
-
 Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
Heavy metal: soaring gold price a crushing weight in Vietnam
-
Kendrick Lamar, Bad Bunny, Lady Gaga face off at Grammys

-
 Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
Trump says 'hopefully' no need for military action against Iran
-
What's behind Trump's risky cheap dollar dalliance?

-
 Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
Minnesota Somalis organize house call care amid ICE raid fears
-
Sumo diplomacy: Japan's heavyweight 'soft power' ambassadors

-
 The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
The foreign POWs stuck in Ukrainian prison limbo
-
'Batman' confronts city over ICE Super Bowl plan

-
 Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
Trump says Putin agrees to pause Kyiv strikes amid harsh cold
-
US sprint star Richardson arrested on speeding charge in Florida

-
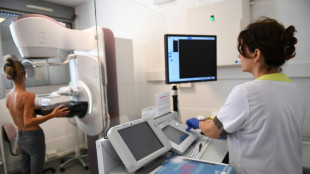 AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
AI helps doctors spot breast cancer in scans: world-first trial
-
Arsenal seek fun factor as Frank searches for home comforts

-
 Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
Argentina declares emergency over Patagonia wildfires
-
Rose leads at Torrey Pines as Koepka makes PGA Tour return

-
 US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
US eases Venezuela sanctions after oil sector reforms
-
Trump turns to Venezuela playbook on Iran, but differences sharp

-
 New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
New York breaks out snow 'hot tubs' to melt winter storm snowfall
-
Anthony Joshua speaks on camera for first time since Nigeria crash

-
 Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
Apple earnings soar as China iPhone sales surge
-
Forest, Celtic head into Europa League play-offs as Villa win

-
 With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump administration watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
What are the key challenges awaiting the new US Fed chair?

-
 Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
Trump's new Minneapolis point man vows 'smarter' operation
-
Trump says Putin to halt Kyiv strikes for week amid harsh cold

-
 De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
De Kock ton clinches T20 series for South Africa against West Indies
-
Chiles's appeal to retain Olympic bronze sent back to CAS

-
 Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
Iran threatens to hit US bases and carriers in event of attack
-
If not now, when? LeBron tears stoke retirement talk

-
 Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
Ex-OPEC president denies bribe-taking at London corruption trial
-
Another Arctic blast bears down on US as snow cleanup drags on

-
 Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
Iran's IRGC: the feared 'Pasdaran' behind deadly crackdown
-
Israeli settler leader lauds Jewish prayer at contested West Bank tomb

-
 Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
Iran blasts EU 'mistake' after Guards terror designation
-
Trump says Putin agreed not to attack freezing Kyiv for a week

-
 US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
US Senate rejects vote to avert government shutdown
-
Moscow records heaviest snowfall in over 200 years

-
 Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
Polar bears bulk up despite melting Norwegian Arctic: study
-
Waymo gears up to launch robotaxis in London this year

-
 Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
Colombia restricts import of drones used in explosives attacks
-
French IT group Capgemini under fire over ICE links

-
 US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
US border chief says not 'surrendering' immigration mission in Minneapolis
-
Oil jumps on Trump's Iran threat; gold retreats from highs

-
 Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
Melania Trump premieres multi-million-dollar documentary
-
Holders PSG, Real Madrid among clubs awaiting Champions League play-offs draw

-
 England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
England look to fine tune for T20 World Cup with Sri Lanka series
-
US Senate vote to avert government shutdown expected to fail

-
 Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
Colombian president angers churches with Jesus sex comments
-
Turkey to offer mediation in US-Iran showdown

-
 World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
World Cup skiing returns to Crans-Montana after deadly fire
-
EU designates Iran Guards as 'terrorist organisation'


Living near green space makes you 2.5 years younger: study
City parks and green spaces help counter heat, boost biodiversity, and instill a sense of calm in the urban jungle.
They also help slow biological aging, with people who have access to green spaces found to be on average 2.5 years biologically younger than those who do not, according to a new study published Wednesday in Science Advances.
"Living near more greenness can help you be younger than your actual age," Kyeezu Kim, the study's lead author and a postdoctoral scholar at Northwestern University's Feinberg School of Medicine, told AFP.
"We believe our findings have significant implications for urban planning in terms of expanding green infrastructure to promote public health and reduce health disparities."
Exposure to green spaces has previously been linked with better cardiovascular health and lower rates of mortality.
It's thought that more physical activity and social interactions are at play, but whether parks actually slowed down aging on a cellular level has been unclear.
To investigate, the team behind the study examined DNA chemical modifications known as "methylation."
Prior work has shown that so-called "epigenetic clocks" based on DNA methylation can be a good predictor of health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, cognitive function, and a more accurate way of measuring age than calendar years.
Kim and colleagues followed more than 900 white and Black people from four American cities -- Birmingham, Chicago, Minneapolis, and Oakland -- over a period of 20 years, from 1986-2006.
Using satellite imaging, the team assessed how close the participants' residential addresses were to surrounding vegetation and parks, and paired this data with blood samples taken in years 15 and years 20 of the study, to determine their biological age.
The team constructed statistical models to evaluate the results, and control for other variables, such as education, income, and behavioral factors like smoking, that might have affected the results.
They found that people whose homes were surrounded by 30 percent green cover within a five kilometer (three mile) radius were on average 2.5 years younger biologically compared to those whose homes were surrounded by 20 percent green cover.
The benefits were not evenly shared. Black people with more access to green space were only one year biologically younger, while white people were three years younger.
"Other factors, such as stress, qualities of the surrounding green space, and other social support, can affect the degree of benefits of green spaces in terms of biological aging," said Kim, explaining the disparities required further study.
For example, parks in deprived neighborhoods used for illicit activities might be less frequented, negating the benefits.
Next steps might involve investigating the link between green spaces and specific health outcomes, she added. It's also not yet clear how exactly greenery reduces aging -- only that it does, added Kim.
Epidemiologist Manuel Franco, of the University of Alcala and Johns Hopkins, called the research a "well designed study."
"We have more and better scientific evidence to increase and promote the use of urban green spaces," added Franco, who was not involved in the study.
B.Shevchenko--BTB


