
-
 Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
Show must go on: London opera chief steps in for ailing tenor
-
UK drugs giant AstraZeneca announces $15 bn investment in China

-
 US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
US scrutiny of visitors' social media could hammer tourism: trade group
-
'Watch the holes'! Paris fashion crowd gets to know building sites

-
 Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
Power, pace and financial muscle: How Premier League sides are ruling Europe
-
'Pesticide cocktails' pollute apples across Europe: study

-
 Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
Ukraine's Svitolina feels 'very lucky' despite Australian Open loss
-
Money laundering probe overshadows Deutsche Bank's record profits

-
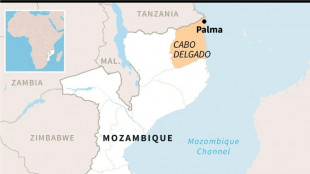 Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
Huge Mozambique gas project restarts after five-year pause
-
Britain's Starmer reports 'good progress' after meeting China's Xi

-
 Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
Sabalenka crushes Svitolina in politically charged Australian Open semi
-
Turkey to offer mediation on US–Iran tensions, weighs border measures

-
 Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
Mali's troubled tourism sector crosses fingers for comeback
-
China issues 73 life bans, punishes top football clubs for match-fixing

-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China

-
 Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
-
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics

-
 China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
-
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike

-
 Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
-
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis

-
 Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
-
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace

-
 No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain


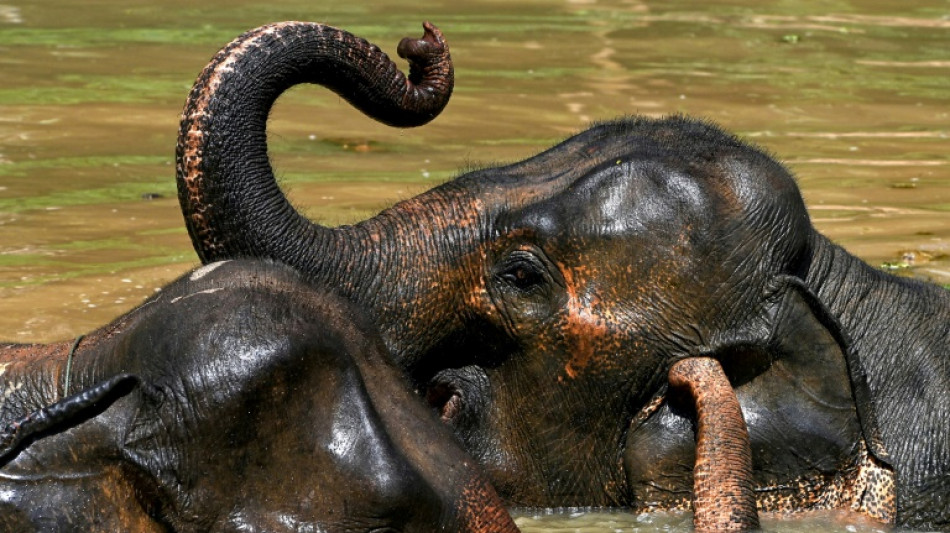
Researchers analyse DNA from dung to save Laos elephants
Slow and silent, former logging elephant Mae Khoun Nung emerges from a forest in northern Laos and follows her guide to an animal hospital for a check-up.
Once abundant in the forests of Laos, Asian elephants like her have been decimated by habitat destruction, gruelling labour in the logging industry, poaching and scarce breeding opportunities.
But conservationists are hoping DNA analysis of elephants' dung will help them track both captive and wild tuskers, so they can secure a healthy genetic pool and craft an effective breeding plan to protect the species.
Laos -- once proudly known as "Lane Xang" or "Land of a Million Elephants" -- has between 500 and 1,000 of the animals left, just one-third of the population two decades ago, according to conservation group WWF-Laos.
Around 10 elephants die each year for every one to two born, a rate that puts the animals at risk of dying out completely in the Southeast Asian nation.
"The ultimate goal would be to secure a healthy population of captive elephants to act as a genetic reservoir if the wild population collapses," wildlife biologist Anabel Lopez Perez told AFP at her laboratory at the Elephant Conservation Center (ECC) in Sainyabuli province.
Once researchers learn how many individual elephants are in the country -- by testing DNA-containing cells in dung -- Perez said a breeding plan will help them manage genetic diversity, prevent inbreeding and produce healthier calves that could be introduced into the wild to bolster the declining population.
- Elephant hospital -
At the hospital of the ECC, which shelters 28 elephants at its 500-hectare (1,200-acre) sanctuary, Mae Khoun Nung backs into a tall metal scaffolding structure, designed specially for check-ups on the animals.
Sounthone Phitsamone, who manages the centre's elephant keepers and acts as an assistant vet, taps the animal's leg and she calmly raises her foot for him to check.
Using a knife, he slices out the cracks and gaps in her hard, mud-baked nail.
Mae Khoun Nung spent her adult life in logging operations until she was given to the ECC by her owner in 2014 after work dried up and it became increasingly difficult to support her.
Elephants like her once roamed across much of Asia, but are now restricted to less than a fifth of their original range, according to WWF.
Their numbers in the wild have fallen by about half since the early 1900s, with only 40,000 to 50,000 left, the organisation says.
In the Nam Poui National Protected Area, researchers are now traversing the rugged hills and forests, collecting DNA from faecal samples of the area's 50 to 60 remaining wild elephants.
WWF-Laos, which is collaborating with the ECC and the Smithsonian Institution on the project, said the DNA analysis from dung would allow researchers to identify individual elephants, determine their sex, track their movements and understand familial relationships within herds.
"Although Nam Poui NPA represents a significant habitat for one of the few large wild elephant populations remaining in Laos, we lack precise data about its composition," WWF-Laos said in a statement to AFP.
-- Decreasing numbers --
In 2018, a government ban on illegal logging -- an industry that used elephants to haul timber out of forests -- resulted in the animals being sent to work in the tourism sector, while others were sold off to zoos, circuses and breeders.
The ECC tries to buy and shelter captive elephants when they are put up for sale, but since 2010, just six pregnancies with three calves have resulted.
Many of the elephants at the centre are of an advanced age and in poor shape from years of arduous labour, Phitsamone told AFP.
Mae Khoun Nung is 45 herself. On the bank of a reservoir, a short walk from the elephant hospital, she stops near the water's edge.
A small herd is diving under the surface and using their trunks to spray their backs, but she grew up isolated from other elephants and has had difficulty socialising.
Bathing is something she prefers to do alone.
Instead, she turns to a pile of banana plants left out for the herd and crunches on a snack.
Phitsamone has worked at the elephant centre for more than a decade and has no illusions about how difficult it will be to save his country's gentle giants.
"If we compare Laos with other countries, the number of elephants in the database is small and is decreasing," he said.
"I don't know if it will be OK in 20 or 30 years -- who knows."
C.Koch--VB



