
-
 Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
Trump brands Minneapolis nurse shot dead by federal agents an 'agitator'
-
Israel says killed 'three terrorists' in Gaza

-
 After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
After Trump-fueled brawls, Canada-US renew Olympic hockey rivalry
-
Eileen Gu - Olympic champion who bestrides rivals US, China

-
 Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
Trump, first lady attend premier of multimillion-dollar 'Melania' documentary
-
US Senate eyes funding deal vote as government shutdown looms

-
 Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
-
UK schoolgirl game character Amelia co-opted by far-right

-
 Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
-
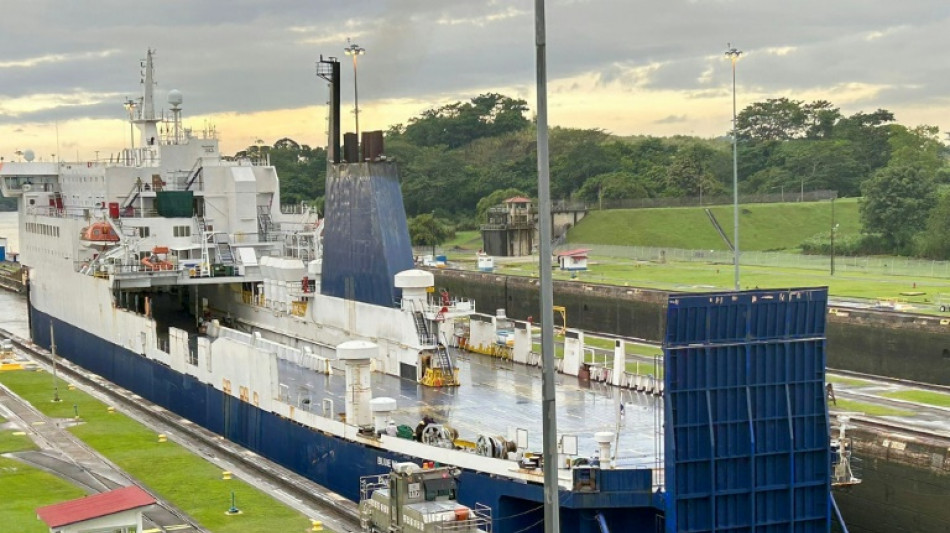
Panama court annuls Hong Kong firm's canal port concession

-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
-
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran

-
 What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
-
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears

-
 Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
-
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo

-
 'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
-
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold

-
 US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
-
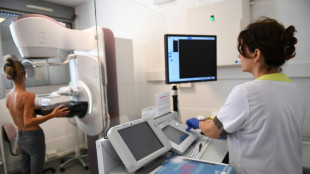
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
 Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
-
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires

-
 Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
-
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms

-
 Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
-
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall

-
 Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
-
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge

-
 Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
-
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
-
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation

-
 Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
-
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies

-
 Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
-
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack


Drought-hit Panama Canal must 'adapt or die' as water levels drop
The Panama Canal, an engineering wonder allowing ships to travel between two oceans, is seeking to adapt to climate change after a biting drought has seen traffic and income dry up.
The canal relies on rainwater to move ships through a series of locks that function like water elevators, raising the vessels up and over the continent between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
However, a water shortage due to low rainfall has forced operators to restrict the number of vessels passing through, which is likely to result in a $200 million drop in earnings in 2024 compared to this year, canal administrator Ricaurte Vasquez said Thursday.
The Pacific warming phenomenon known as El Nino, which can cause drought in some nations and flooding in others, is making the situation worse, meteorologists say.
"The big disadvantage that the Panama Canal has as a maritime route, is that we operate with freshwater, while others use seawater," said Vasquez during a presentation to the media.
"We have to find other solutions to remain a relevant route for international trade. If we don't adapt, we are going to die."
The 50-mile (80-kilometer) byway moves some six percent of all global maritime commerce, and 2023 revenue is forecast at $4.9 billion, said Vasquez.
The canal opened in 1914 after a monumental construction project through dense jungles and mountains, with workers suffering tropical diseases, intense heat and rain.
Since then, more than a million vessels have transited through the canal, saving them a lengthy journey around the tip of South America.
- 'Unusually severe' crisis -
Meteorologist Alcely Lau told AFP that the country has "observed considerable deficits" in rainfall this year, boosted by El Nino.
The drought has forced canal administrators to restrict the waterway to ships with a draft of 13,11 meters (43 feet) -- which refers to how deep they sit in the water.
In 2022, an average of 40 ships crossed through the canal a day, a number which has now dropped to 32 to save water.
For each ship, 200 million liters of freshwater is used to move it through the locks before being dumped into the sea.
"This crisis is unusually severe," said Vasquez, adding that the "significant restrictions" would be in place until September next year.
Due to the draft restrictions, some merchant ships are forced to unload their containers and send the lighter vessel through the canal, while the goods traverse Panama by rail before being reloaded for shipping.
If the drought and resulting restrictions continue, Vasquez fears shipping companies will "opt for other routes."
This includes the Strait of Magellan -- a natural passage at the tip of South America between the mainland and the Tierra del Fuego archipelago.
"We think that if we find a solution relatively soon, not necessarily an immediate solution but one customers know is on the way, it should alleviate long-term concern," said Vasquez.
- Saltier water going to cities -
The lack of rain has also increased the salinity of the lakes and rivers that make up the canal's watershed -- which also provides water to three cities, including the capital Panama City.
"Every time we open the gate that leads to the sea, seawater is mixed with fresh water," said Vasquez.
"We have to keep that level of salt water within a certain range, because the water treatment plants do not have desalination capacity," he added.
The dwindling freshwater cannot be replaced with sea water -- as used by the Suez Canal which connects the Mediterranean with the Red Sea -- as this would require massive excavations.
"Suez was much flatter and it was sand. In our case it is rock and there is a mountain range which is not very high, but it is there and it is a challenge," said Vasquez.
J.Fankhauser--BTB



