
-
 Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
-
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys

-
 Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
-
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?

-
 Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
-
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors

-
 The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
-
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan

-
 Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
-
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida

-
 AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts

-
 Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
-
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return

-
 US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
-
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp

-
 New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
-
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash

-
 Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
-
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win

-
 With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?

-
 Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
-
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold

-
 De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
-
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS

-
 Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
-
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk

-
 Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
-
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
-
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb

-
 Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
-
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week

-
 US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
-
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years

-
 Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
-
Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year

-
 Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
-
French IT group Capgemini under fire over ICE links

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
-
Oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat; gold retreats from highs

-
 Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
-
Holders PSG, Real Madrid among clubs awaiting Champions League play-offs draw

-
 England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
-
US Senate vote to avert government shutdown expected to fail

-
 Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
-
Turkey to offer mediation in US-Iran showdown

-
 World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
-
EU designates Iran Guards as 'terrorist organisation'


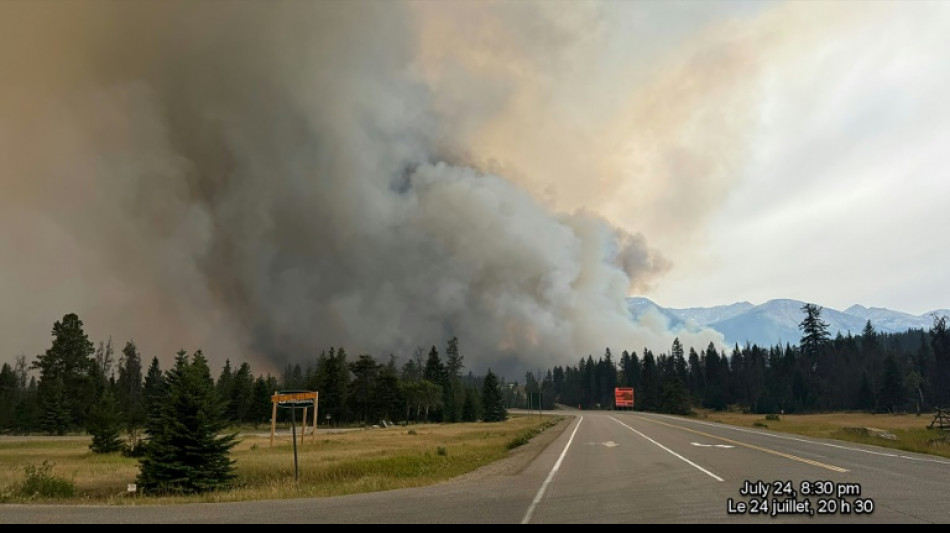
Wildfires push Canada into top four CO2 emitters
Record wildfires last year bumped Canada into the top four CO2-emitting countries in the world, according to a study Wednesday that also cast doubt on its forests' future ability to capture and store significant amounts of carbon dioxide.
Last year saw a catastrophic number of wildfires across the country, with 15 million hectares -- or about four percent of Canada's total forest area -- burned and more than 200,000 people displaced.
Looking at satellite data of carbon monoxide in smoke plumes from fires that burned from May to September of last year, researchers determined that 2,371 megatonnes of CO2 was released, pushing Canada's ranking up from eleventh to fourth among the world's top CO2 emitters.
It put the country behind only China, the United States and India last year.
The researchers warn that hot, dry weather responsible for those blazes is forecast to become the norm by the 2050s, and is "likely to drive an increase in fire activity."
"This raises concerns about whether potentially more frequent and intense fires in the coming decades will suppress the ability of Canadian forests to continue serving as carbon sinks," Brendan Byrne, lead author of the study, told AFP.
Canada's boreal forest, a vast swath stretching from the Pacific to the Atlantic oceans, holds significant amounts of what is known as "sequestered" CO2.
As scorched forests regrow over decades, the CO2 released by wildfires is usually reabsorbed.
But a jump in the size and number of annual fires, coupled with droughts in some regions, could mean forests take longer to grow back.
That in turn "could suppress carbon uptake by the forests," said the study.
Canada would have to adjust downward its level of allowable fossil fuel emissions in order "to compensate for reduced carbon uptake by forests," it concluded.
Ottawa has agreed under the Paris agreement to reduce carbon emissions by 40 to 45 percent from 2005 levels by 2030.
Canada's total CO2-equivalent emissions from burning fossil fuels in 2022 were 708 megatonnes, according to government data.
As human activity has warmed the planet over the past two decades, the frequency and intensity of extreme wildfires have more than doubled worldwide, according to another study published in June in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution.
The wildfire situation in Canada this year has been more subdued but still calamitous in some parts, with the beloved tourist town of Jasper in the western part of the country partially destroyed in July.
I.Stoeckli--VB


