
-
 Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba
Trump threatens tariffs on nations selling oil to Cuba
-
From fragile youngster to dominant star, Sabalenka chases more glory

-
 Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt
Lowly Montauban 'not dead' in French Top 14 survival hunt
-
'Winter signing' Musiala returns to boost weary Bayern

-
 Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist
Elena Rybakina: Kazakhstan's ice-cool Moscow-born Melbourne finalist
-
Power battle as Sabalenka clashes with Rybakina for Melbourne title

-
 Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad
Contrasting fortunes add Basque derby edge for Matarazzo's revived Sociedad
-
Asian stocks hit by fresh tech fears as gold retreats from peak

-
 Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive
Kim vows to 'transform' North Korea with building drive
-
Peers and Gadecki retain Australian Open mixed-doubles crown

-
 Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning
Britain's Starmer seeks to bolster China ties despite Trump warning
-
Kaori Sakamoto - Japan skating's big sister eyes Olympic gold at last

-
 Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
-
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys

-
 Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
-
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?

-
 Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
-
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors

-
 The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
-
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan

-
 Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
-
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida

-
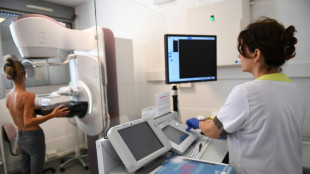 AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts

-
 Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
-
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return

-
 US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
-
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp

-
 New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
-
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash

-
 Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
-
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win

-
 With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?

-
 Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
-
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold

-
 De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
-
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS

-
 Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
-
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk

-
 Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
-
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
-
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb

-
 Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
-
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week

-
 US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
-
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years

-
 Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
-
Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year


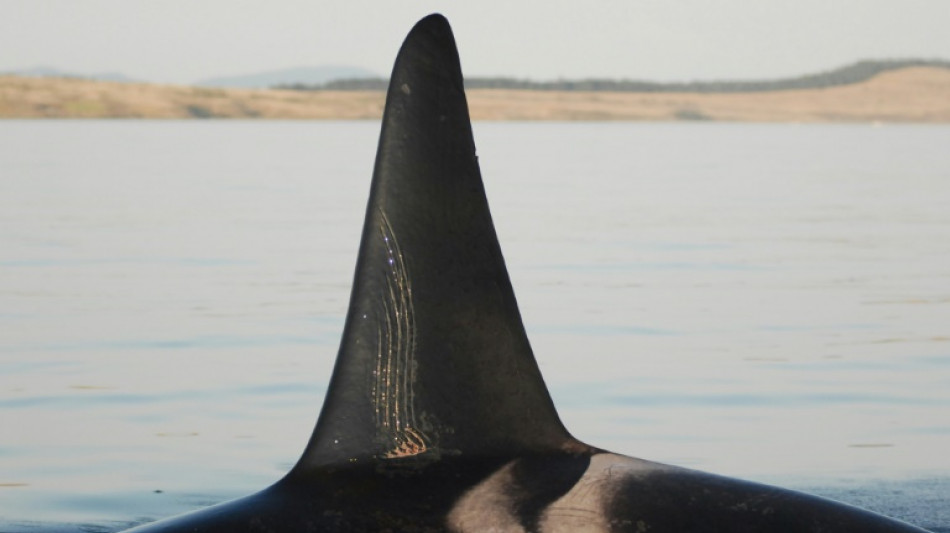
Mama's boys: Elder orca moms protect sons from fights
A male orca's best friend is his old mother.
That's according to a new scientific paper published Thursday in Current Biology, which found female killer whales that have undergone menopause prevent their sons -- though not their daughters -- from getting injured in fights.
Lead author Charli Grimes told AFP what drew her to the subject was just how rare menopause is in the natural world. Most animals with ovaries remain capable of reproducing until they die, with humans and five species of toothed whales the only known exceptions.
"A big question in our own evolutionary history is, how and why has menopause evolved?" she said.
"In human societies, older females play a role in moderating conflict, and now this latest research has found that that might also be the case in killer whales," added the animal behavior scientist at the University of Exeter.
The study looked at Southern Resident killer whales, which live off the Pacific coast of North America.
These whales live in matriarchal social units -- typically consisting of a grandmother, her male and female offspring, and her daughters' daughters. Female killer whales survive up to 90 years in the wild, and live more than 20 years beyond menopause.
Males will outbreed with females from other pods, but both males and females will stay within the social unit of their birth. Sons remain especially close to their mothers throughout their lives.
- Bite marks -
For their research, Grimes and colleagues examined the accumulation of "tooth rake marks" -- scarring left behind when an orca bites another during rough play or fighting.
"These marks are really great for quantifying social interactions that are otherwise really difficult to observe, since most of the behavior takes place below the surface," she said.
The Center for Whale Research in Washington state has carried out photographic censuses of Southern Resident killer whales since 1976, identifying individuals by their unique dorsal fins and saddle patches.
Orcas have no natural predators, and this subspecies feeds exclusively on salmon, as opposed to prey that can bite back. This means the tooth marks could only be inflicted by their own kind.
By analyzing thousands of photos in a computer program, the team found males who lived with post-reproductive mothers had 35 percent fewer tooth rake injuries compared to males who lived with breeding mothers, and 45 percent fewer than those who lived without their mothers.
It's thought that ceasing breeding frees up time and energy for mothers to protect their sons.
How exactly the post-menopausal moms are helping isn't yet clear, said Grimes. It could be that older females use their knowledge of other pods to steer their sons away from troublemakers.
Or, they could be intervening more directly when a fight is brewing, perhaps using vocalizations to call off their sons. It's not thought that they get involved in fighting themselves, since they have very low rates of scarring.
- Pass the fish -
Daughters, however, were not found to have fewer tooth rakes with their mothers around.
Females are probably less involved in conflict to begin with, said Grimes. Sons moreover breed with multiple females, meaning there is a higher chance of their mother passing on their genes.
Ruth Mace, an anthropologist and biologist at the University College London who was not involved in the study, told AFP that the idea that post-reproductive life had evolved so women can help children is well established in humans.
"So it is very interesting that this is also being established in killer whales," she said.
"It's (a) remarkable study, utilizing an extremely valuable long-term dataset," added Stephanie King, who specializes in dolphin research at the University of Bristol and was also not involved.
Prior work has shown older female orcas share their own fish, pass on ecological knowledge of where and when to find food, and improve their grandchildren's survival rates.
An outstanding question is how exactly they bring about some of these benefits -- something Grimes and her colleagues hope to answer by flying drones over the orcas, documenting what they do under the waves.
J.Horn--BTB


