-
 Pollock shines as England eventually overpower Australia
Pollock shines as England eventually overpower Australia
-
Villarreal crush Rayo to move second, Atletico beat Sevilla

-
 Sinner crushes Zverev to reach Paris Masters final, brink of No. 1
Sinner crushes Zverev to reach Paris Masters final, brink of No. 1
-
Pollock shines as England beat Australia in Autumn opener

-
 Ukraine sends special forces to embattled eastern city
Ukraine sends special forces to embattled eastern city
-
Arsenal cruise against Burnley as Man Utd held

-
 Pollock shines as England beat Australia 25-7 in Autumn Nations Series
Pollock shines as England beat Australia 25-7 in Autumn Nations Series
-
Gyokeres on target as leaders Arsenal beat Burnley

-
 Woman charged over Louvre heist tears up in court
Woman charged over Louvre heist tears up in court
-
Diomande dazzles as Leipzig go two points behind Bayern

-
 Auger-Aliassime downs Bublik to reach Paris Masters final
Auger-Aliassime downs Bublik to reach Paris Masters final
-
Villarreal crush Rayo to move second in La Liga

-
 Female suspect, 38, charged in Louvre heist: AFP
Female suspect, 38, charged in Louvre heist: AFP
-
US not sending any high-level officials to COP30

-
 India captain Kaur sees World Cup final as possible turning point
India captain Kaur sees World Cup final as possible turning point
-
'Not out of the woods': What now for Britain's ex-prince Andrew?

-
 Tens of thousands of Serbians mark first anniversary of deadly train station collapse
Tens of thousands of Serbians mark first anniversary of deadly train station collapse
-
Tanzania president wins 98% in election as opposition says hundreds killed

-
 Vieira 'no longer' manager of troubled Genoa: club
Vieira 'no longer' manager of troubled Genoa: club
-
Tanzania president wins 98% of votes after violence-marred polls

-
 South Korea hosts Xi as Chinese leader rekindles fraught ties
South Korea hosts Xi as Chinese leader rekindles fraught ties
-
England's batting exposed as New Zealand seal ODI series sweep

-
 Funk legend turned painter George Clinton opens show in Paris
Funk legend turned painter George Clinton opens show in Paris
-
Traditional mass wedding held in Nigeria to ensure prosperity

-
 Canada PM says Xi talks 'turning point', apologises to Trump
Canada PM says Xi talks 'turning point', apologises to Trump
-
Iranian tech prodigies battle it out with robots

-
 Maldives begins 'generational ban' on smoking
Maldives begins 'generational ban' on smoking
-
Explorers seek ancient Antarctica ice in climate change study

-
 India's Iyer discharged from hospital after lacerated spleen
India's Iyer discharged from hospital after lacerated spleen
-
Serbia marks first anniversary of deadly train station collapse

-
 Latin America weathered Trump tariffs better than feared: regional bank chief
Latin America weathered Trump tariffs better than feared: regional bank chief
-
Bangladesh dockers strike over foreign takeover of key port

-
 Tanzania president wins election landslide after deadly protests
Tanzania president wins election landslide after deadly protests
-
Dodgers, Blue Jays gear up for winner-take-all World Series game seven

-
 Taiwan's new opposition leader against defence spending hike
Taiwan's new opposition leader against defence spending hike
-
Dodgers hold off Blue Jays 3-1 to force World Series game seven

-
 Crowns, beauty, fried chicken: Korean culture meets diplomacy at APEC
Crowns, beauty, fried chicken: Korean culture meets diplomacy at APEC
-
Panama wins canal expansion arbitration against Spanish company

-
 Myanmar fireworks festival goers shun politics for tradition
Myanmar fireworks festival goers shun politics for tradition
-
China to exempt some Nexperia orders from export ban

-
 Sixers suffer first loss as NBA Cup begins
Sixers suffer first loss as NBA Cup begins
-
China's Xi to meet South Korean leader, capping APEC summit

-
 Japan's Chiba leads after Skate Canada short program
Japan's Chiba leads after Skate Canada short program
-
Finland's crackdown on undocumented migrants sparks fear

-
 Climbers test limits at Yosemite, short-staffed by US shutdown
Climbers test limits at Yosemite, short-staffed by US shutdown
-
Gstaad gives O'Brien record 21st Breeders' Cup win

-
 After the tears, anger on Rio's blood-stained streets
After the tears, anger on Rio's blood-stained streets
-
Sinner boosts number one bid in Paris, to face Zverev in semis

-
 Springer back in Toronto lineup as Blue Jays try to close out Dodgers
Springer back in Toronto lineup as Blue Jays try to close out Dodgers
-
Nationals make Butera MLB's youngest manager since 1972


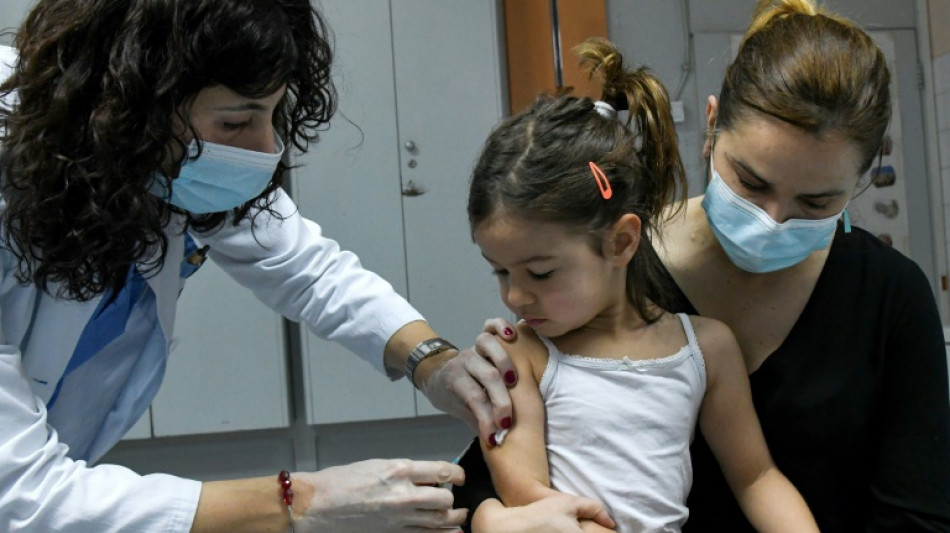
Measles cases surge 80%, other diseases could follow: UN
Measles cases have surged by nearly 80 percent worldwide this year, the UN said Wednesday, warning that the rise of the "canary in a coal mine" illness indicates that outbreaks of other diseases are likely on the way.
The coronavirus pandemic has interrupted vaccination campaigns for non-Covid diseases around the world, creating a "perfect storm" that could put millions of children's lives at risk, the UN's children's agency UNICEF and the World Health Organization said in a statement.
More than 17,300 measles cases were reported globally in January and February, compared to around 9,600 during those months last year, according to new data from the UN agencies.
There have been 21 large and disruptive measles outbreaks in the last 12 months to April, most of them in Africa and the eastern Mediterranean, the data showed.
Christopher Gregory, senior health adviser in UNICEF's immunisation section, told AFP that because measles is the "most contagious vaccine-preventable disease" it often serves as a warning sign.
"Measles is what we call the tracer, or the canary in the coal mine, that really shows us where those weaknesses in the immunisation system are," he said.
He said yellow fever was among the diseases that could surge next, after rising cases were reported in West Africa.
"We're particularly worried about those countries that are most fragile, where the healthcare systems are already really struggling, where they're still trying to deal with the impacts of Covid on top of these outbreaks," he said.
Somalia recorded by far the most measles cases in the last 12 months with more than 9,000, the UN data showed, followed by Yemen, Afghanistan, Nigeria and Ethiopia -- all countries battling some form of conflict.
There are also fears that the war in Ukraine could spark a resurgence in the country after it recorded Europe's highest rate of measles between 2017-2019.
Gregory said that it had been very difficult to keep track of any disease in Ukraine since the war began, adding that the biggest concern was "what we could be missing".
- Impact 'felt for decades' -
More than 23 million children missed out on routine vaccinations in 2020 as the Covid pandemic descended, the largest number in more than a decade.
The UN agencies said that 57 vaccination campaigns in 43 countries postponed at the start of the pandemic had still not been completed, affecting 203 million people -- most of them children.
Covid also continues to pile pressure on healthcare facilities and drag staffing and attention away from vaccination for long-standing deadly diseases.
"The impact of these disruptions to immunisation services will be felt for decades to come," WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said in the statement.
"Now is the moment to get essential immunisation back on track and launch catch-up campaigns so that everybody can have access to these life-saving vaccines."
Gregory said it was time to put childhood immunisation on "at least the same level of priority as finishing Covid vaccination".
Measles is a disease caused by a virus that attacks mainly children. The most serious complications include blindness, brain swelling, diarrhoea, and severe respiratory infections.
Vaccination uptake of at least 95 percent is the best way to avoid it spreading, though many countries fall far short of that goal -- Somalia is at just 46 percent, according to the UN data.
B.Shevchenko--BTB



