
-
 Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
-
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys

-
 Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
-
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?

-
 Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
-
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors

-
 The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
-
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan

-
 Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
-
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida

-
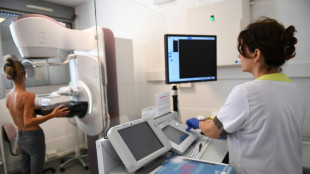 AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts

-
 Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
-
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return

-
 US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
-
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp

-
 New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
-
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash

-
 Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
-
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win

-
 With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?

-
 Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
-
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold

-
 De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
-
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS

-
 Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
-
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk

-
 Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
-
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
-
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb

-
 Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
-
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week

-
 US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
-
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years

-
 Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
-
Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year

-
 Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
-
French IT group Capgemini under fire over ICE links

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
-
Oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat; gold retreats from highs

-
 Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
-
Holders PSG, Real Madrid among clubs awaiting Champions League play-offs draw

-
 England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
-
US Senate vote to avert government shutdown expected to fail

-
 Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
-
Turkey to offer mediation in US-Iran showdown

-
 World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
-
EU designates Iran Guards as 'terrorist organisation'


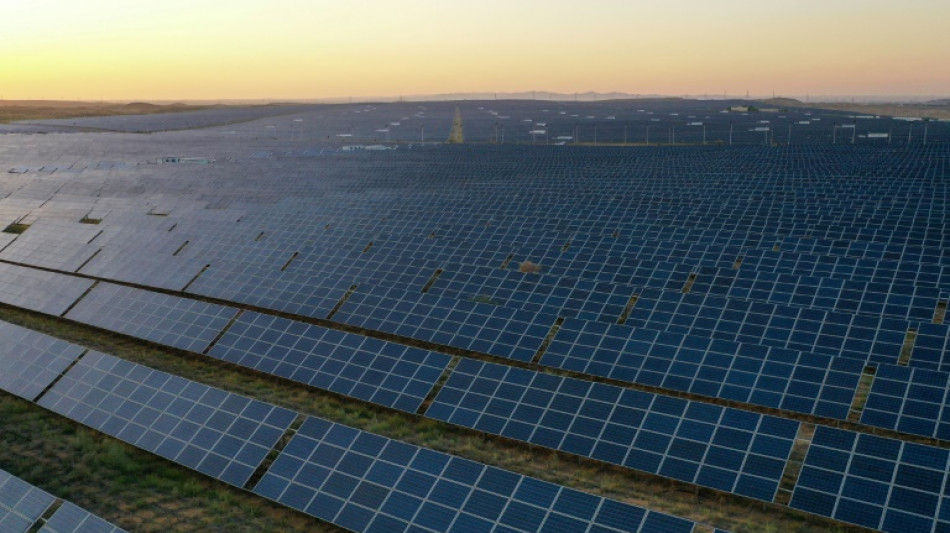
China's solar sector blazes trail in commitment to renewables
Hundreds of rows of gleaming panels blanket swathes of scrubby sand at sunset in a remote northern Chinese desert -- once the biggest solar farm in the world.
On the edge of the forbidding Tengger desert, the solar park produces 1.5 gigawatts of power -- but it has since been eclipsed and the largest is now further west with more than double the capacity.
China, the world's biggest emitter of greenhouse gases, is building almost twice as much wind and solar capacity as every other country combined.
Last week, its wind and solar capacity overshot a target set by President Xi Jinping nearly six years ahead of schedule.
The vast solar arrays in the Ningxia region are a testament to a state-led industrial policy that has driven that breakneck growth.
South of the regional capital Yinchuan, huge lorries roar down a highway flanked by photovoltaic panels and wind turbines stretching to the horizon.
Ningxia, like much of China's northwest, is sparsely populated and sun-soaked, pockmarked with small farms, vineyards and hulking power stations.
This geography makes it a prime location for generating solar power, which is then sent to China's eastern and southern provinces where electricity demand is highest.
"China's solar energy is developing at an unprecedented pace and scale," said analyst Wu Di from Peking University's Institute of Energy.
The country increased its installed solar capacity by more than 55 percent last year, according to the National Energy Administration.
China now accounts for over 40 percent of the total installed capacity worldwide, said Wu.
- 'Need for coal waning' -
Beijing aims to bring emissions of planet-heating carbon dioxide to a peak by 2030 and to net zero by 2060, part of its commitments under the Paris climate accord that seeks to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
"Carbon can't peak unless incremental consumption demand is covered entirely by incremental growth in clean energy," said David Fishman, a senior manager at the Lantau Group specialising in China's power sector.
"Incremental solar capacity growth is an important part of making sure all power demand growth is met by clean sources."
The government only permitted around nine gigawatts of new coal power in the first half of 2024, a year-on-year reduction of 83 percent, according to a report published this month by the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air.
"With new renewable energy installations now capable of meeting all incremental power demand in China, the need for new coal is waning," the Finland-based independent research group said.
But it also warned that construction continued on existing coal projects, potentially slowing Beijing's energy transition.
- Industry shake-out -
The blistering pace at which extra solar capacity has been added has not quite been matched by developments in the power grid, causing some energy to be lost -- a phenomenon known as curtailment.
In May, Fitch Ratings said this could continue to rise in the near term, with the solar curtailment rate for the first quarter of 2024 increasing to four percent.
"In the future, in order to control the solar curtailment ratio within a reasonable range, China still has lots of work to do," said Wu.
Transferring power from west to east is also "not the most cost-effective approach", said Gao Yuhe from environmental group Greenpeace East Asia.
Besides the behemothic parks in the north, China's solar revolution has also relied on distributed solar energy -- smaller panels set onto rooftops in residential and commercial areas, which reduce transmission losses.
But even this smaller-scale infrastructure needs upgrading to cope with recent increased capacity, said Wu.
Long backed by generous government subsidies, China's domestic solar-panel industry is struggling with a global oversupply crisis that has driven down prices and pushed some firms into bankruptcy.
Fishman, of the Lantau Group, said the intense competition "is good news for builders, who continue to benefit from the cheapest panels the world has ever seen".
"Once a few of them go toes-up because they can't endure the competition, the market should stabilise," he added.
Chinese subsidies have also created friction with global trading partners, with the EU launching an investigation to discern whether the subsidies have helped homegrown firms undercut European rivals.
Beijing denies that its industrial policies are unfair and has initiated a series of probes into European imports in apparent retaliation.
S.Leonhard--VB


