
-
 Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues
-
South Africa drops 'Melania' just ahead of release

-
 Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
Senegal coach Thiaw banned, fined after AFCON final chaos
-
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle

-
 Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
Australian Open chief Tiley says 'fine line' after privacy complaints
-
Trump-era trade stress leads Western powers to China

-
 Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran
-
Russia's Petrosian skates in Valieva shadow at Milan-Cortina Olympics

-
 China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
China executes 11 linked to Myanmar scam compounds
-
Germany to harden critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike

-
 Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
Colombia plane crash investigators battle poor weather to reach site
-
Serena Williams refuses to rule out return to tennis

-
 Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
Vietnam, EU vow stronger ties as bloc's chief visits Hanoi
-
New glove, same fist: Myanmar vote ensures military's grip

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Thai foreign minister says hopes Myanmar polls 'start of transition' to peace

-
 No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
No white flag from Djokovic against Sinner as Alcaraz faces Zverev threat
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
Starmer, Xi stress need for stronger UK-China ties to face global headwinds
-
Senegal coach Thiaw gets five-match ban after AFCON final chaos

-
 Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
Phan Huy: the fashion prodigy putting Vietnam on the map
-
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'

-
 Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
Britain's Starmer meets China's Xi for talks on trade, security
-
Chinese quadriplegic runs farm with just one finger
-
 Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
'Bombshell': What top general's fall means for China's military
-
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment

-
 Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence
-
Online platforms offer filtering to fight AI slop

-
 With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
With Trump allies watching, Canada oil hub faces separatist bid
-
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand

-
 Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
Rockets veteran Adams out for rest of NBA season
-
Holders PSG happy to take 'long route' via Champions League play-offs

-
 French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art
-
Allrounder Molineux named Australian women's cricket captain

-
 Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
Sabalenka faces Svitolina roadblock in Melbourne final quest
-
Barcelona rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
Liverpool, Man City and Barcelona ease into Champions League last 16
-
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge

-
 Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Real Madrid face Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
LA mayor urges US to reassure visiting World Cup fans

-
 Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
Madrid condemned to Champions League play-off after Benfica loss
-
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report

-
 Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
Haaland ends barren run as Man City reach Champions League last 16
-
PSG and Newcastle drop into Champions League play-offs after stalemate

-
 Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
Salah ends drought as Liverpool hit Qarabag for six to reach Champions League last 16
-
Barca rout Copenhagen to reach Champions League last 16

-
 Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
Arsenal complete Champions League clean sweep for top spot
-
Kolo Muani and Solanke send Spurs into Champions League last 16


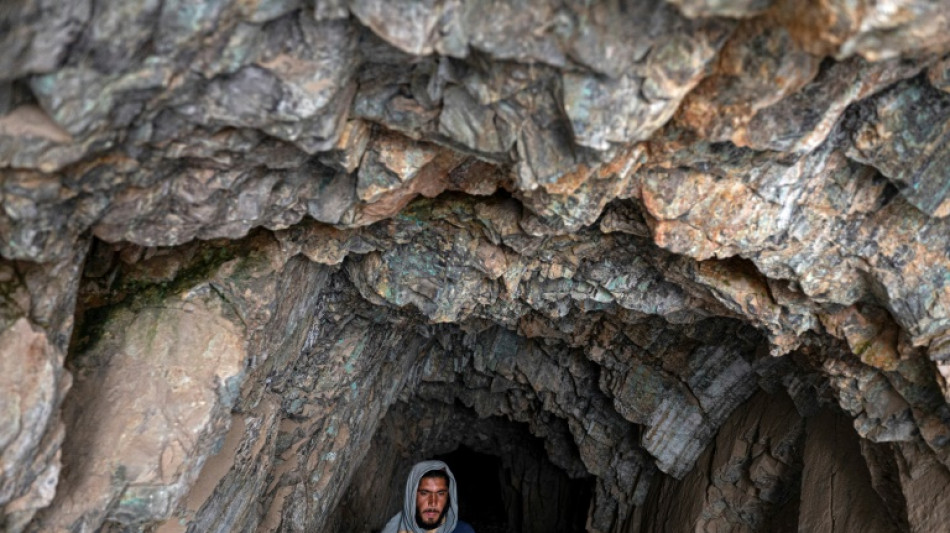
Ancient Afghan Buddhist city threatened by Chinese copper mine
An ancient Buddhist city carved out of immense peaks near Kabul is in danger of disappearing forever, swallowed up by a Chinese consortium exploiting one of the world's largest copper deposits.
Located at the confluence of Hellenistic and Indian cultures, Mes Aynak -- believed to be between 1,000 and 2,000 years old -- was once a vast city organised around the extraction and trade of copper.
Archaeologists have uncovered Buddhist monasteries, stupas, fortresses, administrative buildings and dwellings, while hundreds of statues, frescoes, ceramics, coins and manuscripts have also been unearthed.
Despite looting at the beginning of the century, Mes Aynak is "one of the most beautiful archaeological sites" in the world, says Bastien Varoutsikos, an archaeologist for the French company Iconem, which is working to digitise the city and its heritage.
But the need for the Taliban -- who returned to power in August last year -- to find new revenue streams after international aid was frozen has made mining the project a priority, and could put an end to further archaeological work.
- Mining consortium -
Objects discovered date mainly from the 2nd to 9th century AD, but an earlier occupation is also believed likely, and pottery dating back to the Bronze Age -- well before the birth of Buddhism -- has also been found.
Forgotten for centuries before being rediscovered by a French geologist in the early 1960s, Mes Aynak, in Logar province, has been compared to Pompeii and Machu Picchu in size and significance.
The ruins, which cover 1,000 hectares, are perched high on a massive peak whose brown flanks betray the presence of copper.
But in 2007 the Chinese mining giant Metallurgical Group Corporation (MCC) headed a state-owned consortium -- that later took the name MJAM -- and signed a $3 billion contract to mine ore over 30 years.
Fifteen years later, the mine still does not exist -- insecurity and disagreements between Beijing and Kabul over financial terms of the contract have caused delays.
The project is once again a priority for both parties, however, and talks are ongoing on how to proceed.
- Duty of preservation -
Fears are rising that a place once considered one of the most prosperous trade hubs on the Silk Road could disappear without oversight.
In the early 2010s, it was "one of the largest archaeological projects in the world", Varoutsikos told AFP.
MJAM originally suspended the start of operations for three years to allow archaeologists to focus on the area directly threatened by the mine.
That period was inadvertently lengthened as the security situation prevented the Chinese from building planned infrastructure.
As a result, thousands of objects were unearthed -- some were taken to the Kabul museum, others kept nearby.
When it was last in power the Taliban shocked the world by dynamiting the giant Buddhas of Bamiyan in March 2001, but today they say they are determined to preserve the findings of Mes Aynak.
"It is the duty of the Ministry of Information and Culture to protect them," Esmatullah Burhan, the spokesman for the Ministry of Mines and Petroleum, told AFP.
But while the rhetoric seems sincere, many of the remains are simply too bulky or fragile to be moved and seem destined to disappear.
The Chinese favour open-pit rather than underground mining. If this goes ahead, it would open up the copper mountain and bury all the fragments of the past.
- Environmental consequences -
Afghanistan is sitting on huge mineral resources of copper, iron, bauxite, lithium and rare earths estimated to be worth more than a trillion dollars.
The Taliban hope to earn more than $300 million a year from Mes Aynak -- about 60 percent of the full state budget for 2022 -- and now want to speed up the process.
"This project must begin, it must not be delayed any longer," they have repeatedly told MJAM in recent weeks, according to Burhan.
The discussions are about "80 percent finished", says the spokesman, with only technical points remaining to be settled, which should be done soon.
The Taliban are demanding that the contract -- which includes the construction of a power station to supply the mine and Kabul, and a railroad to Pakistan -- be respected.
They also insist that the copper be processed locally with an Afghan workforce.
China, whose economy is in dire need of copper, is reluctant to meet these demands.
MJAM, which did not respond to AFP, also continues to demand a reduction in royalties due.
The project is also coupled with concerns about its environmental consequences.
Copper mining is polluting and requires large quantities of water, and Logar is already an arid region.
According to Burhan, the Taliban are paying "strict attention" to these issues and will ensure that the consortium meets its obligations in this regard.
For now, the delay is some salvation for archeologists.
While there is currently no work going on at the site, Varoutsikos hopes to restart the excavation before the start of mining operations.
But even that will depend on international collaboration and funding, he notes.
G.Schulte--BTB

