medvedev arrives in Indian Wells after being stranded in Dubai
-
Trump fires homeland security chief Kristi Noem

-
 Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
Mideast war risks pulling more in as conflict boils over
-
Wales' James Botham 'sledged' by grandfather Ian Botham after Six Nations error

-
 India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
India hero Samson eyes 'one more' big knock in T20 World Cup final
-
Britney Spears detained on suspicion of driving while intoxicated

-
 Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
Grooming makes Crufts debut as UK dog show widens offer
-
Townsend insists Scots' focus solely on France not Six Nations title race

-
 UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
UK sends more fighter jets to Gulf: PM
-
EU to ban plant-based 'bacon' but veggie 'burgers' survive chop

-
 Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
Leagues Cup to hold matches in Mexico for first time
-
India reach T20 World Cup final after England fail in epic chase

-
 Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
Conservative Anglicans press opposition to Church's first woman leader
-
Iran players sing anthem and salute at Women's Asian Cup

-
 India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
India beat England in high-scoring T20 World Cup semi-final
-
Mideast war traps 20,000 seafarers, 15,000 cruise passengers in Gulf


Less mapped than the Moon: quest to reveal the seabed
It covers nearly three-quarters of our planet but the ocean floor is less mapped than the Moon, an astonishing fact driving a global push to build the clearest-ever picture of the seabed.
Understanding the ocean depths is crucial for everything from laying undersea cables and calculating tsunami paths, to projecting how seas will rise as the climate warms.
When Seabed 2030 launched in 2017, just six percent of the ocean floor was properly mapped.
The project has since boosted that figure to over 25 percent, harnessing historic data, sonar from research and industry vessels, and growing computing power.
"As we put more data together, we get this beautiful picture of the seafloor, it's really like bringing it into focus," said Vicki Ferrini, head of the project's Atlantic and Indian Ocean Centre.
"You start to see the details and the patterns, you start to understand the (ocean) processes in a different way," added Ferrini, a senior research scientist at Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory.
Satellite technology means we can now zoom in on the surface of the Moon, or a neighbourhood half-way around the world, but when it comes to the ocean floor, there's a basic problem.
"It's physics," said Ferrini. "The water is in the way."
While instruments can peer through relatively shallow depths to the sea floor, for most of the ocean only acoustic methods are viable -- sonar that pings the seabed and returns data on depths.
In the past, most ships used single beam sonar, sending down a single echo and offering one data point at a time.
Nowadays, multibeam sonar is common, explained Martin Jakobsson, dean of earth and environmental science at Stockholm University and co-head of Seabed 2030's Arctic and North Pacific centre.
"You get a swathe, almost like a 3D view directly, and that's really what we want to map the ocean with."
- 'More geopolitical than ever' -
But the availability of multibeam sonar did not translate into a central clearing house for data, and not all data collection is equal.
Different vessels collect at different resolutions, and data capture can be affected by the turbidity of the ocean and even the tides.
Collating, correcting and integrating that data is where Seabed 2030 has come in.
"We have this real patchwork," said Ferrini. "We do our best to weave it all together... making sure that we are normalising and justifying all of these measurements."
The project has set relatively coarse resolution targets for mapping -- grid cell sizes of 400 metres squared (4,300 square feet) for most of the ocean floor -- but even achieving that is a complicated process.
"It's a cost issue, it's also a 'people don't know why it's needed' issue," Jakobsson said.
"And right now it's more geopolitical than ever before," he added, particularly in the heavily contested Arctic.
- 'Just beautiful' -
The project has benefitted from some technological advances, including the spread of multibeam sonar and growing computing power.
Machine learning helps with data processing and pattern recognition, and can even enhance imagery and try to fill in some gaps.
"As we start to bring together each trackline and paint the picture more completely... we start to see these incredible meandering channels on the seafloor that look just like what we see on land," said Ferrini.
It is "just beautiful," she added.
Part of the project, which is funded by the Japanese non-profit Nippon Foundation, has been finding the biggest gaps in seafloor knowledge, most often in the open sea and areas outside common shipping routes.
Autonomous platforms equipped with sonar that can float at sea could speed up data collection, although for now uncovering "hidden" data that is sitting unshared is helping fill many gaps.
The work comes as countries debate whether to open stretches of the seabed to the mining of minerals used in the energy transition.
It is a divisive question, and like many scientists Ferrini warns against proceeding without more research.
"We need to have the data so we can make data-informed decisions, and we don't yet."
H.Kuenzler--VB




