
-
 Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
Cuddly Olympics mascot facing life or death struggle in the wild
-
UK schoolgirl game character Amelia co-opted by far-right

-
 Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
Anger as bid to ramp up Malaysia's football fortunes backfires
-
Panama court annuls Hong Kong firm's canal port concession

-
 Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
Pioneer African Olympic skier returns to Sarajevo slopes for documentary
-
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba

-
 From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory
-
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt

-
 'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern
-
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist

-
 Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title
-
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad

-
 Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak
-
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive

-
 Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown
-
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning

-
 Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last
-
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam

-
 Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys
-
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran

-
 What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?
-
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears

-
 Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors
-
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo

-
 'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan
-
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold

-
 US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida
-
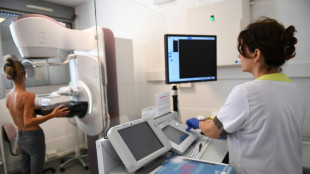
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
 Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts
-
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires

-
 Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return
-
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms

-
 Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp
-
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall

-
 Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash
-
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge

-
 Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win
-
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid

-
 What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?
-
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation

-
 Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold
-
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies

-
 Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS
-
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack

-
 If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk
-
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial

-
 Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on
-
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown

-
 Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb
-
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation


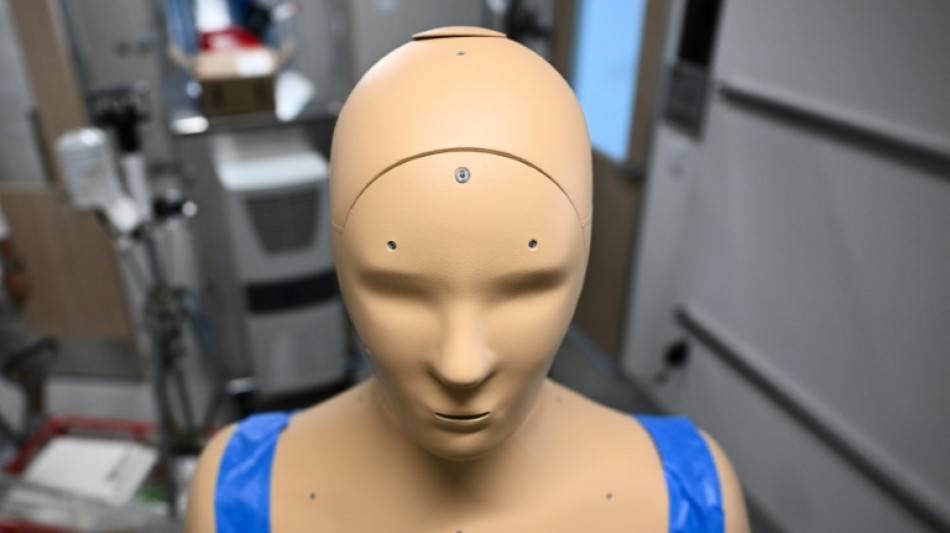
A sweaty robot may help humans understand impact of soaring heat
What happens to the body when a human gets heatstroke? How can we protect ourselves in a warming planet? To answer these burning questions, Arizona researchers have deployed a robot that can breathe, shiver and sweat.
The southwestern state's capital Phoenix is currently enduring its longest heat wave in history: on Friday, the mercury exceeded 110 degrees Fahrenheit (43 degrees Celsius) for the 22nd day in a row, an ominous demonstration of what's to come in a world impacted by climate change.
For humans, such heat represents a potentially lethal threat, one that is still not fully understood. But for ANDI -- a one-of-a-kind humanoid robot at Arizona State University -- it's a lovely day out.
"He's the world's first outdoor thermal mannequin that we can routinely take outside and ... measure how much heat he is receiving from the environment," mechanical engineering professor Konrad Rykaczewski told AFP.
ANDI is "a very realistic way to experimentally measure how a human person responds to extreme climate" without putting people themselves at risk, Rykaczewski says.
At first glance, ANDI -- which stands for Advanced Newton Dynamic Instrument -- resembles a simple crash-test dummy.
But its epoxy/carbon fiber skin conceals a treasure trove of technology, such as a network of connected sensors that assess heat diffused through the body.
ANDI also has an internal cooling system and pores allowing it to breathe and sweat. There are 35 independent thermal zones and, like humans, the robot -- which cost more than half a million dollars to build -- sweats more from its back.
Until now, only a dozen or so mannequins of this type existed, and none of them could venture outdoors.
They were mainly used by sports equipment manufacturers to test their technical clothing in thermal chambers.
- Hyperthermia, a 21st century condition -
Researchers hope the robot will provide a better understanding of hyperthermia -- that is, when a body overheats, a condition that is threatening a growing proportion of the world's population as a result of global warming.
For obvious ethical reasons, "nobody measures core temperature increase while somebody's getting heatstroke," says Rykaczewski. But the effects of heat on the human body are still not fully comprehended. ANDI gives researchers a chance to understand.
Accompanied by MaRTy (Mean Radiant Temperature), a mobile weather station that measures the heat reflected by the buildings around it, the robot is taking its first steps outside in Phoenix -- an ideal laboratory in which to prepare for tomorrow's climate.
"How do we change what we wear? How do we change our behavioral patterns, and adjust them to temperatures that are of this order of magnitude?" says Rykaczewski.
Andi is also infinitely reprogrammable. The research team can make "digital twins of the mannequin to look at different segments of the population," explains Jennifer Vanos, a climatologist involved in the project.
For example, the older you get, the less you sweat. Young people will need different protection from athletes or people in poor health. With ANDI, scientists can simulate the thermoregulatory mechanisms specific to each individual.
- Phoenix, test lab for the future -
They can also test the robot in a variety of situations. For example, Phoenix is dry -- what about humid heat? How does the human body cope in hot winds?
Their research will be useful for designing heat-resistant clothing, rethinking urban planning and protecting the most vulnerable.
In Phoenix, which opens dozens of cooling centers for the homeless every summer, their findings could guide the actions of social workers.
"How long should a person stay in a cooling center to cool off, so that their core temperature goes down to a level that's safe again? We can answer that question with Andi," says Vanos.
The team also dreams of developing low-cost sensors to be used on building sites to adjust working hours according to the heat actually felt on site and the health of the workers -- rather than based on general weather conditions.
That could be a "step towards better safety than just these blank recommendations per city, per state, per country," Rykaczewski says.
Such specific, tailored solutions could have global impacts, redrawing entire cities.
"If the future of Paris looks like Phoenix now, we can learn a lot about how do we design buildings," says Rykaczewski.
C.Meier--BTB


