-
 Minneapolis activists track Trump's immigration enforcers
Minneapolis activists track Trump's immigration enforcers
-
Court orders Dutch to protect Caribbean island from climate change

-
 Sterling agrees Chelsea exit after troubled spell
Sterling agrees Chelsea exit after troubled spell
-
Rules-based trade with US is 'over': Canada central bank head

-
 Lucas Paqueta signs for Flamengo in record South American deal
Lucas Paqueta signs for Flamengo in record South American deal
-
Holocaust survivor urges German MPs to tackle resurgent antisemitism

-
 'Extraordinary' trove of ancient species found in China quarry
'Extraordinary' trove of ancient species found in China quarry
-
Villa's Tielemans ruled out for up to 10 weeks

-
 Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
-
UK proposes to let websites refuse Google AI search

-
 'I wanted to die': survivors recount Mozambique flood terror
'I wanted to die': survivors recount Mozambique flood terror
-
Trump issues fierce warning to Minneapolis mayor over immigration
-
 Anglican church's first female leader confirmed at London service
Anglican church's first female leader confirmed at London service
-
Germany cuts growth forecast as recovery slower than hoped

-
 Amazon to cut 16,000 jobs worldwide
Amazon to cut 16,000 jobs worldwide
-
One dead, five injured in clashes between Colombia football fans

-
 Dollar halts descent, gold keeps climbing before Fed update
Dollar halts descent, gold keeps climbing before Fed update
-
US YouTuber IShowSpeed gains Ghanaian nationality at end of Africa tour

-
 Sweden plans to ban mobile phones in schools
Sweden plans to ban mobile phones in schools
-
Turkey football club faces probe over braids clip backing Syrian Kurds

-
 Deutsche Bank offices searched in money laundering probe
Deutsche Bank offices searched in money laundering probe
-
US embassy angers Danish veterans by removing flags

-
 Netherlands 'insufficiently' protects Caribbean island from climate change: court
Netherlands 'insufficiently' protects Caribbean island from climate change: court
-
Fury confirms April comeback fight against Makhmudov

-
 Susan Sarandon to be honoured at Spain's top film awards
Susan Sarandon to be honoured at Spain's top film awards
-
Trump says 'time running out' as Iran rejects talks amid 'threats'

-
 Spain eyes full service on train tragedy line in 10 days
Spain eyes full service on train tragedy line in 10 days
-
Greenland dispute 'strategic wake-up call for all of Europe,' says Macron

-
 'Intimidation and coercion': Iran pressuring families of killed protesters
'Intimidation and coercion': Iran pressuring families of killed protesters
-
Europe urged to 'step up' on defence as Trump upends ties

-
 Sinner hails 'inspiration' Djokovic ahead of Australian Open blockbuster
Sinner hails 'inspiration' Djokovic ahead of Australian Open blockbuster
-
Dollar rebounds while gold climbs again before Fed update

-
 Aki a doubt for Ireland's Six Nations opener over disciplinary issue
Aki a doubt for Ireland's Six Nations opener over disciplinary issue
-
West Ham sign Fulham winger Traore

-
 Relentless Sinner sets up Australian Open blockbuster with Djokovic
Relentless Sinner sets up Australian Open blockbuster with Djokovic
-
Israel prepares to bury last Gaza hostage

-
 Iran rejects talks with US amid military 'threats'
Iran rejects talks with US amid military 'threats'
-
Heart attack ends iconic French prop Atonio's career

-
 SKorean chip giant SK hynix posts record operating profit for 2025
SKorean chip giant SK hynix posts record operating profit for 2025
-
Greenland's elite dogsled unit patrols desolate, icy Arctic

-
 Dutch tech giant ASML posts bumper profits, cuts jobs
Dutch tech giant ASML posts bumper profits, cuts jobs
-
Musetti rues 'really painful' retirement after schooling Djokovic

-
 Russian volcano puts on display in latest eruption
Russian volcano puts on display in latest eruption
-
Thailand uses contraceptive vaccine to limit wild elephant births

-
 Djokovic gets lucky to join Pegula, Rybakina in Melbourne semi-finals
Djokovic gets lucky to join Pegula, Rybakina in Melbourne semi-finals
-
Trump says to 'de-escalate' Minneapolis, as aide questions agents' 'protocol'

-
 'Extremely lucky' Djokovic into Melbourne semi-finals as Musetti retires
'Extremely lucky' Djokovic into Melbourne semi-finals as Musetti retires
-
'Animals in a zoo': Players back Gauff call for more privacy

-
 Starmer heads to China to defend 'pragmatic' partnership
Starmer heads to China to defend 'pragmatic' partnership
-
Uganda's Quidditch players with global dreams


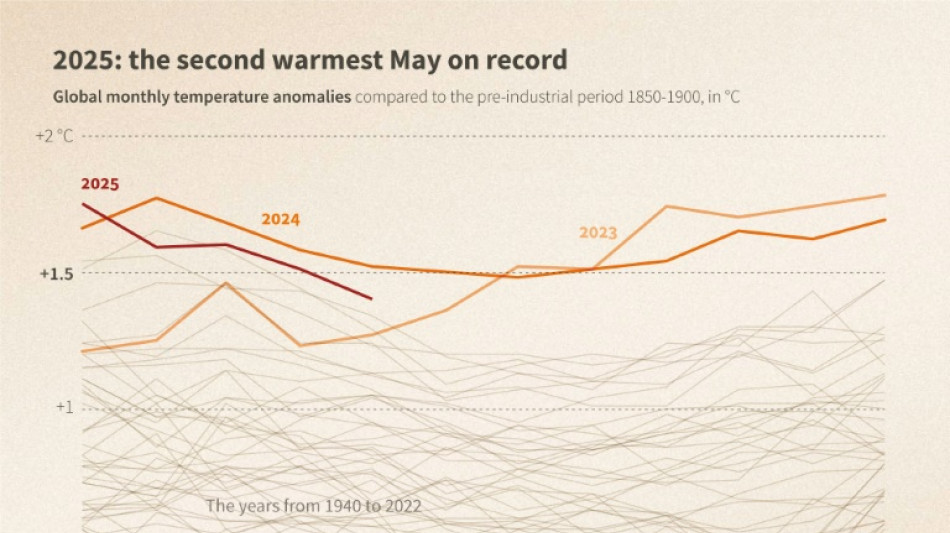
May 2025 second warmest on record: EU climate monitor
Global heating continued as the new norm, with last month the second warmest May on record on land and in the oceans, according to the European Union's climate monitoring service.
The planet's average surface temperature dipped below the threshold of 1.5 degree Celsius above preindustrial levels, just shy of the record for May set last year, according to the Copernicus Climate Change Service.
The same held for the world's oceans. With a surface temperature of 20.79C, last month was second only to May 2024, with some unprecedented warmth regionally.
"Large areas in the northeast North Atlantic, which experienced a marine heatwave, had record surface temperatures for the month," Copernicus reported. "Most of the Mediterranean Sea was much warmer than average."
The increasingly dire state of the oceans is front-and-centre at the third UN Ocean Conference (UNOC), which kicked off Monday in Nice, France.
Ocean heatwaves are driving marine species to migrate, damaging ecosystems, and reducing the ability of ocean layers to mix, thus hindering the distribution of nutrients.
Covering 70 percent of the globe's surface, oceans redistribute heat and play a crucial role in regulating Earth's climate.
Surface water warmed by climate change drive increasingly powerful storms, causing new levels of destruction and flooding in their wake.
Some parts of Europe, meanwhile, "experienced their lowest levels of precipitation and soil moisture since at least 1979," Copernicus noted.
Britain has been in the grips of its most intense drought in decades, with Denmark and the Netherlands also suffering from a lack of rain.
- 'Brief respite' -
Earth's surface last month was 1.4C above the preindustrial benchmark, defined as the average temperature from 1850 to 1900, before the massive use of fossil fuels caused the climate to dramatically warm.
"May 2025 interrupts an unprecedentedly long sequence of months above 1.5C," noted Carlo Buontempo, director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service.
All but one of the previous 22 months crossed this critical threshold, which marks the 2015 Paris Agreement's most ambitious target for capping global warming.
"This may offer a brief respite for the planet, but we expect the 1.5C threshold to be exceeded again in the near future due to the continued warming of the climate system," he added.
Over the 12-month period June 2024 to May 2025, warming averaged 1.57C compared to the 1850-1900 benchmark.
The Paris treaty target, however, is pegged to a 20-year average, in order to account for the influence of natural variability.
The UN's climate science advisory panel, the IPCC, has said there's a 50-percent change of breaching the 1.5C barrier in line with these criteria between 2030 and 2035.
Using this method of calculation, the world today has warmed by at least 1.3C.
The UN's World Meterological Organization (WMO), meanwhile, has said there's a 70 percent chance the five-year period 2025-2029, on average, will exceed the 1.5C limit.
Scientists stress the importance of limiting global warming as soon and as much as possible because every fraction of a degree increases the risks of more deadly and destructive impacts, on land and in the sea.
Limiting warming to 1.5C rather than 2C would significantly reduce the most catastrophic consequences, the IPCC concluded in a major report in 2018.
S.Gantenbein--VB


