
-
 Beating Italy is not a 'God-given right', says Wales coach Tandy
Beating Italy is not a 'God-given right', says Wales coach Tandy
-
Sri Lanka to treat Iranian sailors according to 'international law'

-
 New Zealand want to 'break a few hearts' in World Cup final
New Zealand want to 'break a few hearts' in World Cup final
-
Farrell welcomes bonus-point win over 'tough' Welsh

-
 Russian strikes kill nine across Ukraine, ravage apartment house
Russian strikes kill nine across Ukraine, ravage apartment house
-
Nepal's Balendra Shah holds unassailable poll lead for seat

-
 Hamilton says 'not where we wanted or expected' for Australian GP
Hamilton says 'not where we wanted or expected' for Australian GP
-
Pole-sitter Russell says his Mercedes more go-kart than 'bouncing bus'

-
 Google gives CEO new pay deal worth up to $692 million
Google gives CEO new pay deal worth up to $692 million
-
Thousands of Taiwan fans turn Tokyo blue at World Baseball Classic

-
 Verstappen baffled by crash in Australian Grand Prix qualifying
Verstappen baffled by crash in Australian Grand Prix qualifying
-
Russell leads Mercedes 1-2 for Australian GP as Verstappen crashes

-
 Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
Russia rains missiles and drones on Ukraine, killing six
-
'Grateful' Osaka returns to action with Indian Wells win

-
 Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
Israel fires 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran as war hits 2nd week
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return, Wemby magic sparks Spurs

-
 Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
Judge homers as USA cruise past Brazil in World Baseball Classic
-
Russian strike on Kharkiv appartment block kills three

-
 Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
Grabbing the bull by the tail: Venezuela's cowboy sport
-
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily

-
 Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'
-
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win

-
 Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs
-
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump

-
 Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes
-
Israel announces new wave of 'broad-scale' strikes on Tehran

-
 Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
-
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level

-
 Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures
-
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win

-
 Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh
-
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola

-
 Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash
-
PSG beaten by Monaco before Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
-
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales

-
 Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
-
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January

-
 Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
-
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
-
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march

-
 Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational
-
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony

-
 Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round

-
 NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun
-
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row

-
 'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial
-
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold


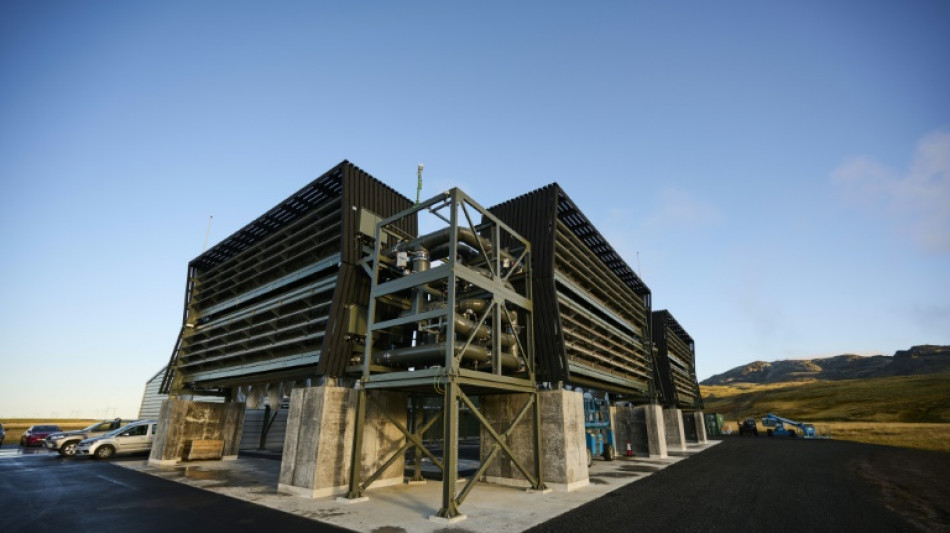
Rapid scale-up of CO2 removal crucial for climate goals
Capping global warming at liveable levels will be impossible without massively scaling up the extraction of planet-warming carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, the first global assessment of CO2 removal warned Thursday.
The persistent failure to draw down greenhouse gas emissions -- nearly 60 billion tonnes a year of CO2 or its equivalent -- has forced once-marginal carbon dioxide removal (CDR) options toward centre stage in climate policy, investment and research.
Across methods ranging from tree planting to factory-sized machines that suck CO2 from the air and store it underground, CDR worldwide currently captures two billion tonnes of the gas each year, according to the State of Carbon Dioxide Report.
More than 99 percent is extracted through "conventional" techniques such as restoring and expanding CO2-absorbing forests and wetlands.
Only a tiny fraction -- about 0.1 percent -- is removed by "novel" technologies such as direct air capture, converting organic waste into rock-like biochar, or capturing the CO2 from plants grown and burned for fuel, more than two dozen experts concluded.
The UN's climate science advisory body, the IPCC, has said carbon emissions must decline some 45 percent compared to 2020 levels by the end of this decade, and to net zero by mid-century, if Paris Agreement goals are to be met.
The 2015 treaty enjoins nations to hold warming to "well below" two degrees Celsius compared to preindustrial levels. The IPCC later concluded that only the agreement's aspirational 1.5C target could prevent severe, and potentially catastrophic, climate impacts.
"Regardless of whether we do a little or a lot of carbon dioxide removal, we will still have to do massive reductions in greenhouse gas emissions," report co-author Gregory Nemet, a professor at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, told AFP.
But CO2 emissions in 2022 remained at near-record levels, thrusting CDR into an even more critical role.
By the end of the century, the report calculates for the first time, CDR must extract between 450 billion and 1.1 trillion tonnes of CO2.
The new report says that conventional, tree-planting CDR -- even if emissions do drop sharply -- must double by 2050 to keep the 1.5C target in play, and increase by 50 percent to hold warming under 2C.
- Scaling up massively -
Research, however, has shown that food, energy and climate needs could result in competition for land, even with efficiency gains in each sector.
A deeply changing climate with only 1.2C of warming to date could also limit potential.
"If warming continues -- and all signs say it will -- then it will be even harder to maintain current levels of conventional CDR because they will be affected by droughts, storms, pests and other impacts," said co-author Oliver Geden, a senior fellow at the German Institute for International and Security Affairs and an IPCC lead author.
That means novel CDR methods have to pick up the slack.
To keep warming under 2C, deployment of these nascent technologies must be ramped up 30-fold by 2030, and by more than 1,000-fold by 2100, according to the report, led by the University of Oxford.
The 1.5C target would require scaling up even faster.
"Many policymakers don't know -- and probably don't want to know -- how much keeping the 1.5C narrative alive actually depends on carbon dioxide removal," Geden told AFP.
One novel CDR technology has attracted more attention -- and money -- than any other, even if it has barely put a dent in global emissions: direct air capture combined with carbon storage (DACCS).
Three quarters of the $200 million (185 million euros) invested in new CDR capacity from 2020 to 2022 went to direct air capture -- a big chunk of it to Switzerland-based Climeworks. The firm announced last week the world's first certified CO2 removal and storage on behalf of paying clients, including Microsoft and software service company Stripe.
"All this investment is based on the assumption that direct air capture can grow from about 10,000 tonnes today to a billion tonnes by 2050" -- a 100,000-fold increase, said Nemet.
That rate of growth is not necessarily out of reach, he said.
In earlier research, Nemet compiled a database of 135 technologies that emerged over the last century, looking at how quickly they scaled up.
The growth rate for solar panels has been about 30 percent a year over 30 years, he found.
"Direct air capture needs to be more than 40 percent for the next 30 years," he said. "It's a huge challenge, but it's not unprecedented."
M.Furrer--BTB

