
-
 Athens hit with several months of rain in one day: expert
Athens hit with several months of rain in one day: expert
-
Ubisoft shares plunge after big-bang restructuring announced

-
 Mendis' unbeaten 93 anchors Sri Lanka to 271-6 against England
Mendis' unbeaten 93 anchors Sri Lanka to 271-6 against England
-
Reeling Napoli face Juve after 'unacceptable' Champions League showing

-
 Actor Liz Hurley in tears as accuses UK tabloid of 'monstrous' conduct
Actor Liz Hurley in tears as accuses UK tabloid of 'monstrous' conduct
-
What we know about Trump's Greenland 'framework' deal

-
 Osaka 'confused' as testy exchange sours Australian Open win
Osaka 'confused' as testy exchange sours Australian Open win
-
Trump launches 'Board of Peace' at Davos

-
 Stocks rally as Trump drops Greenland tariff threats
Stocks rally as Trump drops Greenland tariff threats
-
Mercedes unveil 2026 F1 car for new 2026 rules

-
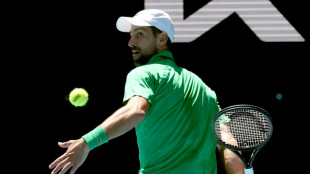 Djokovic, Sinner plough on in Melbourne, Wawrinka makes history
Djokovic, Sinner plough on in Melbourne, Wawrinka makes history
-
Kitzbuehel's Hahnenkamm, the terrifying Super Bowl of skiing

-
 'Oasis of stability': Madrid becomes luxury housing haven
'Oasis of stability': Madrid becomes luxury housing haven
-
Swiatek says packed tennis season makes it 'impossible' to switch off

-
 Sloppy Osaka grinds past 'mad' Cirstea to stay alive at Australian Open
Sloppy Osaka grinds past 'mad' Cirstea to stay alive at Australian Open
-
Iran Guards chief says 'finger on trigger', warns US against 'miscalculations'

-
 Imperious Sinner barrels into Australian Open round three
Imperious Sinner barrels into Australian Open round three
-
Storms, heavy rain kill 9 children across Afghanistan

-
 Games giant Ubisoft suffers share price collapse
Games giant Ubisoft suffers share price collapse
-
Exhausted Wawrinka battles on in Melbourne farewell after five-set epic

-
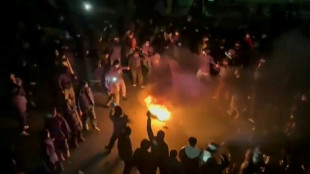 'Too dangerous to go to hospital': a glimpse into Iran's protest crackdown
'Too dangerous to go to hospital': a glimpse into Iran's protest crackdown
-
Bruised European allies wary after Trump's Greenland climbdown

-
 Austrian ex-agent goes on trial in Russia spying case
Austrian ex-agent goes on trial in Russia spying case
-
Japan suspends restart of world's biggest nuclear plant

-
 Djokovic, Swiatek roll into Melbourne third round, Keys defence alive
Djokovic, Swiatek roll into Melbourne third round, Keys defence alive
-
New Zealand landslips kill at least two, others missing

-
 Djokovic says heaving Australian Open crowds 'good problem'
Djokovic says heaving Australian Open crowds 'good problem'
-
Swiatek in cruise control to make Australian Open third round

-
 Austrian ex-agent to go on trial in Russia spying case
Austrian ex-agent to go on trial in Russia spying case
-
Bangladesh launches campaigns for first post-Hasina elections

-
 Afghan resistance museum gets revamp under Taliban rule
Afghan resistance museum gets revamp under Taliban rule
-
Multiple people missing in New Zealand landslips

-
 Sundance Film Festival hits Utah, one last time
Sundance Film Festival hits Utah, one last time
-
Philippines convicts journalist on terror charge called 'absurd'
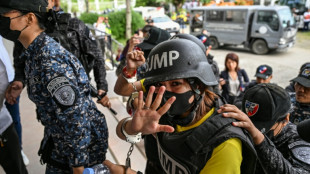
-
 Anisimova grinds down Siniakova in 'crazy' Australian Open clash
Anisimova grinds down Siniakova in 'crazy' Australian Open clash
-
Djokovic rolls into Melbourne third round, Keys defence alive

-
 Vine, Narvaez take control after dominant Tour Down Under stage win
Vine, Narvaez take control after dominant Tour Down Under stage win
-
Chile police arrest suspect over deadly wildfires

-
 Djokovic eases into Melbourne third round - with help from a tree
Djokovic eases into Melbourne third round - with help from a tree
-
Keys draws on champion mindset to make Australian Open third round

-
 Knicks halt losing streak with record 120-66 thrashing of Nets
Knicks halt losing streak with record 120-66 thrashing of Nets
-
Philippine President Marcos hit with impeachment complaint

-
 Trump to unveil 'Board of Peace' at Davos after Greenland backtrack
Trump to unveil 'Board of Peace' at Davos after Greenland backtrack
-
Bitter-sweet as Pegula crushes doubles partner at Australian Open

-
 Hong Kong starts security trial of Tiananmen vigil organisers
Hong Kong starts security trial of Tiananmen vigil organisers
-
Keys into Melbourne third round with Sinner, Djokovic primed

-
 Bangladesh launches campaigns for first post-Hasina polls
Bangladesh launches campaigns for first post-Hasina polls
-
Stocks track Wall St rally as Trump cools tariff threats in Davos

-
 South Korea's economy grew just 1% in 2025, lowest in five years
South Korea's economy grew just 1% in 2025, lowest in five years
-
Snowboard champ Hirano suffers fractures ahead of Olympics


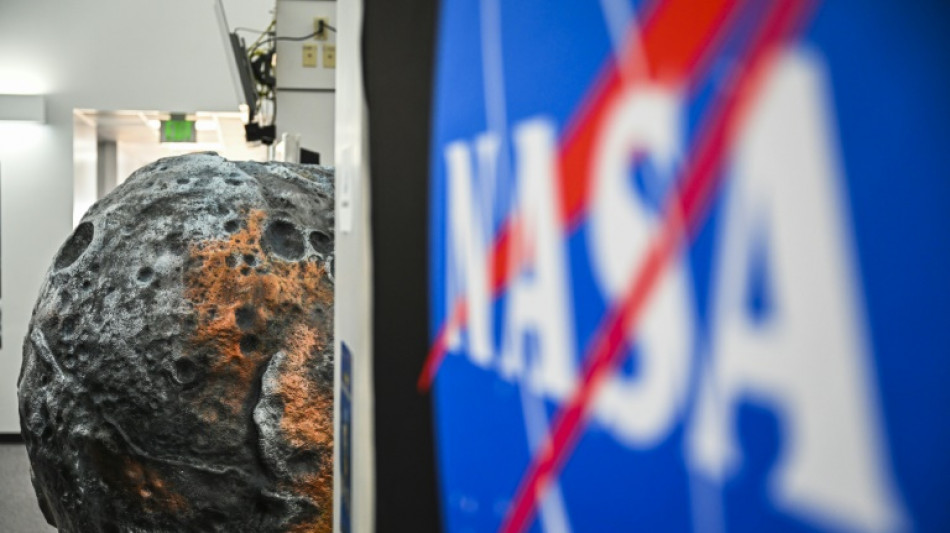
NASA journeys to the metal-rich asteroid Psyche
It's a world like no other: a metal-rich asteroid that could be the remnants of a small planet, or perhaps an entirely new type of celestial body unknown to science.
A NASA spacecraft blasted off from the Kennedy Space Center Friday bound for Psyche, an object 2.2 billion miles (3.6 billion kilometers) away that could offer clues about the interior of planets like Earth.
"We're going to learn all kinds of new things, how these things fly through the solar system, and they hit each other and they cause the evolution of what we have today, our solar system," NASA chief Bill Nelson said shortly before lift off at 10:19 am Eastern Time (1419 GMT) on a reusable SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
"We've visited either in person or robotically worlds made of rock, worlds made of ice and worlds made of gas... but this will be our first time visiting a world that has a metal surface," lead scientist Lindy Elkins-Tanton told reporters during a briefing this week.
Trailing a blue glow from its next-generation electric propulsion system and flanked by two large solar arrays, the van-sized probe should arrive at its destination in the Asteroid Belt, between Mars and Jupiter, in July 2029.
- Studying cores of rocky planets -
Over the course of two years, it will deploy its suite of advanced instruments to probe Psyche for evidence of an ancient magnetic field and to study its chemical and mineral composition, as well as topography.
Scientists think Psyche, named after the goddess of the soul in Greek mythology, could be part of the iron-nickel core of a "planetesimal," a building block of all rocky planets, that was left exposed after an ancient collision blasted off the exterior.
It could also be something else -- a primordial solar system object that's never been documented before.
"This is our one way to see a core," said Elkins-Tanton. "We say tongue in cheek that we're going to outer space to explore inner space."
Psyche is thought to have an irregular, potato-like shape, measuring 173 miles (280 kilometers) across at its widest point -- though it's never actually been seen up close.
Until recently, scientists thought it was overwhelmingly composed of metal -- but analyses based on reflected radar and light now indicate that metal probably comprises between 30-60 percent, with the rest being rock.
- Solar electric propulsion -
The mission will include several technological innovations.
The Psyche spacecraft, named after the asteroid, will test out next generation communications based on lasers -- a step NASA compares to upgrading old telephone lines on Earth to fiber optics.
Deep Space Optical Communications, as the system is called, "was designed to demonstrate 10 to 100 times the data-return capacity of state-of-the-art radio systems used in space today," said Abi Biswas of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in a statement.
Psyche also uses a special kind of propulsion system called "Hall-effect thrusters" that harnesses the energy from solar panels to create electric and magnetic fields that, in turn, expel charged atoms of xenon gas.
The thrust it exerts is roughly equal to the weight of an AA battery in your hand. But in the void of space, the spacecraft will accelerate continuously to tens of thousands of miles per hour.
Such systems avoid the need to carry thousands of pounds of chemical fuel into space, and Psyche will be the first time they are used beyond lunar orbit.
D.Bachmann--VB



