
-
 Beating Italy is not a 'God-given right', says Wales coach Tandy
Beating Italy is not a 'God-given right', says Wales coach Tandy
-
Sri Lanka to treat Iranian sailors according to 'international law'

-
 New Zealand want to 'break a few hearts' in World Cup final
New Zealand want to 'break a few hearts' in World Cup final
-
Farrell welcomes bonus-point win over 'tough' Welsh

-
 Russian strikes kill nine across Ukraine, ravage apartment house
Russian strikes kill nine across Ukraine, ravage apartment house
-
Nepal's Balendra Shah holds unassailable poll lead for seat

-
 Hamilton says 'not where we wanted or expected' for Australian GP
Hamilton says 'not where we wanted or expected' for Australian GP
-
Pole-sitter Russell says his Mercedes more go-kart than 'bouncing bus'

-
 Google gives CEO new pay deal worth up to $692 million
Google gives CEO new pay deal worth up to $692 million
-
Thousands of Taiwan fans turn Tokyo blue at World Baseball Classic

-
 Verstappen baffled by crash in Australian Grand Prix qualifying
Verstappen baffled by crash in Australian Grand Prix qualifying
-
Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes

-
 Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
-
'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win

-
 Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs

-
 Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
-
Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three

-
 Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
-
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily

-
 Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
-
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win

-
 Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
-
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump

-
 Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
-
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran

-
 Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
-
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level

-
 Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
-
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win

-
 Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
-
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola

-
 Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
-
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
-
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales

-
 Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
-
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January

-
 Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
-
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
-
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march

-
 Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
-
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony

-
 Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round

-
 NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
-
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row

-
 'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
-
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold


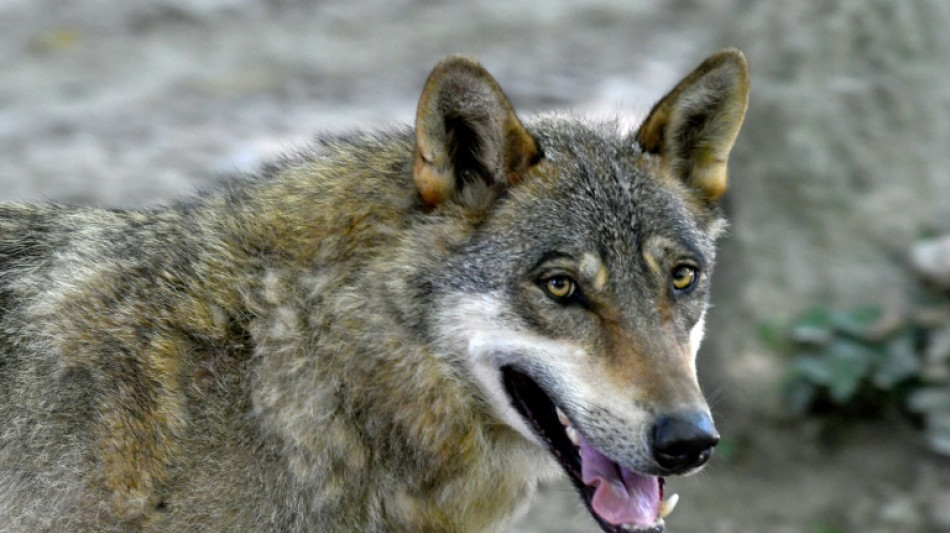
Rapid development is main threat to big carnivores: study
Declines in populations of big carnivores like lions, tigers and wolves may be driven more by rapid human economic development than habitat loss or climate change, according to a new study Tuesday.
The researchers hope the findings could help to improve policies for protecting carnivore populations, which have been driven to the brink of extinction in many parts of the world.
The study found that faster economic development was linked to a quicker decline in carnivore populations.
"In the midst of rapid development, people appear to become less tolerant of carnivores, conflicts explode, and we suspect that incidences of poaching and persecution rocket," lead author Thomas Johnson said in a press release.
Some carnivores are poached for their meat or for the wildlife trade, while others like lions may be killed if they pose a threat to someone's livelihood -- such as their cattle -- or their life, Johnson told AFP.
"These human elements are actually having a far greater impact than the habitat loss elements," Johnson said.
Traditionally, habitat loss has been considered the primary threat to carnivore populations, but the researchers said that was "dwarfed" by human development.
The study, published in Nature Communications, concluded that as human communities become wealthier and socioeconomic growth slows, carnivore populations can recover.
The authors said this was partly due to better habitat protection, but mainly because people start to care more about the animals and have less of a desire -- and need -- to kill them.
"What you want is this growth to slow before [the carnivore population] completely vanishes, so there's at least an opportunity to recover," Johnson said.
- Wolf rebound -
Grey wolf populations have already rebounded in Europe, growing 1,800 percent since the 1960s thanks to an improved quality of life and slower economic development on the continent, according to the researchers from the University of Reading.
That recovery is not only happening in protected parks but also in wild areas.
Brown bears and lynxes are also starting to recover in Europe, Johnson said, while tiger populations in India have similarly started to rebound.
But several parts of Africa did not support the overarching findings -- the continent has not seen rapid development but its carnivore populations have declined -- and Johnson said this may be because much of the population decline occurred decades ago under colonial regimes.
The findings present an inherent tension between prioritising human development versus protecting carnivores, and Johnson suggested that wealthier nations -- responsible for much of large carnivore decline -- could support less developed nations through targeted financial support.
This could include paying communities in biodiversity hotspots enough to earn a living, while promoting conservation.
"If you lock people into poverty, people will never live alongside biodiversity," Johnson said, adding that he hopes policy will move beyond treating carnivore loss as a narrow issue.
"My real hope is we start thinking about this as a socioeconomic problem, as well as an environmental problem."
The work looked at 50 species of carnivores in over 80 countries over the last 50 years.
Carnivore populations have seen dramatic declines globally in the last century, with lions and tigers absent from more than 90 percent of their historic range.
In the United Kingdom, many local carnivore species such as lynx, wolf and bear have already been hunted into extinction.
F.Pavlenko--BTB

