
-
 Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
-
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys

-
 Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
-
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?

-
 Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
-
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors

-
 The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
-
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan

-
 Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
-
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida

-
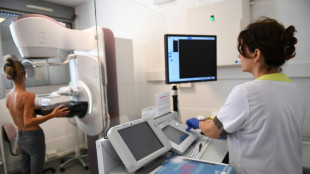 AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts

-
 Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
-
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return

-
 US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
-
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp

-
 New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
-
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash

-
 Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
-
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win

-
 With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?

-
 Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
-
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold

-
 De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
-
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS

-
 Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
-
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk

-
 Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
-
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
-
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb

-
 Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
-
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week

-
 US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
-
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years

-
 Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
-
Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year

-
 Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
-
French IT group Capgemini under fire over ICE links

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
-
Oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat; gold retreats from highs

-
 Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
-
Holders PSG, Real Madrid among clubs awaiting Champions League play-offs draw

-
 England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
-
US Senate vote to avert government shutdown expected to fail

-
 Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
-
Turkey to offer mediation in US-Iran showdown

-
 World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
-
EU designates Iran Guards as 'terrorist organisation'


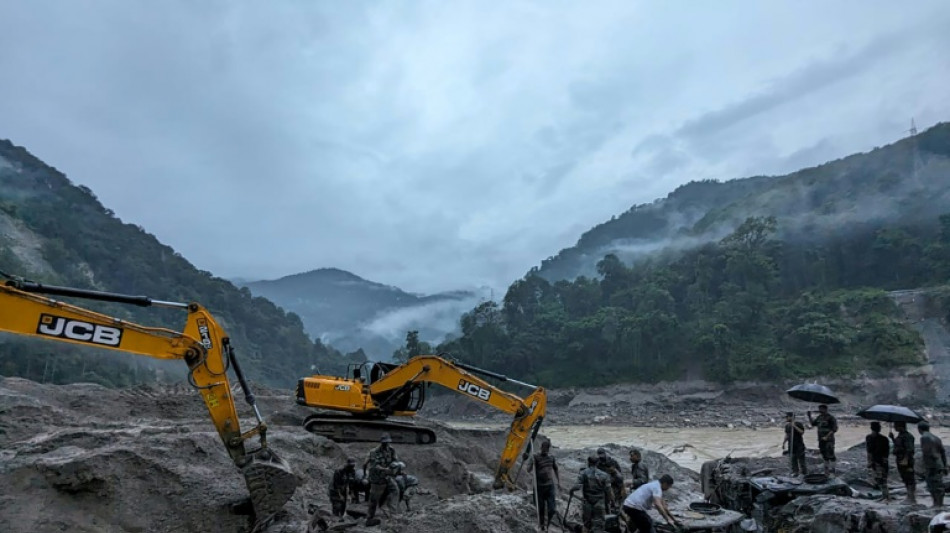
India launches flood warning systems at Himalayan glacial lakes
India is setting up high-tech warning systems at nearly 200 Himalayan glacial lakes at risk of bursting their banks, a deadly threat exacerbated by climate change, disaster officials said Tuesday.
India's Himalayas contain at least 7,500 glacial lakes, many of which pose risks of dangerous flash floods.
Teams from India's National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) are targeting 190 high-altitude lakes deemed to be the most dangerous in a mission slated to take three years.
"We have already made significant strides in mitigating risks", Safi Ahsan Rizvi, a senior NDMA official directing the mission, told AFP.
A glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) is the sudden release of water that has collected in former glacier beds.
These lakes are formed by the retreat of glaciers, a naturally occurring phenomenon turbocharged by the warmer temperatures of human-caused climate change.
One expedition is currently working to install early warning systems around six high-risk lakes in the northeastern state of Sikkim, where at least 77 people died in such a flood in October 2023.
"We have done 20 lakes so far, and will complete 40 this summer," Rizvi said.
The project will also include "lowering lake levels" of accumulated water and ice slush in lakes.
Teams include experts from the army and multiple government agencies, including the Indian Space Research Organisation, geologists, hydrologists, computing engineers and weather specialists.
India's air force is also expected to join the mission later, flying heavy equipment into remote sites.
- 'Catastrophic impacts' -
The mission will cover the Himalayan regions in India, from Kashmir and Ladakh in the north to Arunachal Pradesh in the northeast, many in areas bordering China.
Climate change is driving the disappearance of glaciers, with half the Earth's 215,000 glaciers projected to melt by the end of the century, even if warming can be capped at 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
The volume of glacial lakes has jumped by 50 percent in 30 years, according to a 2020 study based on satellite data.
A study, published in Nature Communications, found that 15 million people live within 50 kilometres (31 miles) of a glacial lake and within one kilometre of potential flooding from a breach.
The risk was greatest in the "High Mountains Asia" region across 12 countries, including India, Pakistan, China and Nepal.
That is partly because more people live closer to glacial lakes in the region than in other parts of the world, making warning times even shorter.
Last month a glacial lake outburst in neighbouring Nepal's Everest region sent a devastating flood of frigid water through the village of Thame, sweeping away buildings.
However, residents were forewarned and there were no casualties.
The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) said it was a clear example of the "catastrophic impacts" increasing global temperatures were having on people who had done the least to contribute to the greenhouse gases driving it.
S.Spengler--VB


