
-
 Gold tops $4,000 for first time as traders pile into safe haven
Gold tops $4,000 for first time as traders pile into safe haven
-
Indian garment exporters reel under US tariffs

-
 NBA back in China after six-year absence sparked by democracy tweet
NBA back in China after six-year absence sparked by democracy tweet
-
Energy storage and new materials eyed for chemistry Nobel

-
 Trump unlikely to win Nobel Peace Prize, but who will?
Trump unlikely to win Nobel Peace Prize, but who will?
-
Qatar, Turkey to join third day of Gaza peace talks in Egypt

-
 Study finds women have higher genetic risk of depression
Study finds women have higher genetic risk of depression
-
Dolly Parton's sister calls for fan prayers over health issues

-
 On Trump's orders, 200 troops from Texas arrive in Illinois
On Trump's orders, 200 troops from Texas arrive in Illinois
-
Two bodies found, two missing after Madrid building collapse

-
 Panthers raise banner as NHL three-peat bid opens with win
Panthers raise banner as NHL three-peat bid opens with win
-
Nobel physics laureate says Trump cuts will 'cripple' US research

-
 UFC star McGregor suspended 18 months over missed drug tests
UFC star McGregor suspended 18 months over missed drug tests
-
Trump talks up Canada trade deal chances with 'world-class' Carney

-
 Ecuador president unharmed after apparent gun attack on motorcade
Ecuador president unharmed after apparent gun attack on motorcade
-
Lyon exact revenge on Arsenal, Barca thrash Bayern in women's Champions League

-
 Trump says 'real chance' to end Gaza war as Israel marks attacks anniversary
Trump says 'real chance' to end Gaza war as Israel marks attacks anniversary
-
Gerrard brands failed England generation 'egotistical losers'

-
 NFL fines Cowboys owner Jones $250,000 over gesture to fans
NFL fines Cowboys owner Jones $250,000 over gesture to fans
-
Bengals sign veteran quarterback Flacco after Burrow injury

-
 New prime minister inspires little hope in protest-hit Madagascar
New prime minister inspires little hope in protest-hit Madagascar
-
Is Trump planning something big against Venezuela's Maduro?

-
 EU wants to crack down on 'conversion therapy'
EU wants to crack down on 'conversion therapy'
-
French sex offender Pelicot says man who abused ex-wife knew she was asleep

-
 Trump says 'real chance' to end Gaza war as Israel marks Oct 7 anniversary
Trump says 'real chance' to end Gaza war as Israel marks Oct 7 anniversary
-
UK prosecutors to appeal dropped 'terrorism' case against Kneecap rapper

-
 Spain, Inter Miami star Alba retiring at end of season
Spain, Inter Miami star Alba retiring at end of season
-
EU targets foreign steel to rescue struggling sector

-
 Trump talks up Canada deal chances with visiting PM
Trump talks up Canada deal chances with visiting PM
-
Knight rides her luck as England survive Bangladesh scare

-
 Pro-Gaza protests flare in UK on anniversary of Hamas attack
Pro-Gaza protests flare in UK on anniversary of Hamas attack
-
Top rugby unions warn players against joining rebel R360 competition

-
 Outcast Willis 'not overthinking' England absence despite Top 14 clean sweep
Outcast Willis 'not overthinking' England absence despite Top 14 clean sweep
-
Trump says 'real chance' of Gaza peace deal

-
 Macron urged to quit to end France political crisis
Macron urged to quit to end France political crisis
-
No.1 Scheffler seeks three-peat at World Challenge

-
 Canadian PM visits Trump in bid to ease tariffs
Canadian PM visits Trump in bid to ease tariffs
-
Stocks falter, gold shines as traders weigh political turmoil

-
 Senators accuse US attorney general of politicizing justice
Senators accuse US attorney general of politicizing justice
-
LeBron's 'decision of all decisions' a PR stunt

-
 Observing quantum weirdness in our world: Nobel physics explained
Observing quantum weirdness in our world: Nobel physics explained
-
WTO hikes 2025 trade growth outlook but tariffs to bite in 2026

-
 US Supreme Court hears challenge to 'conversion therapy' ban for minors
US Supreme Court hears challenge to 'conversion therapy' ban for minors
-
Italy's Gattuso expresses Gaza heartache ahead of World Cup qualifier with Israel

-
 EU targets foreign steel to shield struggling sector
EU targets foreign steel to shield struggling sector
-
Djokovic vanquishes exhaustion to push through to Shanghai quarterfinals

-
 Stocks, gold rise as investors weigh AI boom, political turmoil
Stocks, gold rise as investors weigh AI boom, political turmoil
-
Swiatek coasts through Wuhan debut while heat wilts players
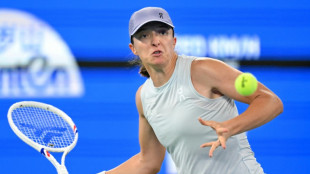
-
 Denmark's Rune calls for heat rule at Shanghai Masters
Denmark's Rune calls for heat rule at Shanghai Masters
-
Japanese football official sentenced for viewing child sexual abuse images


Trump admin leaves door open for tougher PFAS drinking water standards
A day after US President Donald Trump's administration announced it was scrapping existing limits on several toxic "forever chemicals" in drinking water, a top official said new standards would be drawn up -- and may end up even stricter.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Administrator Lee Zeldin said Thursday its decision -- which retains previous limits for just two of the most notorious PFAS compounds while rescinding them for four others -- was procedural and temporary in nature.
When former president Joe Biden's EPA issued the original rule in 2024, it was challenged by chemical industry and water utility groups who argued, among other things, that the agency had improperly combined two key steps in the process: determining that a chemical poses health risks and proposing a rule.
Biden's rule had set the maximum allowable concentration for the four additional PFAS -- including GenX, a dangerous chemical that has contaminated drinking water in the Cape Fear river basin of North Carolina -- at 10 parts per trillion.
Rather than wait for a court ruling, Zeldin told reporters he agreed "there was a procedural error that we are addressing."
"Quite frankly, there's a possibility that at the end of the process, a new number could be lower, could be higher," he added, stressing that the revised standards would be guided by science. He did not provide a timeline for their finalization.
- 'Have it both ways' -
The announcement was met with skepticism from Melanie Benesh of the Environmental Working Group.
"Administrator Zeldin is almost posturing like they have no choice but to go back and redo it -- but they are making a choice, to switch sides in the litigation," she told AFP. "It seems like the EPA is trying to have it both ways."
There is bipartisan support for action on PFAS, with some of the hardest-hit communities -- in West Virginia, rural New York, and North Carolina -- located in Republican strongholds, and billions earmarked by Congress to address the problem in the 2021 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law.
At least 158 million Americans are estimated to have drinking water contaminated with perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances, which accumulate in the body and have been linked to cancer, birth defects, reduced fertility, and behavioral disorders -- even at extremely low levels.
Nicknamed "forever chemicals" because they can take millions of years to break down, PFAS were first synthesized in the 1930s and are defined by their ultra-strong carbon-fluorine bonds, which give them extreme heat resistance as well as water and grease-repellent properties.
Today, they blanket the planet -- from the Tibetan Plateau to the ocean floor -- and circulate in the blood of nearly every American.
H.Gerber--VB




